Flutter 鸿蒙跨端开发实践-组件化设计与抽离
上月我们完成了鸿蒙开发的基础学习,本月将继续深入探索 Flutter 鸿蒙跨端开发的相关内容。
一、前期准备
1.1 下载Flutter
之前我已经安装好了,完整安装步骤可参考我的这篇文章
注:不能使用官方的Flutter SDK,官方的并未适配鸿蒙。要使用OpenHarmony社区适配的Flutter SDK)
1.2 查看Flutter SDK版本
安装完成后,通过命令行验证 SDK 是否正常可用,步骤如下:
- 打开 Windows 命令提示符(CMD);
- 输入以下命令,查看 SDK 版本信息及运行状态:flutter --version;
- 若命令正常输出版本号,说明 SDK 配置成功;若报错,需检查 SDK 路径是否添加至系统环境变量。
flutter --version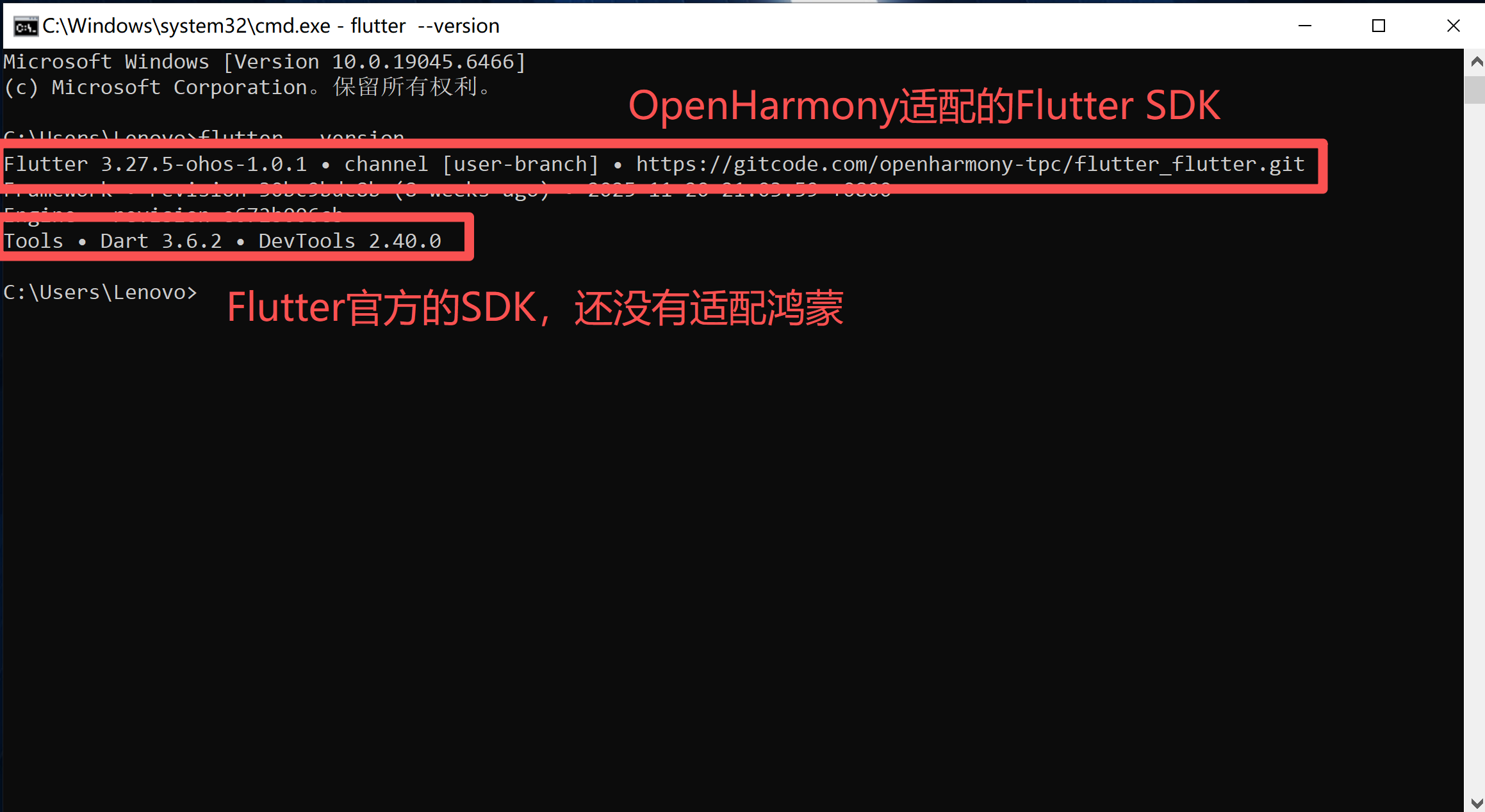
1.3 安装Vscode插件
为提升 Flutter 开发效率,需安装对应插件并重启编辑器,步骤如下:
打开 VS Code,进入插件市场(快捷键 Ctrl+Shift+X);
搜索并安装以下三款插件:
- Dart:提供 Dart 语言语法高亮、智能提示及编译支持;
- Flutter Widget Snippets:提供 Flutter 组件代码片段,快速生成常用控件;
- Flutter:集成 Flutter 项目调试、运行、热重载等核心功能
安装完成后重启 VS Code,使插件生效。
1.4 安装Android插件
下载安装好Dart、Flutter插件
1.5 创建Flutter-鸿蒙项目
1.5.1 创建项目
在Android Studio创建Flutter项目。找到之前下载的flutter_sdk的路径。
如果不记得就打开文件资源管理器,在搜索框输入 flutter.bat
然后在cmd输入命令验证一下
# 示例(替换成你复制的实际路径)
F:\替换成你复制的实际路径\bin\flutter.bat --version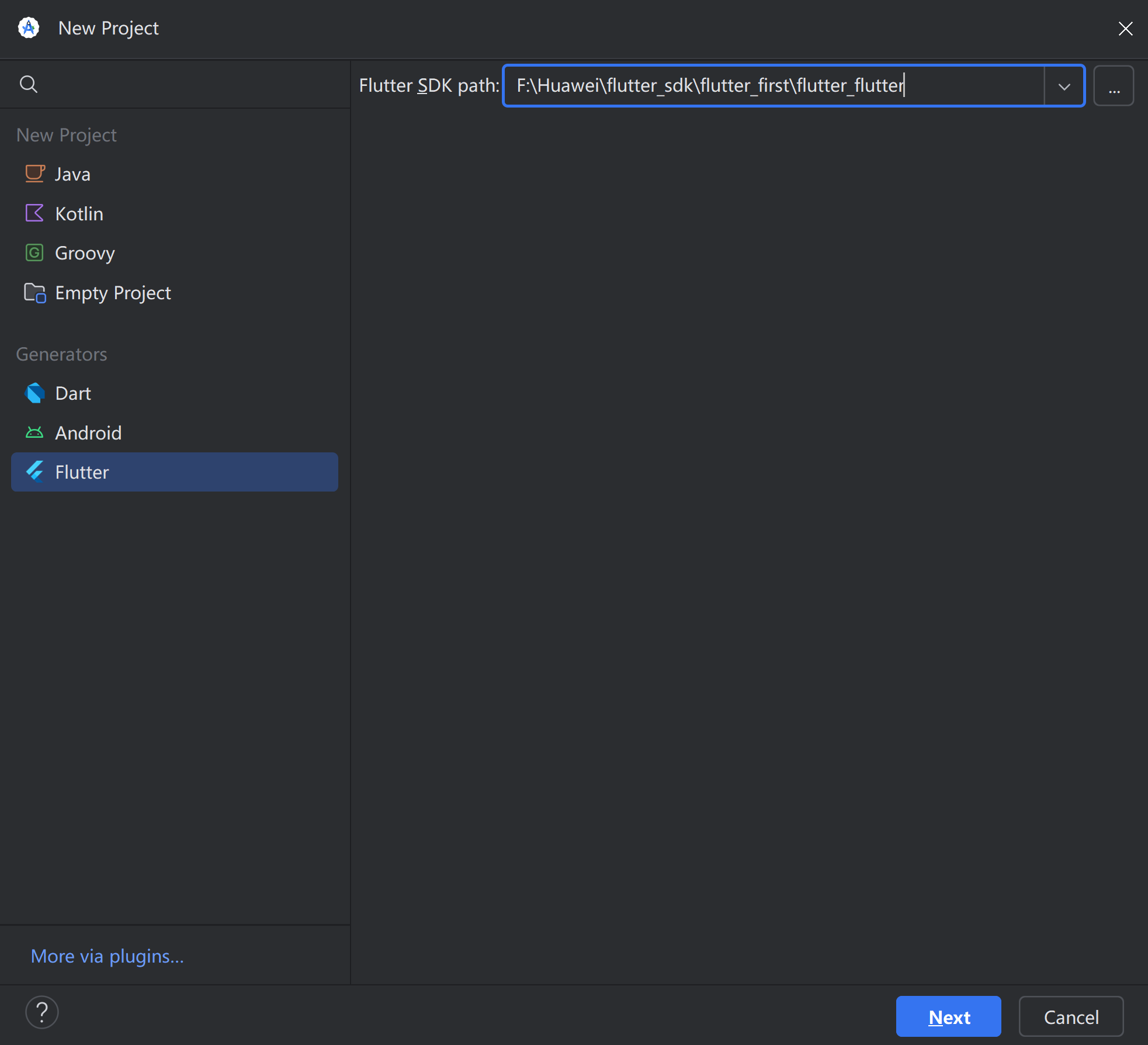
1.5.2 生成鸿蒙适配目录
输入以下命令,查看flutter版本号以及创建ohos文件
flutter --version
flutter create --platforms ohos .#在项目根目录生成 ohos 文件夹(“.”表示当前目录,不可省略)。创建ohos文件成功
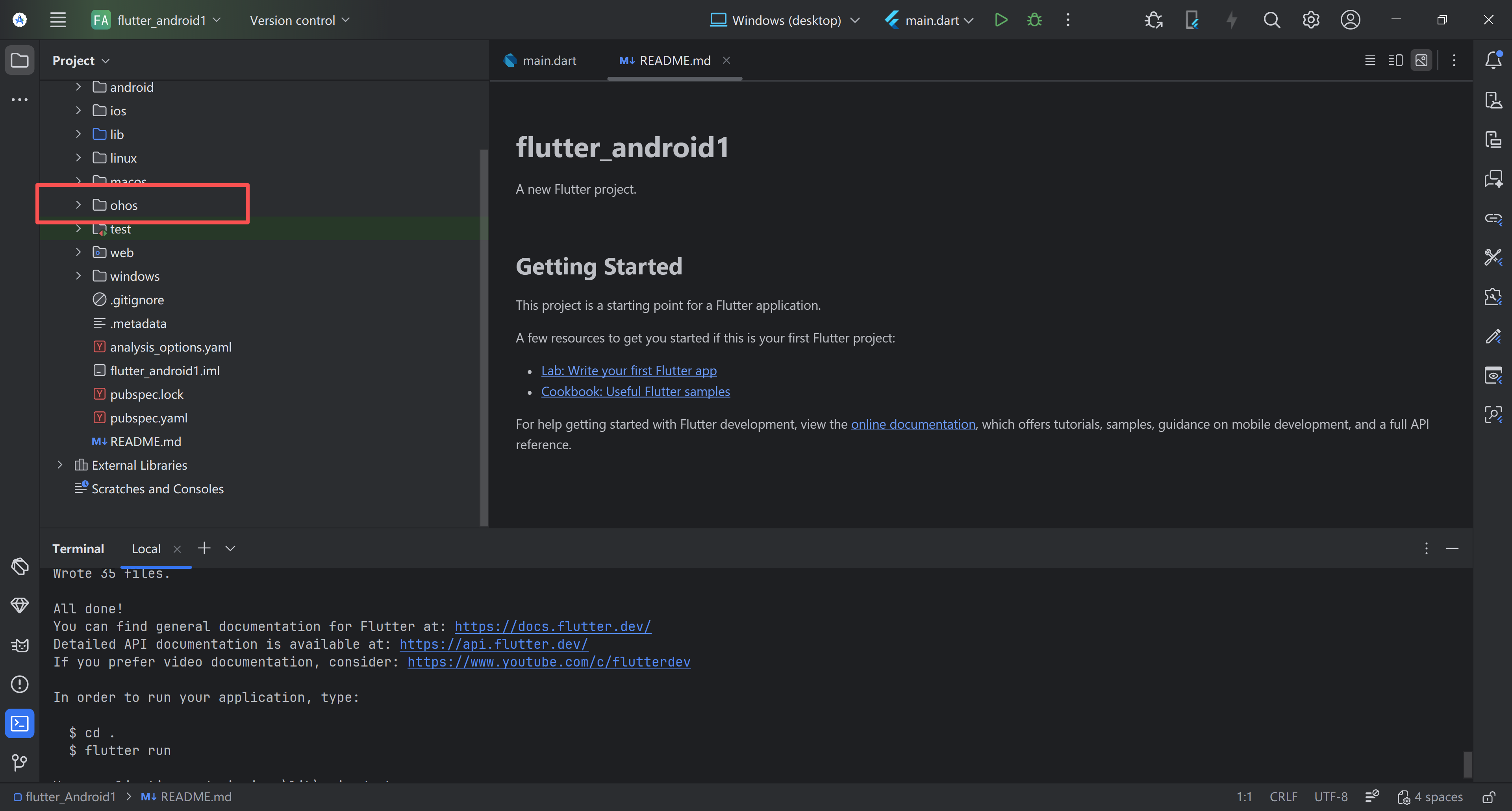
使用DevEco Studio运行鸿蒙的项目
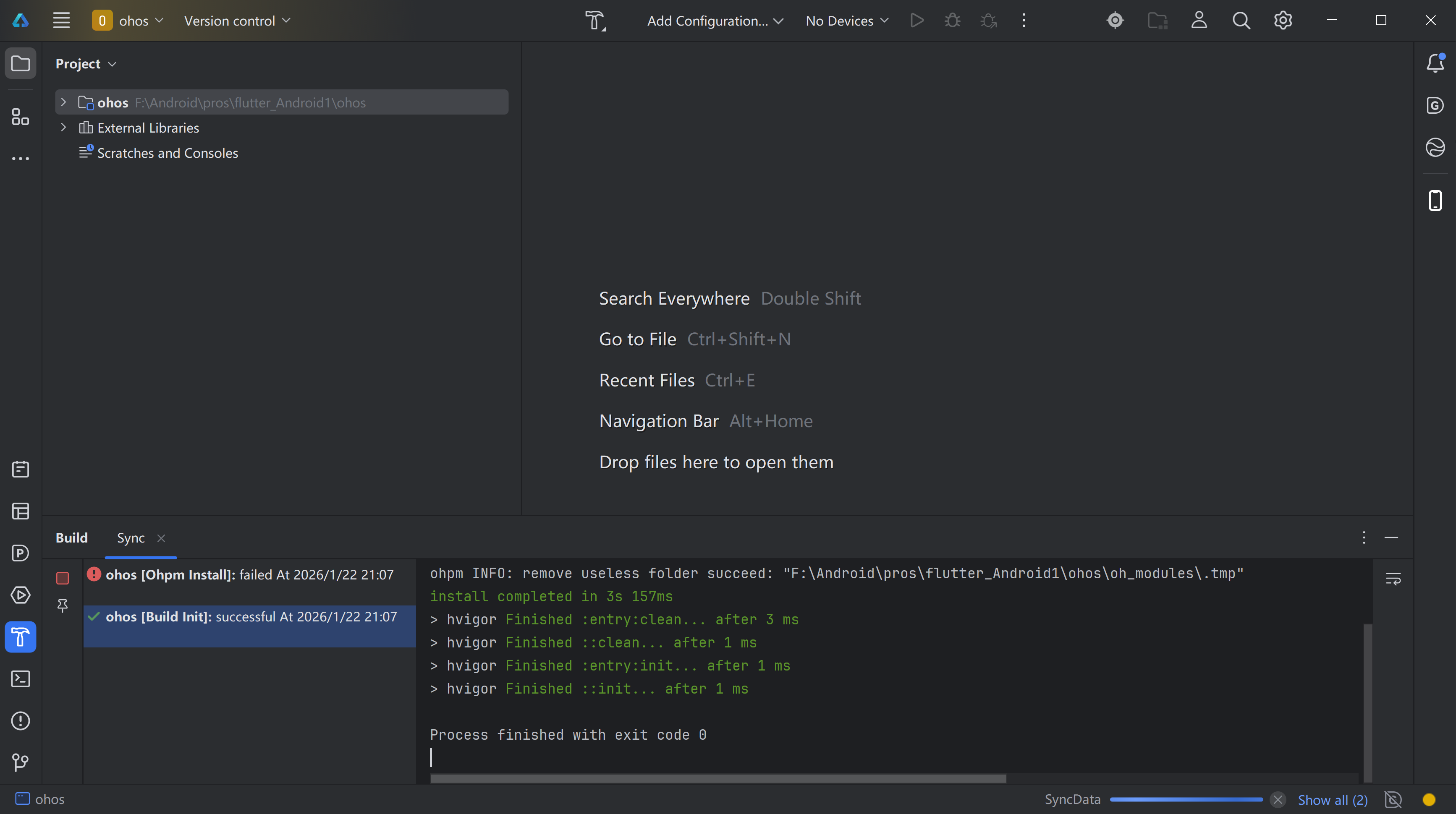
运行成功
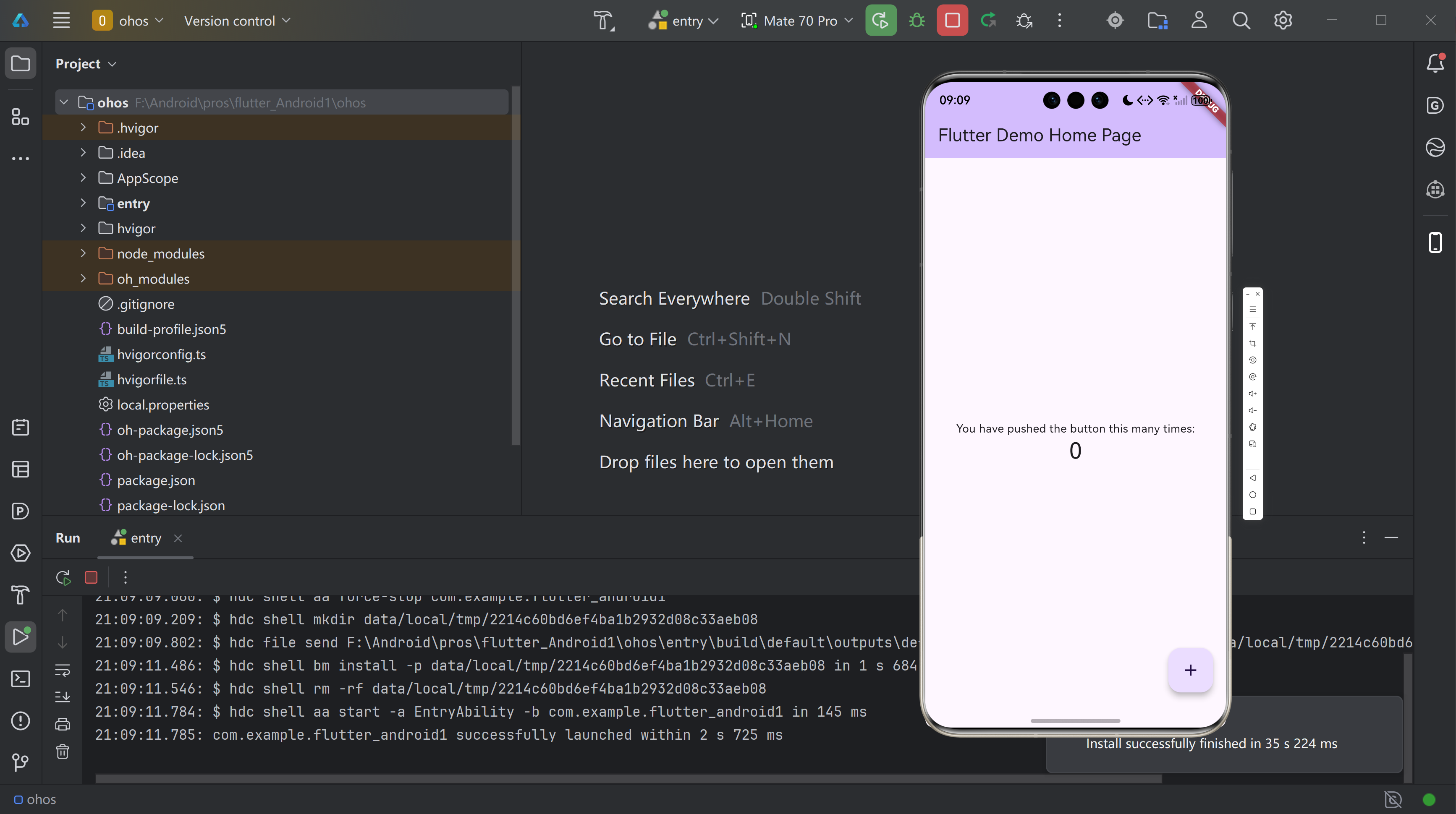
二、抽离组件
2.1 查看Flutter默认项目并抽离组件
Flutter 默认项目包含 MyApp(无状态组件)、MyHomePage(有状态组件)及计数器逻辑,所有代码集中在 main.dart 中,不利于后续扩展。需将不同类型组件抽离至独立文件,按功能分类管理。
默认项目代码:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
// This is the theme of your application.
//
// TRY THIS: Try running your application with "flutter run". You'll see
// the application has a purple toolbar. Then, without quitting the app,
// try changing the seedColor in the colorScheme below to Colors.green
// and then invoke "hot reload" (save your changes or press the "hot
// reload" button in a Flutter-supported IDE, or press "r" if you used
// the command line to start the app).
//
// Notice that the counter didn't reset back to zero; the application
// state is not lost during the reload. To reset the state, use hot
// restart instead.
//
// This works for code too, not just values: Most code changes can be
// tested with just a hot reload.
colorScheme: ColorScheme.fromSeed(seedColor: Colors.deepPurple),
useMaterial3: true,
),
home: const MyHomePage(title: 'Flutter Demo Home Page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// TRY THIS: Try changing the color here to a specific color (to
// Colors.amber, perhaps?) and trigger a hot reload to see the AppBar
// change color while the other colors stay the same.
backgroundColor: Theme.of(context).colorScheme.inversePrimary,
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
//
// TRY THIS: Invoke "debug painting" (choose the "Toggle Debug Paint"
// action in the IDE, or press "p" in the console), to see the
// wireframe for each widget.
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
用vscode打开文件并抽离组件
按组件类型创建 components 文件夹,将无状态组件、有状态组件、生命周期组件分别抽离至独立文件,优化后的 main.dart 代码如下,结构更清晰、可扩展性更强:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
// ignore: unused_import
import 'components/01_抽离组件.dart';
// ignore: unused_import
import 'components/02_无状态组件.dart';
// ignore: unused_import
import 'components/03_有状态组件.dart';
import 'components/04_组件生命周期.dart';
//程序入口
void main() {
runApp(MaterialApp(
home: MyApp1(),
// home: MyApp2(age:99),
// home: MyApp3(),
// home: MyApp4(parentName: '张三丰',)
)); // MaterialApp
}2.2 成功完成
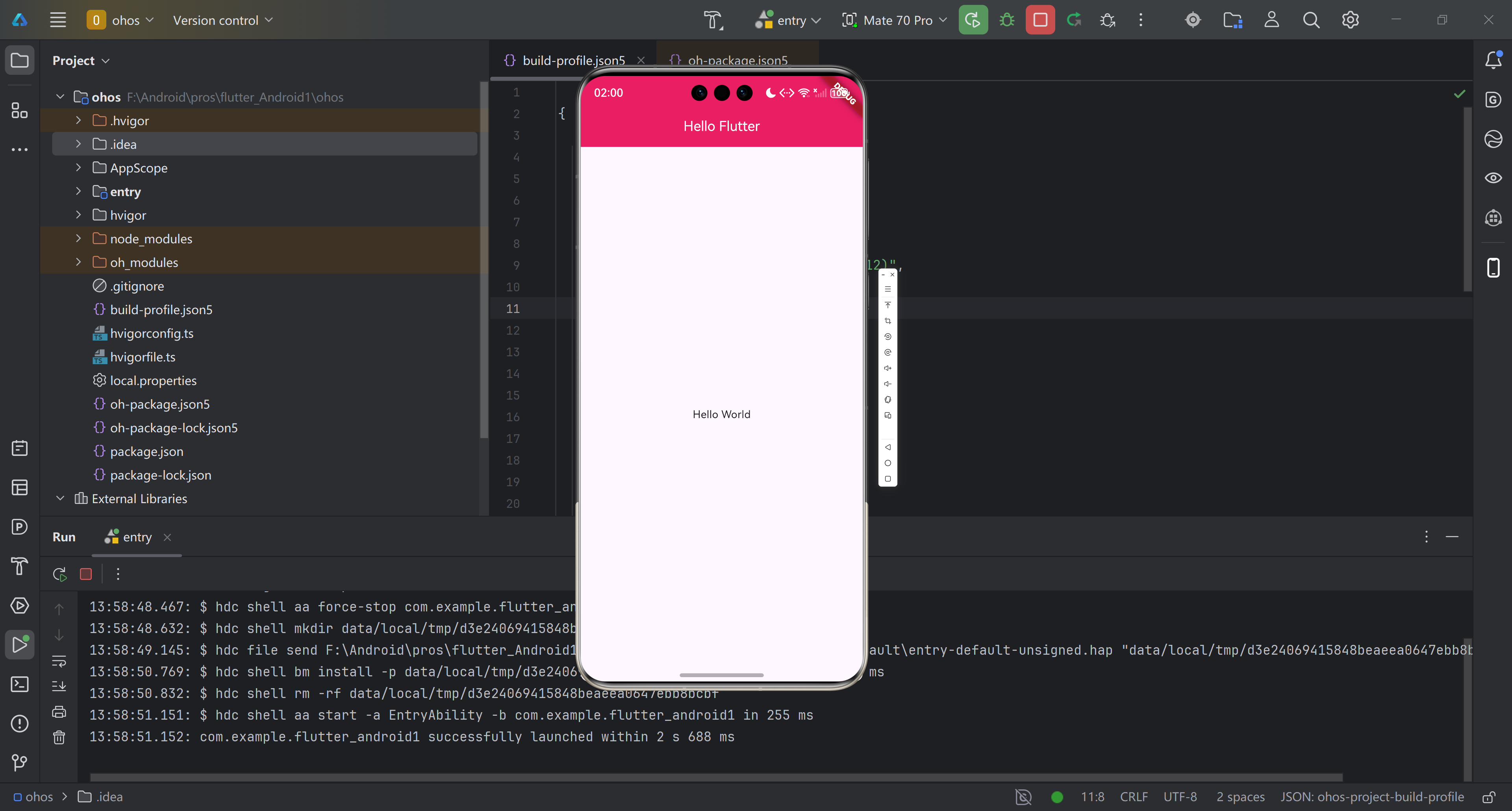
2.3 组件抽离完成总结
本次已成功将 Flutter 默认项目的核心组件抽离至独立目录,实现代码模块化管理。抽离后的组件可在鸿蒙及其他跨端平台复用,为后续复杂业务开发、多人协作奠定基础。后续可基于抽离的组件,进一步扩展鸿蒙功能适配。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容








所有评论(0)