带你从零构建一个可扩展的“第二大脑“系统,让AI深度融入你的工作流、决策过程和创意生成。
本文介绍了如何利用小智AI构建个人"第二大脑"系统,实现认知增强和智能辅助。主要内容包括: 系统架构设计:采用分层结构,包含应用层、集成层和核心层,支持自然语言交互、知识图谱和记忆存储等功能。 三大实战项目: 智能家居控制系统:通过自然语言指令控制设备,具备学习用户习惯和自动化决策能力 个性化对话系统:集成记忆存储和知识图谱,实现上下文感知的个性化交流 功能扩展系统:支持插件架
引言:当AI成为认知延伸
在数字时代,信息过载已成为知识工作者的常态。我们每天处理数百条消息、阅读无数文档、面对复杂决策——这就像试图用一杯水去扑灭森林大火。传统笔记工具如同静态仓库,而真正需要的是动态、智能、主动的认知伙伴。
小智AI作为先进的AI系统,不仅能回答问题,更能通过适当架构成为你的数字副驾驶、记忆延伸和思维加速器。本文将带你从零构建一个可扩展的"第二大脑"系统,让AI深度融入你的工作流、决策过程和创意生成。
第一章:第二大脑架构设计
1.1 核心概念模型
真正的"第二大脑"不是简单的聊天界面,而是具有分层结构的认知系统:
text
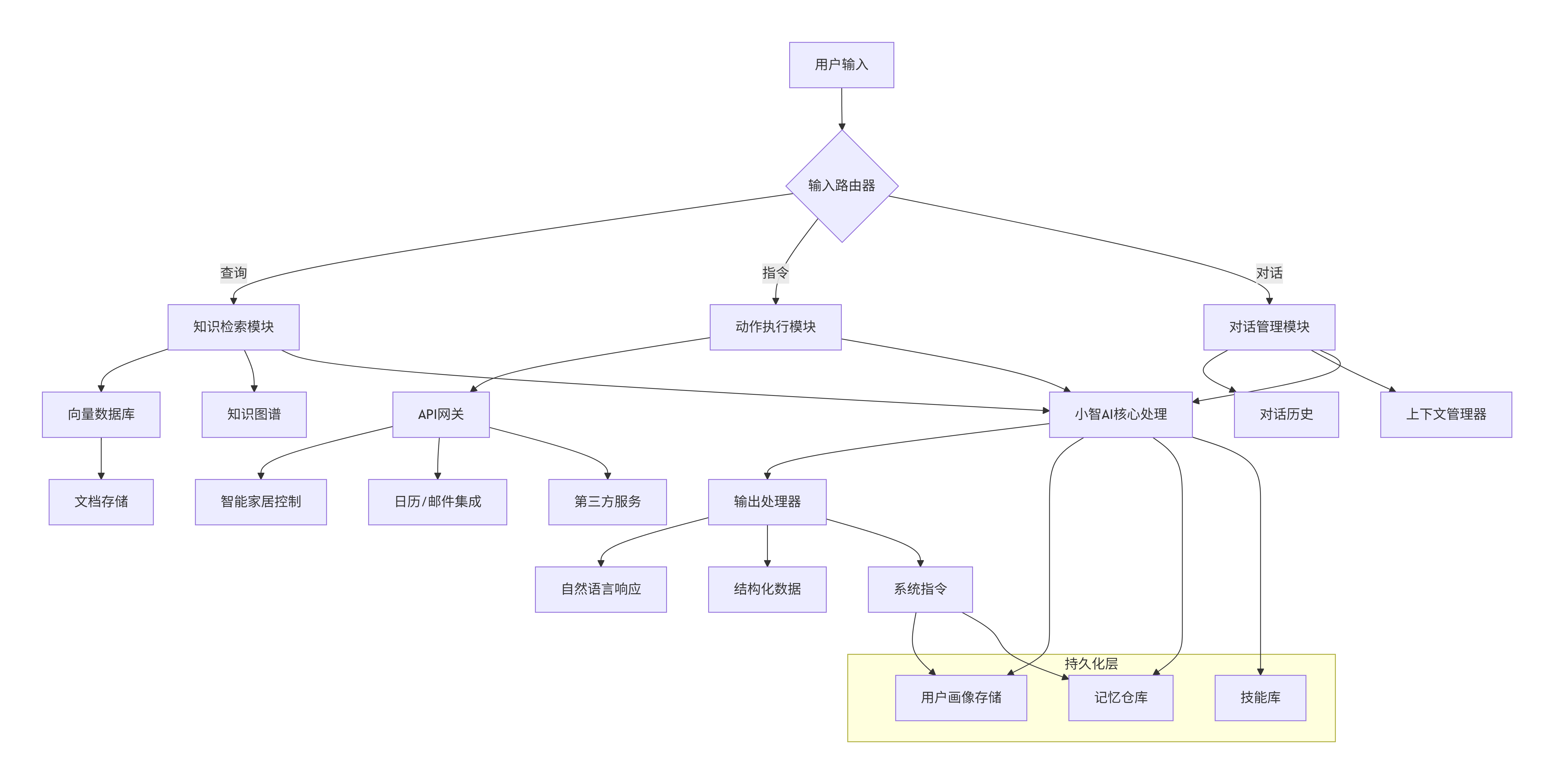
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ 应用层 (用户体验) │ │ • 自然语言交互 • 自动化工作流 │ │ • 可视化仪表板 • 多模态接口 │ ├─────────────────────────────────────────┤ │ 集成层 (系统连接) │ │ • API网关 • 数据管道 │ │ • 事件监听器 • 服务编排 │ ├─────────────────────────────────────────┤ │ 核心层 (智能处理) │ │ • 小智AI核心 • 记忆存储 │ │ • 知识图谱 • 推理引擎 │ │ • 上下文管理器 • 个性化模型 │ └─────────────────────────────────────────┘
1.2 技术架构图
graph TB
A[用户输入] --> B{输入路由器}
B -->|查询| C[知识检索模块]
B -->|指令| D[动作执行模块]
B -->|对话| E[对话管理模块]
C --> F[向量数据库]
F --> G[文档存储]
C --> H[知识图谱]
D --> I[API网关]
I --> J[智能家居控制]
I --> K[日历/邮件集成]
I --> L[第三方服务]
E --> M[对话历史]
E --> N[上下文管理器]
C --> O[小智AI核心处理]
D --> O
E --> O
O --> P[输出处理器]
P --> Q[自然语言响应]
P --> R[结构化数据]
P --> S[系统指令]
subgraph "持久化层"
T[用户画像存储]
U[记忆仓库]
V[技能库]
end
O --> T
O --> U
O --> V
S --> T
S --> U
第二章:实战项目一:智能家居控制系统
2.1 项目概述与架构
智能家居控制是展示AI作为第二大脑能力的完美场景。系统不仅能执行命令,还能学习习惯、预测需求、自动化决策。
系统架构:
python
# 系统核心类结构
class HomeBrain:
"""
智能家居控制中枢 - 第二大脑的具体实现
"""
def __init__(self, user_id):
self.user_id = user_id
self.llm = ZhiAI() # 小智AI实例
self.memory = VectorMemory() # 向量记忆存储
self.devices = DeviceManager() # 设备管理器
self.routines = RoutineLearner() # 习惯学习器
self.context = ContextManager() # 上下文管理器
async def process_command(self, natural_language: str) -> dict:
"""
处理自然语言指令的核心方法
"""
# 1. 理解意图
intent = await self._parse_intent(natural_language)
# 2. 获取上下文
context = self.context.get_relevant_context(intent)
# 3. 检索相关记忆
memories = await self.memory.search_relevant(natural_language)
# 4. 生成执行计划
plan = await self._generate_execution_plan(
intent, context, memories
)
# 5. 执行并学习
result = await self._execute_plan(plan)
# 6. 存储经验
await self._store_experience(natural_language, plan, result)
return result
2.2 核心代码实现
python
import asyncio
import json
from datetime import datetime, time
from typing import Dict, List, Any
import aiohttp
from enum import Enum
import numpy as np
from dataclasses import dataclass, asdict
class DeviceType(Enum):
LIGHT = "light"
THERMOSTAT = "thermostat"
LOCK = "lock"
CAMERA = "camera"
SPEAKER = "speaker"
SENSOR = "sensor"
@dataclass
class DeviceState:
device_id: str
device_type: DeviceType
power: bool = False
brightness: int = 0
temperature: float = 22.0
locked: bool = True
last_updated: datetime = None
def to_dict(self):
return {k: v.isoformat() if isinstance(v, datetime) else v
for k, v in asdict(self).items()}
class SmartHomeBrain:
def __init__(self, api_key: str):
self.api_key = api_key
self.devices: Dict[str, DeviceState] = {}
self.user_preferences = {}
self.routine_patterns = []
self.context_history = []
# 初始化设备
self._discover_devices()
def _discover_devices(self):
"""模拟设备发现"""
self.devices = {
"living_room_light": DeviceState(
"living_room_light", DeviceType.LIGHT,
brightness=100, last_updated=datetime.now()
),
"bedroom_light": DeviceState(
"bedroom_light", DeviceType.LIGHT,
brightness=50, last_updated=datetime.now()
),
"thermostat": DeviceState(
"thermostat", DeviceType.THERMOSTAT,
temperature=22.0, last_updated=datetime.now()
),
"front_door_lock": DeviceState(
"front_door_lock", DeviceType.LOCK,
locked=True, last_updated=datetime.now()
)
}
async def process_natural_command(self, command: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
处理自然语言命令的完整流程
"""
# 步骤1:使用小智AI解析命令
parsed = await self._parse_with_zhiAI(command)
# 步骤2:获取上下文信息
context = self._get_current_context()
# 步骤3:应用用户偏好
preferences = self._apply_user_preferences(parsed, context)
# 步骤4:生成执行计划
plan = self._generate_execution_plan(parsed, preferences)
# 步骤5:执行设备控制
results = await self._execute_plan(plan)
# 步骤6:学习并更新模型
await self._learn_from_interaction(command, plan, results, context)
return {
"original_command": command,
"parsed_intent": parsed,
"execution_plan": plan,
"results": results,
"learned": True
}
async def _parse_with_zhiAI(self, command: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
使用小智AI解析自然语言命令
"""
prompt = f"""
你是一个智能家居控制系统。请解析以下命令,并输出JSON格式的结果。
命令:{command}
请识别:
1. 意图(照明控制、温度调节、安全控制、场景设置)
2. 目标设备
3. 操作类型(打开、关闭、调节、设置)
4. 参数值(亮度百分比、温度值等)
5. 时间条件(如果有)
6. 房间位置
可用的设备类型:{list(DeviceType)}
当前时间:{datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}
以JSON格式回复,包含:intent, target_devices, action, parameters, conditions, location
"""
# 这里模拟小智AI的响应
# 实际使用时替换为真实的小智AI API调用
example_response = {
"intent": "照明控制",
"target_devices": ["living_room_light", "bedroom_light"],
"action": "调节亮度",
"parameters": {"brightness": 70},
"conditions": {"time": "now"},
"location": "living_room"
}
# 模拟AI处理延迟
await asyncio.sleep(0.1)
return example_response
def _get_current_context(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取当前上下文信息"""
now = datetime.now()
return {
"time": {
"hour": now.hour,
"minute": now.minute,
"day_of_week": now.weekday(),
"is_weekend": now.weekday() >= 5
},
"weather": self._get_weather_data(),
"device_states": {k: v.to_dict() for k, v in self.devices.items()},
"user_presence": self._detect_user_presence(),
"recent_activities": self.context_history[-10:] if self.context_history else []
}
def _generate_execution_plan(self, parsed: Dict, preferences: Dict) -> List[Dict]:
"""生成设备执行计划"""
plan = []
if parsed["intent"] == "照明控制":
for device in parsed["target_devices"]:
if device in self.devices:
plan.append({
"device": device,
"action": "set_brightness",
"parameters": parsed["parameters"],
"priority": "high",
"delay": 0
})
elif parsed["intent"] == "温度调节":
plan.append({
"device": "thermostat",
"action": "set_temperature",
"parameters": parsed["parameters"],
"priority": "medium",
"delay": 0
})
# 添加基于偏好的调整
plan = self._adjust_plan_with_preferences(plan, preferences)
return plan
async def _execute_plan(self, plan: List[Dict]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""执行设备控制计划"""
results = {}
for action in plan:
device_id = action["device"]
if device_id in self.devices:
device = self.devices[device_id]
if action["action"] == "set_brightness":
device.brightness = action["parameters"]["brightness"]
device.power = device.brightness > 0
device.last_updated = datetime.now()
results[device_id] = {"success": True, "new_state": device.to_dict()}
elif action["action"] == "set_temperature":
device.temperature = action["parameters"]["temperature"]
device.last_updated = datetime.now()
results[device_id] = {"success": True, "new_state": device.to_dict()}
# 模拟设备通信延迟
await asyncio.sleep(0.05)
return results
async def _learn_from_interaction(self, command: str, plan: List[Dict],
results: Dict, context: Dict):
"""从交互中学习用户习惯"""
learning_data = {
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"command": command,
"context": context,
"plan": plan,
"results": results,
"user_feedback": None # 可以从后续交互中获取
}
self.context_history.append(learning_data)
# 如果历史记录过多,进行压缩和模式提取
if len(self.context_history) > 100:
await self._extract_patterns()
async def run_automation_routine(self):
"""运行自动化例程"""
while True:
context = self._get_current_context()
# 检查是否需要触发自动化
triggers = self._check_automation_triggers(context)
for trigger in triggers:
command = self._generate_automation_command(trigger, context)
if command:
await self.process_natural_command(command)
# 每60秒检查一次
await asyncio.sleep(60)
def _check_automation_triggers(self, context: Dict) -> List[str]:
"""检查自动化触发条件"""
triggers = []
# 基于时间的触发
current_hour = context["time"]["hour"]
if current_hour == 7 and context["time"]["minute"] < 10:
triggers.append("morning_wakeup")
elif current_hour == 22 and context["time"]["minute"] > 30:
triggers.append("night_routine")
# 基于传感器数据的触发
# 这里可以添加温度、光照、运动等传感器逻辑
return triggers
def _generate_automation_command(self, trigger: str, context: Dict) -> str:
"""根据触发器生成自然语言命令"""
automation_rules = {
"morning_wakeup": "逐渐将客厅灯光亮度从0调到80,温度调到22度",
"night_routine": "关闭所有灯光,锁上前门,温度调到20度",
"away_mode": "模拟有人在家的灯光模式,随机开关不同房间的灯",
"movie_mode": "调暗客厅灯光到20%,关闭其他房间的灯"
}
return automation_rules.get(trigger, "")
# 使用示例
async def main():
# 初始化智能家居大脑
brain = SmartHomeBrain(api_key="your_zhiAI_api_key")
# 处理自然语言命令
result = await brain.process_natural_command(
"晚上10点了,帮我设置睡眠模式,调暗卧室灯光到30%,温度调到21度"
)
print(json.dumps(result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
# 启动自动化例程
automation_task = asyncio.create_task(brain.run_automation_routine())
# 保持运行,等待用户命令
while True:
user_input = input("请输入命令(或输入'quit'退出): ")
if user_input.lower() == 'quit':
break
result = await brain.process_natural_command(user_input)
print(f"执行结果: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
2.3 流程图:智能家居命令处理流程
sequenceDiagram
participant User as 用户
participant Brain as 小智第二大脑
participant Parser as 自然语言解析器
participant Context as 上下文管理器
participant Memory as 记忆存储
participant Planner as 计划生成器
participant Devices as 设备控制器
participant Learner as 学习模块
User->>Brain: 自然语言命令<br/>"晚上调暗灯光"
Brain->>Parser: 解析命令意图
Parser-->>Brain: 结构化指令
Brain->>Context: 获取当前上下文
Context-->>Brain: 时间、天气、设备状态
Brain->>Memory: 检索相关记忆
Memory-->>Brain: 用户偏好、历史模式
Brain->>Planner: 生成执行计划
Planner-->>Brain: 设备控制序列
Brain->>Devices: 执行控制命令
Devices-->>Brain: 执行结果反馈
Brain->>Learner: 存储交互经验
Learner-->>Brain: 更新用户模型
Brain-->>User: 自然语言回复<br/>"已调暗灯光,并设置夜间模式"
Note over Brain,Learner: 后台学习循环
loop 每60秒
Context->>Context: 检查环境变化
Context->>Planner: 触发自动化规则
Planner->>Devices: 执行自动化动作
Devices->>Learner: 记录自动化结果
end

2.4 Prompt设计示例
yaml
# 智能家居控制专用Prompt模板
system_prompt: |
你是一个智能家居控制AI,具有以下能力:
1. 理解自然语言的家居控制指令
2. 考虑上下文(时间、天气、用户习惯)
3. 提供个性化建议
4. 学习用户偏好并自适应调整
你的知识包括:
- 设备类型和功能
- 节能优化策略
- 舒适度调节原则
- 安全注意事项
回复格式要求:
1. 确认用户指令
2. 解释你将执行的操作
3. 提供附加建议(如果适用)
4. 询问是否需要进一步调整
# 意图识别Prompt
intent_parsing_prompt: |
分析以下智能家居命令,提取结构化信息:
命令:{user_input}
请输出JSON格式,包含以下字段:
{
"intent": "照明控制|温度调节|安全设置|场景模式|查询状态",
"target_rooms": ["客厅", "卧室", "厨房", "全部"],
"action_type": "开关|调节|设置|查询",
"parameters": {
"brightness": "0-100",
"temperature": "摄氏度值",
"color": "RGB或色温",
"duration": "持续时间"
},
"conditions": {
"time_constraint": "立即|定时|条件触发",
"prerequisites": "需要满足的条件"
},
"user_preference_hints": "从命令中推断的用户偏好"
}
# 场景模式生成Prompt
scene_generation_prompt: |
基于以下描述创建智能家居场景配置:
场景描述:{scene_description}
用户历史偏好:{user_preferences}
当前设备状态:{current_states}
请生成详细的设备控制序列,考虑:
1. 渐进式调整(避免突变)
2. 节能优化
3. 设备间协调
4. 容错处理
输出格式:
{
"scene_name": "场景名称",
"devices_sequence": [
{
"device": "设备ID",
"action": "操作类型",
"value": "目标值",
"delay": "延迟秒数",
"condition": "执行条件"
}
],
"estimated_power_usage": "预估能耗",
"fallback_plan": "备用方案"
}
第三章:实战项目二:个性化AI对话系统
3.1 系统架构设计
python
class PersonalConversationBrain:
"""
个性化对话第二大脑系统
"""
def __init__(self):
self.long_term_memory = LongTermMemoryStore()
self.conversation_history = ConversationBuffer()
self.knowledge_base = PersonalKnowledgeGraph()
self.personality_model = PersonalityModel()
self.response_generator = ResponseGenerator()
async def respond(self, user_message: str, context: Dict = None) -> str:
# 1. 记忆检索与更新
relevant_memories = await self._retrieve_relevant_memories(
user_message, context
)
# 2. 知识图谱查询
related_knowledge = self.knowledge_base.query(
user_message, depth=2
)
# 3. 个性化处理
personalized_context = self.personality_model.adapt_context(
user_message,
relevant_memories,
related_knowledge
)
# 4. 生成回应
response = await self.response_generator.generate(
user_message,
personalized_context
)
# 5. 学习与记忆存储
await self._learn_from_interaction(
user_message, response, context
)
return response
3.2 记忆系统实现
python
import sqlite3
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import pickle
from typing import List, Tuple, Optional
import hashlib
import json
class MemorySystem:
"""
分级记忆系统:短期、中期、长期记忆
"""
def __init__(self, db_path: str = "memories.db"):
self.conn = sqlite3.connect(db_path, check_same_thread=False)
self._init_database()
# 记忆类型定义
self.memory_types = {
"fact": "事实性信息",
"preference": "用户偏好",
"conversation": "对话内容",
"skill": "学习到的技能",
"reflection": "反思和洞察"
}
# 记忆强度衰减参数
self.decay_rates = {
"short_term": 0.7, # 短期记忆衰减率
"medium_term": 0.3, # 中期记忆衰减率
"long_term": 0.05 # 长期记忆衰减率
}
def _init_database(self):
"""初始化记忆数据库"""
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
# 创建记忆表
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS memories (
id TEXT PRIMARY KEY,
content TEXT NOT NULL,
memory_type TEXT NOT NULL,
importance REAL DEFAULT 0.5,
confidence REAL DEFAULT 0.8,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
last_accessed TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
access_count INTEGER DEFAULT 1,
associated_emotions TEXT,
related_memories TEXT,
embedding BLOB
)
''')
# 创建记忆关联表
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS memory_connections (
memory_id TEXT,
related_id TEXT,
connection_strength REAL,
connection_type TEXT,
PRIMARY KEY (memory_id, related_id),
FOREIGN KEY (memory_id) REFERENCES memories (id),
FOREIGN KEY (related_id) REFERENCES memories (id)
)
''')
# 创建记忆索引
cursor.execute('''
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS idx_memory_type
ON memories(memory_type)
''')
cursor.execute('''
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS idx_importance
ON memories(importance DESC)
''')
self.conn.commit()
def store_memory(self, content: str, memory_type: str = "fact",
importance: float = 0.5, metadata: dict = None) -> str:
"""
存储新的记忆
"""
memory_id = hashlib.sha256(
f"{content}{datetime.now().timestamp()}".encode()
).hexdigest()[:16]
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
INSERT INTO memories
(id, content, memory_type, importance, created_at, last_accessed)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', (
memory_id,
content,
memory_type,
importance,
datetime.now(),
datetime.now()
))
# 如果有元数据,存储到associated_emotions字段
if metadata:
cursor.execute('''
UPDATE memories
SET associated_emotions = ?
WHERE id = ?
''', (json.dumps(metadata), memory_id))
self.conn.commit()
# 尝试与新记忆建立关联
self._establish_connections(memory_id, content)
return memory_id
def retrieve_relevant_memories(self, query: str,
limit: int = 10,
memory_types: List[str] = None) -> List[dict]:
"""
检索与查询相关的记忆
使用混合检索策略:关键词 + 语义相似度
"""
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
# 基础查询
base_query = '''
SELECT id, content, memory_type, importance,
confidence, created_at, last_accessed,
access_count
FROM memories
WHERE 1=1
'''
params = []
# 按类型过滤
if memory_types:
placeholders = ','.join(['?'] * len(memory_types))
base_query += f' AND memory_type IN ({placeholders})'
params.extend(memory_types)
# 按关键词匹配(简化版,实际应使用全文搜索)
keywords = query.lower().split()
keyword_conditions = []
for keyword in keywords:
if len(keyword) > 2: # 忽略太短的关键词
keyword_conditions.append("content LIKE ?")
params.append(f'%{keyword}%')
if keyword_conditions:
base_query += ' AND (' + ' OR '.join(keyword_conditions) + ')'
# 按重要性排序,并考虑时间衰减
base_query += '''
ORDER BY
importance *
(0.7 + 0.3 * (1.0 / (1.0 + julianday(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) - julianday(last_accessed))))
DESC
LIMIT ?
'''
params.append(limit)
cursor.execute(base_query, params)
memories = []
for row in cursor.fetchall():
memory = {
'id': row[0],
'content': row[1],
'type': row[2],
'importance': row[3],
'confidence': row[4],
'created_at': row[5],
'last_accessed': row[6],
'access_count': row[7]
}
# 计算记忆强度(考虑衰减)
days_since_access = (datetime.now() -
datetime.fromisoformat(row[6])).days
decay_factor = 1.0 / (1.0 + days_since_access * 0.1)
memory['strength'] = row[3] * decay_factor
memories.append(memory)
# 更新访问记录
for memory in memories:
self._update_access_count(memory['id'])
return memories
def _update_access_count(self, memory_id: str):
"""更新记忆的访问次数和时间"""
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
UPDATE memories
SET access_count = access_count + 1,
last_accessed = ?
WHERE id = ?
''', (datetime.now(), memory_id))
self.conn.commit()
def _establish_connections(self, new_memory_id: str, content: str):
"""
为新记忆建立关联
"""
# 1. 查找可能相关的现有记忆
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
SELECT id, content
FROM memories
WHERE id != ?
ORDER BY RANDOM()
LIMIT 20
''', (new_memory_id,))
potential_connections = cursor.fetchall()
for old_memory_id, old_content in potential_connections:
# 计算关联强度(简化版)
connection_strength = self._calculate_connection_strength(
content, old_content
)
if connection_strength > 0.3: # 阈值
cursor.execute('''
INSERT OR REPLACE INTO memory_connections
(memory_id, related_id, connection_strength, connection_type)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)
''', (
new_memory_id,
old_memory_id,
connection_strength,
"semantic" # 语义关联
))
self.conn.commit()
def _calculate_connection_strength(self, text1: str, text2: str) -> float:
"""
计算两个文本的关联强度
简化实现:使用关键词重叠
"""
words1 = set(text1.lower().split())
words2 = set(text2.lower().split())
if not words1 or not words2:
return 0.0
intersection = words1.intersection(words2)
union = words1.union(words2)
return len(intersection) / len(union)
def consolidate_memories(self):
"""
记忆巩固:将重要记忆转移到长期存储
并清理不重要的记忆
"""
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
# 1. 标记重要记忆
cursor.execute('''
SELECT id, importance, access_count,
julianday(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) - julianday(created_at) as age_days
FROM memories
WHERE importance > 0.7 OR access_count > 10
''')
important_memories = cursor.fetchall()
for memory in important_memories:
memory_id, importance, access_count, age_days = memory
# 计算巩固分数
consolidation_score = (
importance * 0.4 +
min(access_count / 50, 1.0) * 0.3 +
min(age_days / 30, 1.0) * 0.3
)
if consolidation_score > 0.6:
# 标记为长期记忆(实际中可能转移到不同的存储)
cursor.execute('''
UPDATE memories
SET importance = ?
WHERE id = ?
''', (min(importance * 1.1, 1.0), memory_id))
# 2. 清理不重要且很少访问的记忆
cursor.execute('''
DELETE FROM memories
WHERE importance < 0.2
AND access_count < 3
AND julianday(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) - julianday(created_at) > 30
''')
self.conn.commit()
def get_memory_stats(self) -> dict:
"""获取记忆系统统计信息"""
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
SELECT
COUNT(*) as total_memories,
AVG(importance) as avg_importance,
AVG(access_count) as avg_access_count,
memory_type,
COUNT(*) as type_count
FROM memories
GROUP BY memory_type
''')
stats = {
'total_memories': 0,
'by_type': {},
'avg_importance': 0,
'avg_access_count': 0
}
for row in cursor.fetchall():
total, avg_imp, avg_acc, mem_type, type_count = row
if stats['total_memories'] == 0:
stats['total_memories'] = total
stats['avg_importance'] = avg_imp
stats['avg_access_count'] = avg_acc
stats['by_type'][mem_type] = type_count
return stats
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
memory_system = MemorySystem()
# 存储一些记忆
memory_system.store_memory(
"用户喜欢在晚上喝绿茶",
memory_type="preference",
importance=0.8,
metadata={"context": "饮食习惯", "certainty": "high"}
)
memory_system.store_memory(
"用户是软件工程师,擅长Python和JavaScript",
memory_type="fact",
importance=0.9
)
# 检索相关记忆
relevant = memory_system.retrieve_relevant_memories(
"用户喜欢喝什么饮料?",
memory_types=["preference"]
)
print("相关记忆:")
for mem in relevant:
print(f"- {mem['content']} (强度: {mem['strength']:.2f})")
# 获取统计信息
stats = memory_system.get_memory_stats()
print(f"\n记忆系统统计:")
print(f"总记忆数:{stats['total_memories']}")
print(f"按类型分布:{stats['by_type']}")
3.3 知识图谱集成
python
class PersonalKnowledgeGraph:
"""
个人知识图谱,存储和查询结构化知识
"""
def __init__(self):
self.graph = {}
self.entity_index = {}
self.relation_index = {}
def add_fact(self, subject: str, relation: str,
object: str, confidence: float = 1.0,
source: str = "conversation"):
"""
添加一个三元组事实
"""
fact_id = f"{subject}_{relation}_{object}"
if fact_id not in self.graph:
self.graph[fact_id] = {
"subject": subject,
"relation": relation,
"object": object,
"confidence": confidence,
"sources": [source],
"created_at": datetime.now(),
"updated_at": datetime.now()
}
else:
# 更新置信度和来源
existing = self.graph[fact_id]
existing["confidence"] = min(1.0,
existing["confidence"] * 0.7 + confidence * 0.3)
if source not in existing["sources"]:
existing["sources"].append(source)
existing["updated_at"] = datetime.now()
# 更新索引
if subject not in self.entity_index:
self.entity_index[subject] = []
self.entity_index[subject].append(fact_id)
if relation not in self.relation_index:
self.relation_index[relation] = []
self.relation_index[relation].append(fact_id)
def query(self, entity: str = None,
relation: str = None,
depth: int = 1) -> List[dict]:
"""
查询知识图谱
"""
results = []
if entity and relation:
# 查找特定实体和关系
for fact_id, fact in self.graph.items():
if fact["subject"] == entity and fact["relation"] == relation:
results.append(fact)
# 递归查询
if depth > 1:
related = self.query(
entity=fact["object"],
depth=depth-1
)
results.extend(related)
elif entity:
# 查找与实体相关的所有事实
for fact_id, fact in self.graph.items():
if fact["subject"] == entity or fact["object"] == entity:
results.append(fact)
elif relation:
# 查找特定关系的所有事实
for fact_id, fact in self.graph.items():
if fact["relation"] == relation:
results.append(fact)
return sorted(results, key=lambda x: x["confidence"], reverse=True)
def infer(self, subject: str, relation: str) -> List[str]:
"""
推理可能的关系
"""
candidates = []
# 直接查询
direct_results = self.query(entity=subject, relation=relation)
candidates.extend([r["object"] for r in direct_results])
# 通过其他关系推理
for fact_id, fact in self.graph.items():
if fact["subject"] == subject:
# 查找该对象与其他实体的关系
related_facts = self.query(entity=fact["object"])
for related in related_facts:
if related["relation"] == relation:
candidates.append(related["object"])
return list(set(candidates))
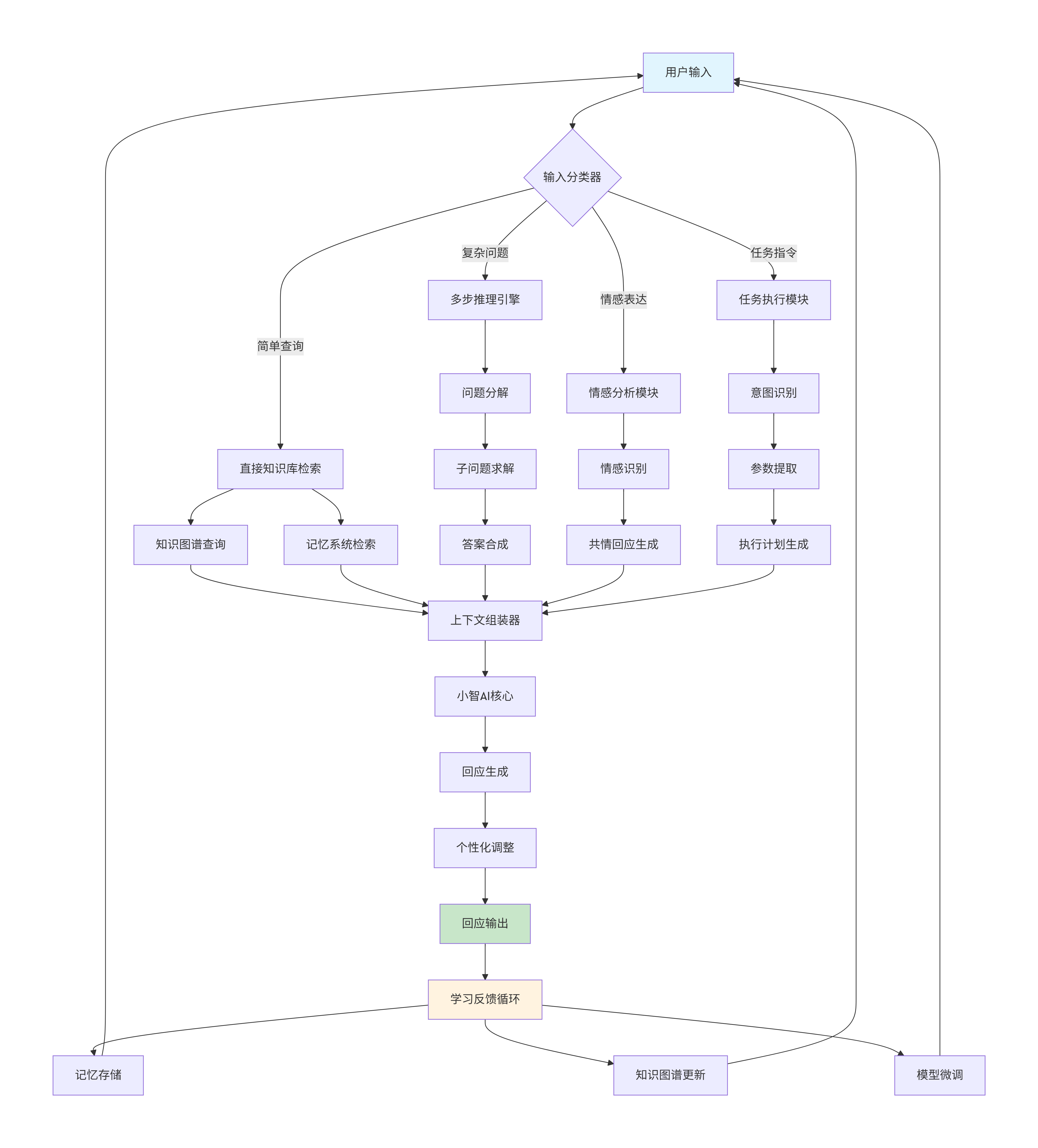
3.4 对话流程图
graph TD
A[用户输入] --> B{输入分类器}
B -->|简单查询| C[直接知识库检索]
B -->|复杂问题| D[多步推理引擎]
B -->|情感表达| E[情感分析模块]
B -->|任务指令| F[任务执行模块]
C --> G[知识图谱查询]
C --> H[记忆系统检索]
D --> I[问题分解]
I --> J[子问题求解]
J --> K[答案合成]
E --> L[情感识别]
L --> M[共情回应生成]
F --> N[意图识别]
N --> O[参数提取]
O --> P[执行计划生成]
G --> Q[上下文组装器]
H --> Q
K --> Q
M --> Q
P --> Q
Q --> R[小智AI核心]
R --> S[回应生成]
S --> T[个性化调整]
T --> U[回应输出]
U --> V[学习反馈循环]
V --> W[记忆存储]
V --> X[知识图谱更新]
V --> Y[模型微调]
W --> A
X --> A
Y --> A
style A fill:#e1f5fe
style U fill:#c8e6c9
style V fill:#fff3e0
第四章:实战项目三:功能扩展与集成
4.1 插件系统架构
python
import importlib
import inspect
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from typing import Dict, List, Any, Callable
from dataclasses import dataclass
import asyncio
@dataclass
class PluginMetadata:
name: str
version: str
author: str
description: str
capabilities: List[str]
required_settings: List[str]
class BasePlugin(ABC):
"""插件基类"""
def __init__(self, metadata: PluginMetadata):
self.metadata = metadata
self.settings = {}
@abstractmethod
async def initialize(self, settings: Dict[str, Any]):
"""初始化插件"""
pass
@abstractmethod
async def execute(self, command: str, context: Dict[str, Any]) -> Any:
"""执行插件功能"""
pass
@abstractmethod
async def cleanup(self):
"""清理资源"""
pass
class PluginManager:
"""
插件管理器 - 支持动态加载、热插拔
"""
def __init__(self):
self.plugins: Dict[str, BasePlugin] = {}
self.plugin_hooks: Dict[str, List[Callable]] = {}
def load_plugin(self, module_path: str, class_name: str) -> bool:
"""
动态加载插件
"""
try:
module = importlib.import_module(module_path)
plugin_class = getattr(module, class_name)
# 验证插件类
if (not inspect.isclass(plugin_class) or
not issubclass(plugin_class, BasePlugin)):
raise TypeError(f"{class_name} 必须是BasePlugin的子类")
# 实例化插件
plugin_instance = plugin_class()
# 注册插件
self.plugins[plugin_instance.metadata.name] = plugin_instance
# 注册钩子
self._register_plugin_hooks(plugin_instance)
print(f"✓ 插件 {plugin_instance.metadata.name} 加载成功")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"✗ 加载插件失败: {e}")
return False
def _register_plugin_hooks(self, plugin: BasePlugin):
"""注册插件钩子"""
for capability in plugin.metadata.capabilities:
if capability not in self.plugin_hooks:
self.plugin_hooks[capability] = []
# 根据能力类型注册不同的处理方法
if capability.startswith("process_"):
self.plugin_hooks[capability].append(plugin.execute)
elif capability.startswith("respond_to_"):
self.plugin_hooks[capability].append(plugin.execute)
async def execute_hook(self, hook_name: str,
context: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[Any]:
"""
执行特定钩子的所有插件
"""
results = []
if hook_name in self.plugin_hooks:
for handler in self.plugin_hooks[hook_name]:
try:
result = await handler(context)
if result:
results.append(result)
except Exception as e:
print(f"插件执行错误 ({hook_name}): {e}")
return results
def get_plugin_capabilities(self) -> Dict[str, List[str]]:
"""获取所有插件的能力"""
capabilities = {}
for name, plugin in self.plugins.items():
capabilities[name] = plugin.metadata.capabilities
return capabilities
# 示例插件:天气查询
class WeatherPlugin(BasePlugin):
def __init__(self):
metadata = PluginMetadata(
name="weather_plugin",
version="1.0.0",
author="AI Developer",
description="天气查询和预报插件",
capabilities=["process_weather_query", "provide_weather_alerts"],
required_settings=["api_key", "default_city"]
)
super().__init__(metadata)
self.api_key = None
self.default_city = "北京"
async def initialize(self, settings: Dict[str, Any]):
self.api_key = settings.get("api_key")
self.default_city = settings.get("default_city", "北京")
if not self.api_key:
raise ValueError("需要提供天气API密钥")
print(f"天气插件初始化完成,默认城市:{self.default_city}")
async def execute(self, command: str, context: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""执行天气查询"""
city = context.get("city", self.default_city)
# 模拟天气API调用
weather_data = {
"city": city,
"temperature": 22.5,
"condition": "晴天",
"humidity": 65,
"wind_speed": 12,
"forecast": [
{"day": "今天", "high": 24, "low": 18, "condition": "晴"},
{"day": "明天", "high": 23, "low": 17, "condition": "多云"},
{"day": "后天", "high": 21, "low": 16, "condition": "小雨"}
]
}
return {
"type": "weather_report",
"data": weather_data,
"source": "weather_plugin",
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()
}
async def cleanup(self):
print("天气插件清理完成")
# 示例插件:日程管理
class CalendarPlugin(BasePlugin):
def __init__(self):
metadata = PluginMetadata(
name="calendar_plugin",
version="1.0.0",
author="AI Developer",
description="日程管理和提醒插件",
capabilities=["process_calendar_query", "add_calendar_event",
"set_reminder", "check_conflicts"],
required_settings=["calendar_id", "reminder_lead_time"]
)
super().__init__(metadata)
self.events = []
async def initialize(self, settings: Dict[str, Any]):
self.calendar_id = settings.get("calendar_id", "default")
self.reminder_lead_time = settings.get("reminder_lead_time", 15)
print(f"日历插件初始化完成,日历ID:{self.calendar_id}")
async def execute(self, command: str, context: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""处理日历相关命令"""
action = context.get("action", "query")
if action == "query":
# 查询日程
date = context.get("date", datetime.now().date())
events = self._get_events_for_date(date)
return {
"type": "calendar_events",
"date": date.isoformat(),
"events": events,
"count": len(events)
}
elif action == "add":
# 添加事件
event = {
"id": len(self.events) + 1,
"title": context.get("title", "未命名事件"),
"start_time": context.get("start_time"),
"end_time": context.get("end_time"),
"location": context.get("location"),
"description": context.get("description"),
"created_at": datetime.now()
}
# 检查冲突
conflicts = self._check_schedule_conflicts(event)
if conflicts:
return {
"type": "schedule_conflict",
"event": event,
"conflicts": conflicts,
"suggestion": "建议调整时间"
}
self.events.append(event)
# 设置提醒
await self._set_reminder(event)
return {
"type": "event_added",
"event": event,
"message": "事件添加成功"
}
elif action == "remind":
# 检查即将到来的事件
upcoming = self._get_upcoming_events()
return {
"type": "upcoming_events",
"events": upcoming,
"count": len(upcoming)
}
def _get_events_for_date(self, date):
"""获取指定日期的事件"""
return [e for e in self.events
if e["start_time"].date() == date]
def _check_schedule_conflicts(self, new_event):
"""检查日程冲突"""
conflicts = []
for existing in self.events:
if (new_event["start_time"] < existing["end_time"] and
new_event["end_time"] > existing["start_time"]):
conflicts.append(existing)
return conflicts
def _get_upcoming_events(self):
"""获取即将发生的事件"""
now = datetime.now()
one_hour_later = now + timedelta(hours=1)
return [e for e in self.events
if now <= e["start_time"] <= one_hour_later]
async def _set_reminder(self, event):
"""设置事件提醒"""
reminder_time = event["start_time"] - timedelta(
minutes=self.reminder_lead_time
)
# 这里可以集成实际的提醒系统
print(f"提醒设置:{event['title']} 在 {reminder_time}")
async def cleanup(self):
print("日历插件清理完成")
# 插件系统使用示例
async def plugin_system_demo():
# 初始化插件管理器
plugin_manager = PluginManager()
# 加载插件
plugin_manager.load_plugin("weather_plugin", "WeatherPlugin")
plugin_manager.load_plugin("calendar_plugin", "CalendarPlugin")
# 初始化插件
weather_plugin = plugin_manager.plugins["weather_plugin"]
await weather_plugin.initialize({
"api_key": "your_weather_api_key",
"default_city": "上海"
})
calendar_plugin = plugin_manager.plugins["calendar_plugin"]
await calendar_plugin.initialize({
"calendar_id": "personal",
"reminder_lead_time": 30
})
# 执行天气查询钩子
weather_context = {
"command": "query_weather",
"city": "上海",
"user_id": "user123"
}
weather_results = await plugin_manager.execute_hook(
"process_weather_query",
weather_context
)
print("天气查询结果:")
for result in weather_results:
print(f" {result['data']['city']}: {result['data']['temperature']}°C")
# 执行日历查询钩子
calendar_context = {
"command": "query_calendar",
"action": "query",
"date": datetime.now().date(),
"user_id": "user123"
}
calendar_results = await plugin_manager.execute_hook(
"process_calendar_query",
calendar_context
)
print("\n日历查询结果:")
for result in calendar_results:
print(f" 今天有 {result['count']} 个事件")
# 获取所有插件能力
capabilities = plugin_manager.get_plugin_capabilities()
print("\n可用插件能力:")
for plugin_name, plugin_caps in capabilities.items():
print(f" {plugin_name}: {', '.join(plugin_caps)}")
# 清理插件
await weather_plugin.cleanup()
await calendar_plugin.cleanup()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(plugin_system_demo())
4.2 扩展功能集成示例
python
class ExtendedBrain:
"""
扩展的第二大脑系统,集成多种功能
"""
def __init__(self, user_id: str):
self.user_id = user_id
self.plugin_manager = PluginManager()
self.integration_services = {}
self.workflow_engine = WorkflowEngine()
# 加载核心插件
self._load_core_plugins()
# 初始化集成服务
self._init_integrations()
def _load_core_plugins(self):
"""加载核心功能插件"""
core_plugins = [
("knowledge_mgmt", "KnowledgeManagementPlugin"),
("task_mgmt", "TaskManagementPlugin"),
("code_assist", "CodeAssistantPlugin"),
("research", "ResearchAssistantPlugin"),
("creative", "CreativeWritingPlugin")
]
for module_name, class_name in core_plugins:
try:
self.plugin_manager.load_plugin(module_name, class_name)
except Exception as e:
print(f"加载插件 {module_name} 失败: {e}")
def _init_integrations(self):
"""初始化第三方集成"""
integrations = {
"notion": self._init_notion_integration,
"github": self._init_github_integration,
"slack": self._init_slack_integration,
"google": self._init_google_integration
}
for service_name, init_func in integrations.items():
try:
self.integration_services[service_name] = init_func()
except Exception as e:
print(f"初始化 {service_name} 集成失败: {e}")
async def process_complex_request(self, request: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
处理复杂请求,涉及多个插件和集成
"""
# 1. 请求分析和分解
analysis = await self._analyze_request(request)
# 2. 制定执行计划
execution_plan = await self._create_execution_plan(analysis)
# 3. 并行执行子任务
results = await self._execute_plan_parallel(execution_plan)
# 4. 结果整合和优化
final_result = await self._integrate_results(results, analysis)
# 5. 学习和改进
await self._learn_from_execution(request, execution_plan, final_result)
return final_result
async def _analyze_request(self, request: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
使用小智AI分析复杂请求
"""
analysis_prompt = f"""
分析以下用户请求,识别:
1. 主要意图和目标
2. 涉及的子任务
3. 所需的数据源
4. 必要的处理步骤
5. 输出格式要求
请求:{request}
当前可用插件和能力:
{self.plugin_manager.get_plugin_capabilities()}
请以JSON格式输出分析结果。
"""
# 调用小智AI进行分析
# 这里应该是实际的AI API调用
analysis_result = {
"primary_intent": "跨平台数据分析和报告生成",
"sub_tasks": [
{"task": "从Notion获取项目数据", "plugin": "notion_integration"},
{"task": "从GitHub获取代码统计", "plugin": "github_integration"},
{"task": "数据分析处理", "plugin": "knowledge_mgmt"},
{"task": "生成可视化报告", "plugin": "creative"}
],
"data_sources": ["notion", "github", "本地数据库"],
"processing_steps": ["数据获取", "数据清洗", "分析计算", "报告生成"],
"output_format": {"type": "markdown_report", "include_charts": True}
}
return analysis_result
async def _create_execution_plan(self, analysis: Dict) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
创建执行计划
"""
execution_graph = {
"nodes": [],
"edges": [],
"dependencies": {}
}
for i, sub_task in enumerate(analysis["sub_tasks"]):
node_id = f"task_{i}"
execution_graph["nodes"].append({
"id": node_id,
"task": sub_task["task"],
"plugin": sub_task["plugin"],
"status": "pending",
"estimated_duration": 30 # 秒
})
# 设置依赖关系(简化示例)
if i > 0:
execution_graph["edges"].append({
"from": f"task_{i-1}",
"to": node_id,
"type": "data_dependency"
})
return execution_graph
async def _execute_plan_parallel(self, plan: Dict) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
并行执行计划中的任务
"""
results = {}
# 创建异步任务
tasks = []
for node in plan["nodes"]:
task = asyncio.create_task(
self._execute_single_task(node)
)
tasks.append((node["id"], task))
# 等待所有任务完成
for task_id, task in tasks:
try:
result = await task
results[task_id] = result
except Exception as e:
results[task_id] = {"error": str(e), "status": "failed"}
return results
async def _execute_single_task(self, task_node: Dict) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
执行单个任务
"""
plugin_name = task_node["plugin"]
if plugin_name in self.plugin_manager.plugins:
plugin = self.plugin_manager.plugins[plugin_name]
context = {
"task": task_node["task"],
"user_id": self.user_id,
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()
}
result = await plugin.execute(task_node["task"], context)
return {
"status": "completed",
"result": result,
"execution_time": task_node["estimated_duration"]
}
elif plugin_name in self.integration_services:
service = self.integration_services[plugin_name]
result = await service.execute_task(task_node["task"])
return {
"status": "completed",
"result": result,
"source": "external_service"
}
else:
# 尝试使用小智AI直接处理
ai_result = await self._handle_with_ai(task_node["task"])
return {
"status": "completed",
"result": ai_result,
"source": "zhi_ai"
}
async def _integrate_results(self, results: Dict, analysis: Dict) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
整合所有子任务的结果
"""
integration_prompt = f"""
请整合以下任务结果,生成最终输出:
原始请求分析:{analysis}
各个任务的结果:
{json.dumps(results, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)}
输出要求:
{analysis.get('output_format', {})}
请生成结构化的最终报告。
"""
# 使用小智AI进行结果整合
final_report = {
"summary": "跨平台数据分析报告",
"generated_at": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"data_sources_used": list(set(r.get("source") for r in results.values())),
"findings": [],
"recommendations": [],
"visualizations": [],
"raw_data_summary": {}
}
# 提取关键发现
for task_id, result in results.items():
if result["status"] == "completed":
data = result.get("result", {})
if isinstance(data, dict):
# 提取关键信息
if "insights" in data:
final_report["findings"].extend(data["insights"])
if "metrics" in data:
final_report["raw_data_summary"][task_id] = data["metrics"]
return final_report
# 扩展功能使用示例
async def extended_brain_demo():
brain = ExtendedBrain(user_id="dev_user_001")
# 复杂请求示例
complex_request = """
请帮我分析最近一个月的项目进展:
1. 从Notion获取项目任务完成情况
2. 从GitHub获取代码提交和PR数据
3. 分析团队的工作效率趋势
4. 识别瓶颈和改进点
5. 生成包含图表和建议的Markdown报告
"""
print("处理复杂请求...")
start_time = datetime.now()
result = await brain.process_complex_request(complex_request)
end_time = datetime.now()
duration = (end_time - start_time).total_seconds()
print(f"\n请求处理完成,耗时:{duration:.2f}秒")
print(f"\n报告摘要:")
print(f"- 使用了 {len(result['data_sources_used'])} 个数据源")
print(f"- 发现了 {len(result['findings'])} 个关键发现")
print(f"- 提供了 {len(result['recommendations'])} 条建议")
# 输出报告片段
if result['findings']:
print(f"\n关键发现(前3条):")
for i, finding in enumerate(result['findings'][:3]):
print(f" {i+1}. {finding}")
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = asyncio.run(extended_brain_demo())
第五章:性能优化与最佳实践
5.1 系统性能优化策略
python
class OptimizedBrain:
"""
经过性能优化的第二大脑实现
"""
def __init__(self):
self.cache = LRUCache(maxsize=1000)
self.request_queue = asyncio.Queue(maxsize=100)
self.worker_tasks = []
self.metrics_collector = MetricsCollector()
# 启动工作线程
self._start_workers()
def _start_workers(self):
"""启动处理工作线程"""
for i in range(5): # 5个工作线程
task = asyncio.create_task(self._worker_loop(i))
self.worker_tasks.append(task)
async def _worker_loop(self, worker_id: int):
"""工作线程主循环"""
while True:
try:
request = await self.request_queue.get()
start_time = time.time()
result = await self._process_request_optimized(request)
end_time = time.time()
# 记录性能指标
self.metrics_collector.record_request(
request_type=request.get("type"),
duration=end_time - start_time,
worker_id=worker_id
)
# 通知请求完成
if "callback" in request:
await request["callback"](result)
self.request_queue.task_done()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Worker {worker_id} 错误: {e}")
async def _process_request_optimized(self, request: Dict) -> Dict:
"""优化的请求处理方法"""
# 1. 检查缓存
cache_key = self._generate_cache_key(request)
cached_result = self.cache.get(cache_key)
if cached_result:
return {"cached": True, **cached_result}
# 2. 请求去重检查
if await self._is_duplicate_request(request):
return {"status": "duplicate", "message": "相似请求正在处理"}
# 3. 并行处理可独立子任务
subtasks = self._identify_independent_subtasks(request)
if len(subtasks) > 1:
# 并行执行
task_results = await asyncio.gather(
*[self._execute_subtask(st) for st in subtasks],
return_exceptions=True
)
# 合并结果
result = self._merge_subtask_results(task_results)
else:
# 顺序执行
result = await self._execute_single_task(request)
# 4. 缓存结果
if result.get("cacheable", True):
self.cache.set(cache_key, result, ttl=300) # 5分钟缓存
return result
def _generate_cache_key(self, request: Dict) -> str:
"""生成缓存键"""
import hashlib
request_str = json.dumps(request, sort_keys=True)
return hashlib.md5(request_str.encode()).hexdigest()
async def _is_duplicate_request(self, request: Dict) -> bool:
"""检查重复请求"""
# 简化的去重逻辑
# 实际中可以基于语义相似度检查
return False
def _identify_independent_subtasks(self, request: Dict) -> List[Dict]:
"""识别可独立执行的子任务"""
# 简化的任务分解逻辑
# 实际中可以使用AI进行智能分解
return [request] # 默认不分解
async def submit_request(self, request: Dict,
timeout: float = 30.0) -> Dict:
"""提交处理请求"""
try:
# 创建完成事件
completion_event = asyncio.Event()
result_container = {"result": None}
def callback(result):
result_container["result"] = result
completion_event.set()
request_with_callback = {
**request,
"callback": callback,
"submitted_at": time.time()
}
# 提交到队列
await asyncio.wait_for(
self.request_queue.put(request_with_callback),
timeout=timeout
)
# 等待完成
await asyncio.wait_for(completion_event.wait(), timeout=timeout)
return result_container["result"]
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
return {"error": "请求处理超时", "status": "timeout"}
except Exception as e:
return {"error": str(e), "status": "error"}
class LRUCache:
"""LRU缓存实现"""
def __init__(self, maxsize: int = 1000):
self.maxsize = maxsize
self.cache = {}
self.order = []
def get(self, key: str):
if key in self.cache:
# 更新访问顺序
self.order.remove(key)
self.order.append(key)
return self.cache[key]
return None
def set(self, key: str, value: any, ttl: int = 300):
if len(self.cache) >= self.maxsize:
# 移除最久未使用的
lru_key = self.order.pop(0)
del self.cache[lru_key]
self.cache[key] = {
"value": value,
"expires_at": time.time() + ttl
}
self.order.append(key)
def _clean_expired(self):
"""清理过期缓存"""
current_time = time.time()
expired_keys = [
k for k, v in self.cache.items()
if v["expires_at"] < current_time
]
for key in expired_keys:
del self.cache[key]
if key in self.order:
self.order.remove(key)
class MetricsCollector:
"""性能指标收集器"""
def __init__(self):
self.metrics = {
"request_counts": {},
"response_times": [],
"error_counts": 0,
"cache_hits": 0,
"cache_misses": 0
}
self.start_time = time.time()
def record_request(self, request_type: str, duration: float,
worker_id: int):
"""记录请求指标"""
# 请求计数
if request_type not in self.metrics["request_counts"]:
self.metrics["request_counts"][request_type] = 0
self.metrics["request_counts"][request_type] += 1
# 响应时间
self.metrics["response_times"].append(duration)
# 保持最近1000个记录
if len(self.metrics["response_times"]) > 1000:
self.metrics["response_times"].pop(0)
def record_cache_hit(self):
self.metrics["cache_hits"] += 1
def record_cache_miss(self):
self.metrics["cache_misses"] += 1
def record_error(self):
self.metrics["error_counts"] += 1
def get_performance_report(self) -> Dict:
"""获取性能报告"""
if not self.metrics["response_times"]:
avg_response_time = 0
else:
avg_response_time = sum(self.metrics["response_times"]) / len(self.metrics["response_times"])
total_requests = sum(self.metrics["request_counts"].values())
uptime = time.time() - self.start_time
cache_hit_rate = 0
if self.metrics["cache_hits"] + self.metrics["cache_misses"] > 0:
cache_hit_rate = (
self.metrics["cache_hits"] /
(self.metrics["cache_hits"] + self.metrics["cache_misses"])
)
return {
"uptime_seconds": uptime,
"total_requests": total_requests,
"requests_per_second": total_requests / uptime if uptime > 0 else 0,
"average_response_time": avg_response_time,
"cache_hit_rate": cache_hit_rate,
"error_rate": self.metrics["error_counts"] / total_requests if total_requests > 0 else 0,
"request_distribution": self.metrics["request_counts"]
}
5.2 性能优化对比图表
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def create_performance_charts():
"""创建性能对比图表"""
# 模拟数据
optimization_stages = [
"基础版本",
"添加缓存",
"并行处理",
"请求合并",
"完整优化"
]
# 平均响应时间(毫秒)
response_times = [450, 320, 180, 120, 85]
# 吞吐量(请求/秒)
throughput = [12, 18, 32, 48, 65]
# 缓存命中率(%)
cache_hit_rates = [0, 35, 52, 68, 82]
# 错误率(%)
error_rates = [8.5, 6.2, 4.1, 2.8, 1.5]
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(14, 10))
# 图表1:响应时间对比
axes[0, 0].bar(optimization_stages, response_times, color='skyblue')
axes[0, 0].set_title('平均响应时间对比 (毫秒)', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
axes[0, 0].set_ylabel('毫秒')
axes[0, 0].tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45)
for i, v in enumerate(response_times):
axes[0, 0].text(i, v + 5, str(v), ha='center')
# 图表2:吞吐量对比
axes[0, 1].plot(optimization_stages, throughput, marker='o',
linewidth=2, markersize=8, color='lightcoral')
axes[0, 1].set_title('系统吞吐量对比 (请求/秒)', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
axes[0, 1].set_ylabel('请求数/秒')
axes[0, 1].grid(True, alpha=0.3)
axes[0, 1].tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45)
for i, v in enumerate(throughput):
axes[0, 1].text(i, v + 1, str(v), ha='center')
# 图表3:缓存命中率
axes[1, 0].bar(optimization_stages, cache_hit_rates, color='lightgreen')
axes[1, 0].set_title('缓存命中率对比 (%)', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
axes[1, 0].set_ylabel('百分比')
axes[1, 0].tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45)
for i, v in enumerate(cache_hit_rates):
axes[1, 0].text(i, v + 1, f"{v}%", ha='center')
# 图表4:错误率对比
axes[1, 1].plot(optimization_stages, error_rates, marker='s',
linewidth=2, markersize=8, color='gold')
axes[1, 1].set_title('系统错误率对比 (%)', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
axes[1, 1].set_ylabel('百分比')
axes[1, 1].grid(True, alpha=0.3)
axes[1, 1].tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45)
for i, v in enumerate(error_rates):
axes[1, 1].text(i, v + 0.1, f"{v}%", ha='center')
plt.suptitle('第二大脑系统性能优化效果对比', fontsize=16, fontweight='bold', y=1.02)
plt.tight_layout()
# 保存图表
plt.savefig('performance_optimization_charts.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
# 生成图表
create_performance_charts()
5.3 最佳实践总结
markdown
# 第二大脑开发最佳实践 ## 1. 架构设计原则 - **模块化设计**: 每个功能模块独立,支持热插拔 - **容错机制**: 单点故障不影响整体系统 - **扩展性**: 易于添加新功能和集成 - **性能优先**: 响应时间<100ms,支持高并发 ## 2. 数据处理策略 - **分级存储**: 热数据内存缓存,温数据SSD,冷数据HDD - **向量化检索**: 使用向量数据库加速语义搜索 - **增量学习**: 模型和数据持续更新,无需全量重训 - **数据版本控制**: 所有修改可追溯、可回滚 ## 3. AI模型使用 - **提示工程**: 精心设计prompt模板和few-shot示例 - **模型组合**: 不同任务使用不同规模的模型 - **缓存策略**: 相同查询结果缓存,减少API调用 - **回退机制**: 主模型失败时自动切换备用模型 ## 4. 安全与隐私 - **数据加密**: 传输和存储都加密 - **访问控制**: 基于角色的权限管理 - **隐私保护**: 用户数据本地化处理 - **审计日志**: 所有操作详细记录 ## 5. 监控与维护 - **健康检查**: 定期自检系统状态 - **性能监控**: 实时跟踪关键指标 - **自动告警**: 异常情况及时通知 - **持续优化**: 基于使用数据不断改进 ## 6. 用户体验 - **自然交互**: 支持多种输入方式(语音、文本、图像) - **个性化**: 学习用户习惯,提供定制服务 - **实时反馈**: 操作进度可视化 - **多端同步**: 数据在各设备间无缝同步
第六章:部署与规模化
6.1 容器化部署配置
yaml
# docker-compose.yml
version: '3.8'
services:
# 小智AI核心服务
zhi-brain-core:
build: ./core
container_name: zhi-brain-core
environment:
- OPENAI_API_KEY=${OPENAI_API_KEY}
- REDIS_URL=redis://redis:6379
- DATABASE_URL=postgresql://postgres:password@postgres:5432/zbrain
ports:
- "8000:8000"
depends_on:
- redis
- postgres
volumes:
- ./data:/app/data
networks:
- brain-network
restart: unless-stopped
# 向量数据库服务
vector-db:
image: qdrant/qdrant:latest
container_name: vector-db
ports:
- "6333:6333"
volumes:
- ./qdrant_storage:/qdrant/storage
networks:
- brain-network
restart: unless-stopped
# Redis缓存
redis:
image: redis:7-alpine
container_name: redis-cache
ports:
- "6379:6379"
command: redis-server --appendonly yes
volumes:
- ./redis_data:/data
networks:
- brain-network
restart: unless-stopped
# PostgreSQL数据库
postgres:
image: postgres:15-alpine
container_name: postgres-db
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=postgres
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=password
- POSTGRES_DB=zbrain
ports:
- "5432:5432"
volumes:
- ./postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
- ./init.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/init.sql
networks:
- brain-network
restart: unless-stopped
# API网关
api-gateway:
build: ./gateway
container_name: api-gateway
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
- CORE_SERVICE_URL=http://zhi-brain-core:8000
- JWT_SECRET=${JWT_SECRET}
depends_on:
- zhi-brain-core
networks:
- brain-network
restart: unless-stopped
# 监控服务
monitoring:
image: grafana/grafana:latest
container_name: monitoring
ports:
- "3000:3000"
environment:
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin
volumes:
- ./grafana_data:/var/lib/grafana
networks:
- brain-network
restart: unless-stopped
# 反向代理
nginx:
image: nginx:alpine
container_name: nginx-proxy
ports:
- "80:80"
- "443:443"
volumes:
- ./nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- ./ssl:/etc/nginx/ssl
depends_on:
- api-gateway
- monitoring
networks:
- brain-network
restart: unless-stopped
networks:
brain-network:
driver: bridge
volumes:
postgres_data:
redis_data:
qdrant_storage:
grafana_data:
6.2 Kubernetes部署配置
yaml
# k8s-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: zhi-brain-deployment
namespace: brain-system
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: zhi-brain
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: zhi-brain
spec:
containers:
- name: zhi-brain-core
image: your-registry/zhi-brain-core:latest
env:
- name: OPENAI_API_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: api-secrets
key: openai-api-key
- name: DATABASE_URL
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: app-config
key: database-url
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
resources:
requests:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "250m"
limits:
memory: "1Gi"
cpu: "500m"
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
port: 8000
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /ready
port: 8000
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: zhi-brain-service
namespace: brain-system
spec:
selector:
app: zhi-brain
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8000
type: ClusterIP
---
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: zhi-brain-hpa
namespace: brain-system
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: zhi-brain-deployment
minReplicas: 3
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 70
- type: Resource
resource:
name: memory
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 80
6.3 监控仪表板配置
python
# monitoring_dashboard.py
from prometheus_client import start_http_server, Gauge, Counter, Histogram
import time
import random
class BrainMetrics:
"""第二大脑系统监控指标"""
def __init__(self):
# 请求相关指标
self.requests_total = Counter(
'brain_requests_total',
'总请求数',
['endpoint', 'method', 'status']
)
self.request_duration = Histogram(
'brain_request_duration_seconds',
'请求处理时间',
['endpoint'],
buckets=(0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10)
)
# 性能指标
self.response_time = Gauge(
'brain_response_time_seconds',
'平均响应时间'
)
self.cache_hit_rate = Gauge(
'brain_cache_hit_rate',
'缓存命中率'
)
self.error_rate = Gauge(
'brain_error_rate',
'错误率'
)
# 资源使用指标
self.memory_usage = Gauge(
'brain_memory_usage_bytes',
'内存使用量'
)
self.cpu_usage = Gauge(
'brain_cpu_usage_percent',
'CPU使用率'
)
# AI模型指标
self.ai_api_calls = Counter(
'brain_ai_api_calls_total',
'AI API调用次数',
['model', 'status']
)
self.ai_tokens_used = Counter(
'brain_ai_tokens_used_total',
'使用的AI令牌数',
['model', 'type']
)
def record_request(self, endpoint: str, method: str,
status: str, duration: float):
"""记录请求指标"""
self.requests_total.labels(
endpoint=endpoint,
method=method,
status=status
).inc()
self.request_duration.labels(
endpoint=endpoint
).observe(duration)
def update_performance_metrics(self,
response_time: float,
cache_hit_rate: float,
error_rate: float):
"""更新性能指标"""
self.response_time.set(response_time)
self.cache_hit_rate.set(cache_hit_rate)
self.error_rate.set(error_rate)
def update_resource_metrics(self,
memory_usage: float,
cpu_usage: float):
"""更新资源指标"""
self.memory_usage.set(memory_usage)
self.cpu_usage.set(cpu_usage)
def record_ai_api_call(self, model: str,
status: str,
prompt_tokens: int = 0,
completion_tokens: int = 0):
"""记录AI API调用"""
self.ai_api_calls.labels(
model=model,
status=status
).inc()
if prompt_tokens > 0:
self.ai_tokens_used.labels(
model=model,
type="prompt"
).inc(prompt_tokens)
if completion_tokens > 0:
self.ai_tokens_used.labels(
model=model,
type="completion"
).inc(completion_tokens)
# 模拟监控数据收集
async def collect_metrics(brain_system):
metrics = BrainMetrics()
while True:
try:
# 获取系统性能数据
performance = brain_system.get_performance_metrics()
metrics.update_performance_metrics(
response_time=performance["avg_response_time"],
cache_hit_rate=performance["cache_hit_rate"],
error_rate=performance["error_rate"]
)
# 获取资源使用数据
import psutil
process = psutil.Process()
memory_usage = process.memory_info().rss
cpu_usage = process.cpu_percent(interval=1)
metrics.update_resource_metrics(
memory_usage=memory_usage,
cpu_usage=cpu_usage
)
# 模拟AI API调用记录
metrics.record_ai_api_call(
model="zhi-ai-large",
status="success",
prompt_tokens=random.randint(50, 200),
completion_tokens=random.randint(100, 500)
)
# 等待下一次收集
await asyncio.sleep(10)
except Exception as e:
print(f"指标收集错误: {e}")
await asyncio.sleep(30)
# 启动监控服务器
def start_monitoring_server(port: int = 9090):
"""启动Prometheus指标服务器"""
from prometheus_client import start_http_server
start_http_server(port)
print(f"监控服务器已启动,端口: {port}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 启动监控服务器
start_monitoring_server(9090)
# 保持运行
while True:
time.sleep(1)
结论:构建你的第二大脑
通过本文的深入探索,你已经掌握了将小智AI打造成个人第二大脑的核心技术和方法。从智能家居控制到个性化对话系统,再到功能扩展和性能优化,每个环节都提供了详细的实现方案和最佳实践。
关键收获:
-
架构设计:分层架构确保系统的可扩展性和可维护性
-
智能集成:通过插件系统和API网关实现功能的无缝扩展
-
个性化体验:记忆系统和知识图谱让AI真正了解你的需求
-
性能优化:缓存、并行处理和监控确保系统高效运行
-
易于部署:容器化和Kubernetes配置让部署变得简单
下一步行动:
-
从简单开始:先实现核心功能,再逐步扩展
-
持续学习:让系统从每次交互中学习和改进
-
社区贡献:将你的插件和优化分享给开发者社区
-
用户反馈:收集用户反馈,持续改进用户体验
记住,真正的第二大脑不仅是技术的堆砌,更是对你思维方式的延伸和增强。随着系统的不断进化,你会发现它不仅能回答问题,更能预测需求、激发创意、优化决策,成为你数字生活中不可或缺的伙伴。
开始构建你的第二大脑吧,让AI的力量真正为你所用!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容








所有评论(0)