LayoutLMv3 模型迁移指导书
本文档详细介绍了将LayoutLMv3多模态文档智能模型从GPU迁移至昇腾NPU(910B)环境的完整流程。主要内容包括:1)模型概述,说明其统一的多模态Transformer架构及预训练任务;2)环境准备,涵盖容器部署、驱动配置和依赖安装;3)迁移核心流程,重点解决detectron2框架适配和代码转换问题;4)常见错误解决方案,如依赖冲突、设备识别等问题;5)验证要点及注意事项。文档提供了修改
LayoutLMv3 模型迁移指导书
文档说明
1.1 文档目的
本指导书详细阐述 LayoutLMv3 多模态文档智能模型从 GPU 环境迁移至昇腾 NPU(910B)环境的全流程,包括环境配置、迁移操作、常见错误及解决方案,旨在帮助技术人员完成模型的高效迁移与验证。
1.2 适用范围
本指导书适用于基于以下软件配置的昇腾 NPU 环境,若配置不同,需适配对应版本的依赖包与工具:
|
配置项 |
版本 / 信息 |
|
镜像名称 |
8.3.rc1-910b-ubuntu22.04-py3.11 |
|
镜像 OS |
Ubuntu 22.04 |
|
Python |
3.11.13 |
|
CANN |
8.3RC1 |
|
PyTorch |
2.7.1+cu130 |
|
Torch-npu |
7.2.0 |
一、LayoutLMv3 模型概述
1.1 模型描述
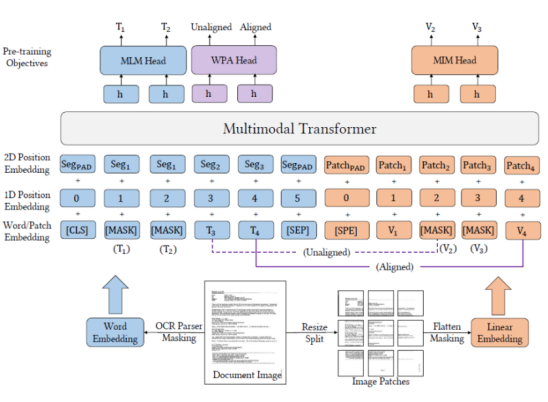
LayoutLMv3 是面向文档智能领域的预训练多模态 Transformer 模型,采用统一的文本与图像掩码策略,通过简洁的架构和训练目标实现通用型文档理解能力。可微调应用于文本核心任务(表格理解、票据解析、文档视觉问答)和图像核心任务(文档图像分类、文档版面分析)。
1.2 网络架构
1.2.1 统一的多模态 Transformer 架构
核心为单一 Transformer 编码器,文本和图像数据均转换为同维度向量序列后拼接输入,通过自注意力机制学习文本、视觉特征及二维位置关系的深层关联,无需多阶段处理。
1.2.2 输入与嵌入层:文本与图像的早期统一
文本嵌入:沿用 BERT 分词与向量化方法,融入一维位置嵌入;图像嵌入(核心改进):摒弃 Faster R-CNN 预训练目标检测器,采用 “直接分块线性投影”—— 将文档图像分割为固定大小图像块,通过线性投影层映射为视觉 Token,并融入图像块二维坐标的位置嵌入。
1.2.3 预训练任务
LayoutLMv3 通过三类联合预训练任务实现多模态理解:
遮盖语言建模:遮盖文本 Token,基于上下文文本和视觉信息预测;遮盖图像建模:遮盖图像块 Token,基于文本和剩余视觉信息重建视觉特征;词 - 块对齐(核心创新):随机选择文本词,判断对应空间位置的图像块,强化文本与图像的细粒度对应关系。
二、模型迁移环境准备
2.1 前置条件
宿主机已安装昇腾 910B NPU 驱动,且可正常识别davinci设备;宿主机已配置 Docker 环境,可拉取 / 使用指定镜像(ID:c1855ae355cb);具备外网访问权限,用于下载依赖包、模型仓库及权重。
2.2 容器部署(挂载 NPU 到容器)
步骤 1:获取宿主机 HwHiAiUser 用户 GID
id HwHiAiUser # 记录输出中的gid值(示例:1000)
 步骤 2:启动容器并挂载 NPU 设备 / 依赖文件
步骤 2:启动容器并挂载 NPU 设备 / 依赖文件
docker run -itd \
--name zxp \
--privileged=true \
--device=/dev/davinci5 \
--device=/dev/davinci_manager \
--device=/dev/devmm_svm \
--device=/dev/hisi_hdc \
-v /usr/local/dcmi:/usr/local/dcmi \
-v /usr/local/bin/npu-smi:/usr/local/bin/npu-smi \
-v /usr/bin/hccn_tool:/usr/bin/hccn_tool \
-v /home/00938648:/root/ \
-v /usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64/common:/usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64/common \
-v /usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64/driver:/usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64/driver \
-v /etc/ascend_install.info:/etc/ascend_install.info \
-v /etc/hccn.conf:/etc/hccn.conf \
-v /usr/local/Ascend/driver/version.info:/usr/local/Ascend/driver/version.info \
c1855ae355cb \
/bin/bash
步骤 3:验证容器内 NPU 设备
# 进入容器docker exec -it zxp /bin/bash
#查看可用davinci设备ls /dev/ | grep davinci*# 预期输出:davinci5.davinci_manager等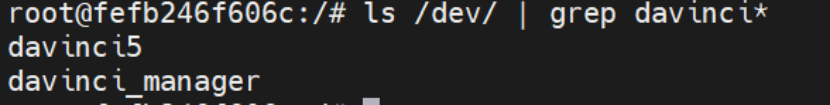
2.3 容器内驱动与用户配置
步骤 1:创建 HwHiAiUser 用户
groupadd -g 1000 HwHiAiUser && useradd -g HwHiAiUser -d /home/HwHiAiUser -m HwHiAiUser && echo ok
![]() 步骤 2:配置驱动环境变量
步骤 2:配置驱动环境变量
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64/common:/usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64/driver:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
说明:该方式仅对当前终端有效,若需持久化,需写入~/.bashrc或/etc/profile.
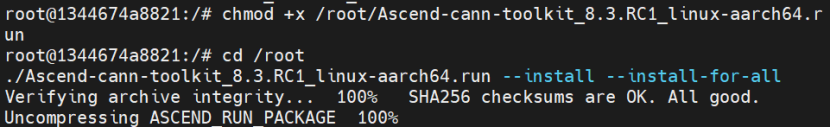
2.4 软件及依赖安装
步骤 1:CANN 安装Toolkit开发套件包
 步骤 2:配置环境变量及安装Kernels算子包
步骤 2:配置环境变量及安装Kernels算子包
![]()

# 下载PyTorch包
Wget https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu/torch-2.7.1%2Bcpu-cp311-cp311-manylinux_2_28_aarch64.whl# 安装PyTorch
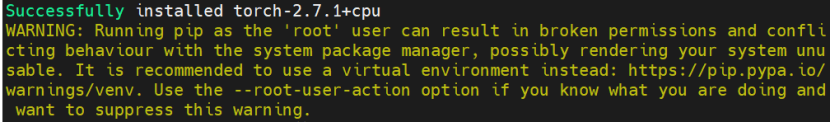 pip3 install torch-2.7.1+cpu-cp311-cp311-manylinux_2_28_aarch64.whl# 下载Torch-npu插件包
pip3 install torch-2.7.1+cpu-cp311-cp311-manylinux_2_28_aarch64.whl# 下载Torch-npu插件包
Wget https://gitcode.com/Ascend/pytorch/releases/download/v7.2.0-pytorch2.7.1/torch_npu-2.7.1-cp311-cp311-manylinux_2_28_aarch64.whl# 安装Torch-npu
pip3 install torch_npu-2.7.1-cp311-cp311-manylinux_2_28_aarch64.whl
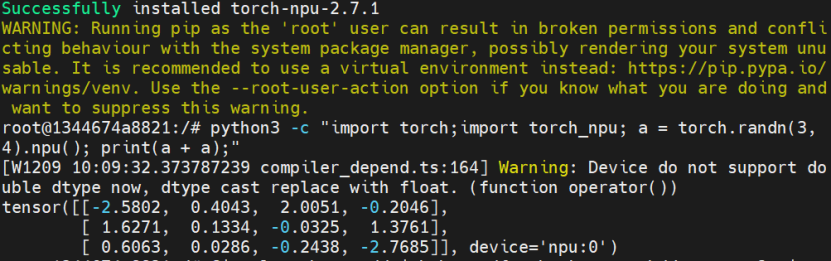 三、模型迁移核心流程
三、模型迁移核心流程
通过分析代码,代码依赖detectron2框架,要对模型迁移适配需要对detectron2进行迁移适配并安装。
3.1 依赖包完整性检查与安装
步骤 1:安装 Git 工具
apt-get update && apt-get install -y git# 克隆detectron2仓库(模型依赖)git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git -b v0.6
步骤 2:检查并安装缺失依赖
(1)依赖检查脚本
python
运行
import pkg_resources
required_packages = [
('pandas', '1.2.4'),
('libcst', None),
('prettytable', None),
('jedi', None)]for pkg, min_version in required_packages:
try:
installed_version = pkg_resources.get_distribution(pkg).version
status = f"✓ 已安装 (版本 {installed_version})"
if min_version and pkg_resources.parse_version(installed_version) < pkg_resources.parse_version(min_version):
status = f"⚠ 版本过低 (当前: {installed_version}, 需要: >={min_version})"
print(f"{pkg:20} {status}")
except pkg_resources.DistributionNotFound:
print(f"{pkg:20} ✗ 未安装")
print("\n提示:如果缺少任何'必选'包,请使用 'pip3 install <包名>' 安装。")
|
依赖包 |
是否必选 |
说明 |
最低版本要求 |
|
pandas |
必选 |
数据处理 |
>= 1.2.4 |
|
libcst |
必选 |
Python语法树解析器 |
- |
|
prettytable |
必选 |
数据可视化表格 |
- |
|
jedi |
可选(建议) |
用于跨文件解析 |
- |
(2)依赖安装命令
bash
运行
# 修复setuptools版本过低问题
apt-get update
apt-get install -y python3-dev build-essential libopenblas-dev liblapack-dev gfortran
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip
python3 -m pip install --upgrade setuptools==68.2.0 wheel
python3 -m pip install cython numpy==1.23.5 -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
# 安装依赖
pip3 install pandas==2.0.3 scipy==1.10.1 scikit-learn==1.3.0 tqdm==4.65.0 openpyxl==3.1.2 xlrd==2.0.1 -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/# 安装语法解析/可视化依赖
pip3 install pandas libcst prettytable jedi -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
(阿里云镜像源速度下载较快)
3.2 模型代码自动转换(GPU→NPU)
步骤 1:获取detectron2源码及执行昇腾迁移工具
bash
运行
Git clone https://github.com/facecbookresearch/detectrob2.git -b v0.6
/usr/local/Ascend/ascend-toolkit/8.3.RC1/tools/ms_fmk_transplt/pytorch_gpu2npu.sh -i /detectron2/detectron2 -o /detectron2/detectron2-npu/ -v 2.1.0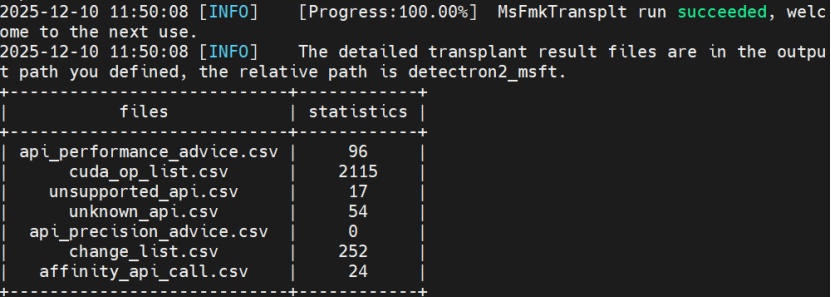
步骤 2:转换后执行
将目录移动到opt目录,方便打包镜像
bash
运行
python -m pip install -e detectron2
 # 创建新虚拟环境(避免依赖冲突)
# 创建新虚拟环境(避免依赖冲突)
python3 -m venv /opt/ascend_venv
source /opt/ascend_venv/bin/activate# 安装detectron2依赖
pip install torch -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
pip install -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ matplotlib
cd /opt/detectron2
pip install -e . --no-build-isolation
步骤 3:修改 detectron2 代码(可选)
bash
运行
vi ./detectron2/engine/defaults.py # 根据迁移工具提示修改适配NPU的代码
 3.3 LayoutLMv3 模型迁移与运行
3.3 LayoutLMv3 模型迁移与运行
步骤 1:克隆模型仓库与权重
bash
运行
# 进入opt目录(统一管理)
cd /opt
# 克隆unilm仓库(含LayoutLMv3代码)
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/unilm.gitcd unilm# 克隆模型权重
git clone https://gitcode.com/hf_mirrors/microsoft/layoutlmv3-base.git
步骤 2:修改运行脚本(run_funsd.py)
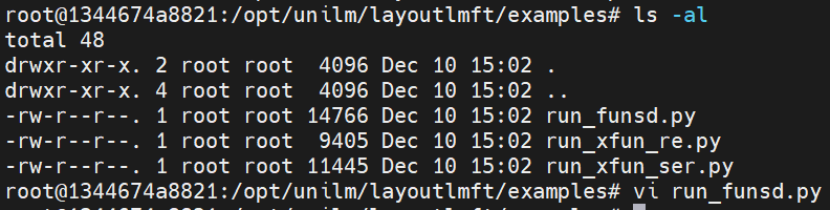 添加 NPU 设备指定环境变量;
添加 NPU 设备指定环境变量;
替换datasets库的load_metric导入方式;
替换真实数据集为虚拟数据集(解决网络获取失败问题);
自定义 Trainer 类适配 NPU 设备;
确保模型 / 数据张量迁移至 NPU.
完整修改后的脚本见附录 A.
步骤 3:安装 LayoutLMv3 专属依赖
bash
运行
# 激活专属虚拟环境(避免版本冲突)
python3 -m venv /opt/layoutlmv3_npu_env
source /opt/layoutlmv3_npu_env/bin/activate# 安装兼容版本依赖
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install numpy==1.23.5 pandas scipy -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/# 安装核心依赖
pip install torch torch_npu transformers datasets evaluate -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/# 安装layoutlmft包cd /opt/unilm/layoutlmft
pip install -e .
步骤 4:执行模型训练 / 推理
bash
运行
cd /opt/unilm/layoutlmft/examples
python run_funsd.py \
--model_name_or_path /opt/detectron2/layoutlmv3-base \
--output_dir ./output_funsd_npu \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--num_train_epochs 10 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 \
--learning_rate 5e-5 \
--overwrite_output_dir
步骤5:创建推理配置文件
cat > inference_config.json << 'EOF'
{
"model_name_or_path": "/opt/unilm/layoutlmft/examples/output_funsd_npu",
"dataset_name": "funsd",
"do_train": false,
"do_eval": false,
"do_predict": true,
"output_dir": "./inference_results",
"per_device_eval_batch_size": 1,
"overwrite_output_dir": true,
"label_all_tokens": false,
"max_test_samples": 2,
"task_name": "ner"
}
EOF
步骤六:实行推理
# 强制离线模式,避免下载
export TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1
export HF_HUB_OFFLINE=1
export HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1
# 运行推理
python run_funsd.py inference_config.json
四、常见错误与解决方案
|
错误阶段 |
错误现象 |
根因分析 |
解决方案 |
|
依赖安装阶段 |
提示 setuptools 版本过低,无法安装依赖包 |
setuptools 版本不兼容昇腾迁移工具 |
执行:python3 -m pip install --upgrade setuptools==68.2.0 wheel |
|
工具转换阶段 |
jedi 库未安装,迁移工具分析 Python 文件失败 |
缺少语法解析依赖 jedi |
pip3 install jedi -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ |
|
工具转换阶段 |
pip install -e detectron2 失败,提示缺少 setup.py |
detectron2 目录结构不完整 / 未用隔离构建 |
cd /opt/detectron2 && pip install -e . --no-build-isolation |
|
脚本运行阶段 |
提示 datasets 模块缺失 |
未安装 LayoutLMv3 运行依赖 |
pip install datasets -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ |
|
脚本运行阶段 |
NumPy 版本冲突,SciPy/Pandas 报版本不兼容错误 |
依赖版本不匹配 |
创建专属虚拟环境,安装 numpy==1.23.5,再重装 pandas/scipy |
|
脚本运行阶段 |
提示 from datasets import load_metric 导入失败 |
datasets 库 API 更新,metric 功能迁移至 evaluate |
修改导入语句:from evaluate import load as load_metric,并安装 evaluate |
|
脚本运行阶段 |
提示找不到 layoutlmft 包 |
未安装项目自身代码包 |
cd /opt/unilm/layoutlmft && pip install -e . |
|
脚本运行阶段 |
数据集加载失败,无法从网络获取 funsd 数据集 |
网络限制 / 数据集 API 变更 |
替换为虚拟数据集(见附录 A 脚本中 dummy_data 部分) |
|
脚本运行阶段 |
PIL.Image 模块无 LINEAR 属性 |
图像处理依赖版本问题 |
升级 Pillow:pip install --upgrade Pillow -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ |
|
脚本运行阶段 |
NPU 设备未被识别,提示 cuda 设备不可用 |
未指定 NPU 设备 / 未安装 torch-npu |
添加环境变量os.environ["NPU_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "5",确保 torch-npu 安装正确 |
五、迁移验证与输出说明
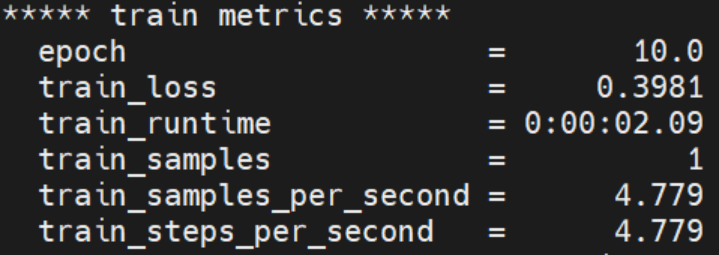
5.1 预期输出
脚本运行后,核心输出如下(示例):
plaintext
INFO: 检测到NPU设备,使用 npu:5
INFO: 正在创建符合LayoutLMv3格式的虚拟数据集。..
INFO: 虚拟数据集创建成功,开始训练流程。
INFO: 正在创建随机初始化的LayoutLMv3模型,用于验证NPU训练流程。
INFO: 模型已移动到设备: npu:5
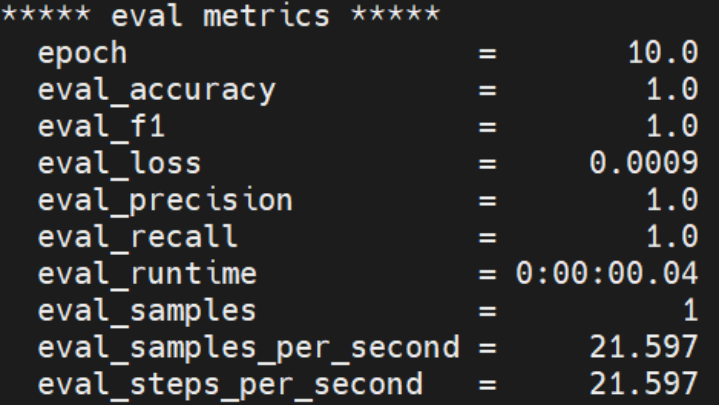
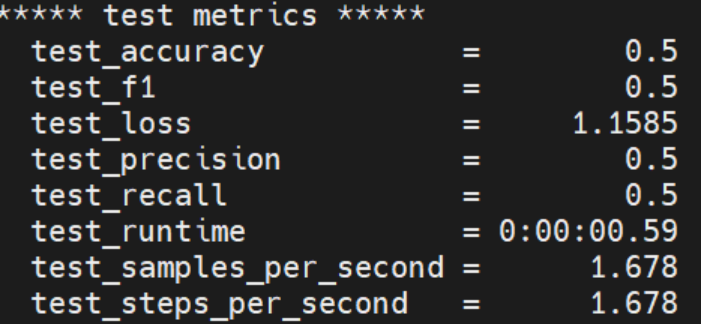
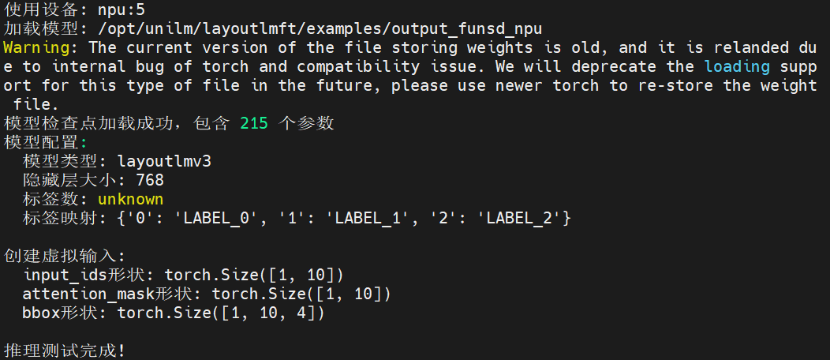
5.2 验证要点
脚本无报错终止,且打印 “检测到 NPU 设备”;
训练 / 评估阶段无设备不兼容错误,损失值正常下降;
output_funsd_npu 目录生成模型权重、metrics.json 等文件。
六、注意事项
虚拟环境建议:不同阶段使用独立虚拟环境(detectron2/LayoutLMv3),避免依赖冲突;
环境变量持久化:若需长期使用 NPU,将LD_LIBRARY_PATH和NPU_VISIBLE_DEVICES写入~/.bashrc;
设备索引:脚本中使用 NPU 索引 5(对应 /dev/davinci5),需根据实际设备调整;
模型权重:若需使用真实权重,确保 layoutlmv3-base 目录下包含 pytorch_model.bin、config.json 等文件;
性能优化:若训练速度慢,可调整per_device_train_batch_size、dataloader_num_workers等参数(需匹配 NPU 算力)。
附录 A:完整 run_funsd.py 脚本
python
运行
#!/usr/bin/env python# coding=utf-8import os# 使用第6个NPU设备(索引5)
os.environ["NPU_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "5"
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = ""
os.environ["MASTER_ADDR"] = "localhost"
os.environ["MASTER_PORT"] = "29500"
os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"] = "1"
os.environ["RANK"] = "0"
os.environ["LOCAL_RANK"] = "-1"
import torch_npufrom torch_npu.contrib import transfer_to_npuimport loggingimport osimport sysfrom dataclasses import dataclass, fieldfrom typing import Optional
import numpy as npfrom datasets import ClassLabel, load_datasetfrom evaluate import load as load_metric
import layoutlmft.data.datasets.funsdimport transformersfrom layoutlmft.data import DataCollatorForKeyValueExtractionfrom layoutlmft.data.data_args import DataTrainingArgumentsfrom layoutlmft.models.model_args import ModelArgumentsfrom layoutlmft.trainers import FunsdTrainer as Trainerfrom transformers import (
AutoConfig,
AutoModelForTokenClassification,
AutoTokenizer,
HfArgumentParser,
PreTrainedTokenizerFast,
TrainingArguments,
set_seed,)from transformers.trainer_utils import get_last_checkpoint, is_main_processfrom transformers.utils import check_min_version
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
check_min_version("4.5.0")
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def main():
# See all possible arguments in layoutlmft/transformers/training_args.py
# or by passing the --help flag to this script.
# We now keep distinct sets of args, for a cleaner separation of concerns.
parser = HfArgumentParser((ModelArguments, DataTrainingArguments, TrainingArguments))
if len(sys.argv) == 2 and sys.argv[1].endswith(".json"):
# If we pass only one argument to the script and it's the path to a json file,
# let's parse it to get our arguments.
model_args, data_args, training_args = parser.parse_json_file(json_file=os.path.abspath(sys.argv[1]))
else:
model_args, data_args, training_args = parser.parse_args_into_dataclasses()
# 打印调试信息
print(f"DEBUG: 训练参数初始化 - local_rank={training_args.local_rank}, n_gpu={training_args.n_gpu}, world_size={training_args.world_size}")
# 修改训练参数,确保使用单设备
training_args.dataloader_num_workers = 0
# 设置单进程训练,避免数据并行
training_args.local_rank = -1
# 设置设备
import torch
if hasattr(torch, 'npu') and torch.npu.is_available():
# 使用第6张NPU卡(索引5)
device = torch.device("npu:5")
torch.npu.set_device(5)
print(f"INFO: 检测到NPU设备,使用 {device}")
else:
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"INFO: 使用设备: {device}")
# Detecting last checkpoint.
last_checkpoint = None
if os.path.isdir(training_args.output_dir) and training_args.do_train and not training_args.overwrite_output_dir:
last_checkpoint = get_last_checkpoint(training_args.output_dir)
if last_checkpoint is None and len(os.listdir(training_args.output_dir)) > 0:
raise ValueError(
f"Output directory ({training_args.output_dir}) already exists and is not empty. "
"Use --overwrite_output_dir to overcome."
)
elif last_checkpoint is not None:
logger.info(
f"Checkpoint detected, resuming training at {last_checkpoint}. To avoid this behavior, change "
"the `--output_dir` or add `--overwrite_output_dir` to train from scratch."
)
# Setup logging
logging.basicConfig(
format="%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(name)s - %(message)s",
datefmt="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S",
handlers=[logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout)],
)
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO if is_main_process(training_args.local_rank) else logging.WARN)
# Log on each process the small summary:
logger.warning(
f"Process rank: {training_args.local_rank}, device: {training_args.device}, n_gpu: {training_args.n_gpu}"
+ f"distributed training: {bool(training_args.local_rank != -1)}, 16-bits training: {training_args.fp16}"
)
# Set the verbosity to info of the Transformers logger (on main process only):
if is_main_process(training_args.local_rank):
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_info()
transformers.utils.logging.enable_default_handler()
transformers.utils.logging.enable_explicit_format()
logger.info(f"Training/evaluation parameters {training_args}")
# Set seed before initializing model.
set_seed(training_args.seed)
# 使用虚拟数据集,立即验证NPU训练流程
# 创建符合LayoutLMv3要求的虚拟数据集
print("INFO: 正在创建符合LayoutLMv3格式的虚拟数据集。..")
from datasets import Dataset, DatasetDict, Features, Value, Sequence, ClassLabel
import numpy as np
# 1. 定义数据特征(结构)
features = Features({
"id": Value("string"),
"words": Sequence(Value("string")),
"bboxes": Sequence(Sequence(Value("int64"))), # 嵌套序列:每个单词对应一个四元组[x0, y0, x1, y1]
"ner_tags": Sequence(ClassLabel(num_classes=3, names=["O", "B-HEADER", "I-HEADER"])), # 示例标签
"image": Value("string"), # LayoutLMv3可能需要图像路径占位符
})
# 2. 创建虚拟数据(确保维度匹配:2个样本,每个样本3个单词)
dummy_data = {
"id": ["sample-1", "sample-2"],
"words": [["Hello", "world", "!"], ["Test", "document", "."]],
# 每个单词一个边界框 [x0, y0, x1, y1]
"bboxes": [
[[0, 0, 100, 100], [110, 0, 210, 100], [220, 0, 250, 100]], # 样本1
[[0, 0, 80, 80], [90, 0, 180, 80], [190, 0, 210, 80]] # 样本2
],
"ner_tags": [[0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 2]], # 标签ID,对应ClassLabel
"image": ["dummy.jpg", "dummy.jpg"] # 虚拟图像路径
}
# 3. 创建DatasetDict
train_dataset = Dataset.from_dict(dummy_data, features=features)
datasets = DatasetDict({
"train": train_dataset,
"validation": train_dataset, # 添加验证集
"test": train_dataset,
})
print("INFO: 虚拟数据集创建成功,开始训练流程。")
if training_args.do_train:
column_names = datasets["train"].column_names
features = datasets["train"].features
else:
column_names = datasets["validation"].column_names
features = datasets["validation"].features
text_column_name = "tokens" if "tokens" in column_names else column_names[0]
label_column_name = (
f"{data_args.task_name}_tags" if f"{data_args.task_name}_tags" in column_names else column_names[1]
)
remove_columns = column_names
# In the event the labels are not a `Sequence[ClassLabel]`, we will need to go through the dataset to get the
# unique labels.
def get_label_list(labels):
unique_labels = set()
for label in labels:
unique_labels = unique_labels | set(label)
label_list = list(unique_labels)
label_list.sort()
return label_list
if isinstance(features[label_column_name].feature, ClassLabel):
label_list = features[label_column_name].feature.names
# No need to convert the labels since they are already ints.
label_to_id = {i: i for i in range(len(label_list))}
else:
label_list = get_label_list(datasets["train"][label_column_name])
label_to_id = {l: i for i, l in enumerate(label_list)}
num_labels = len(label_list)
# Load pretrained model and tokenizer
#
# Distributed training:
# The .from_pretrained methods guarantee that only one local process can concurrently
# download model & vocab.
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(
model_args.config_name if model_args.config_name else model_args.model_name_or_path,
num_labels=num_labels,
finetuning_task=data_args.task_name,
cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
revision=model_args.model_revision,
use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
model_args.tokenizer_name if model_args.tokenizer_name else model_args.model_name_or_path,
cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
use_fast=True,
revision=model_args.model_revision,
use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
)
# 加载模型 - 使用随机初始化的模型验证流程
print("INFO: 正在创建随机初始化的LayoutLMv3模型,用于验证NPU训练流程。")
from transformers import LayoutLMv3ForTokenClassification
model = LayoutLMv3ForTokenClassification(config)
# 将模型移动到NPU设备
model.to(device)
print(f"INFO: 模型已移动到设备: {device}")
# Tokenizer check: this script requires a fast tokenizer.
if not isinstance(tokenizer, PreTrainedTokenizerFast):
raise ValueError(
"This example script only works for models that have a fast tokenizer. Checkout the big table of models "
"at https://huggingface.co/transformers/index.html#bigtable to find the model types that meet this "
"requirement"
)
# Preprocessing the dataset
# Padding strategy
padding = "max_length" if data_args.pad_to_max_length else False
# Tokenize all texts and align the labels with them.
def tokenize_and_align_labels(examples):
# 提取文本和边界框
texts = examples[text_column_name]
boxes = examples["bboxes"]
# 确保边界框格式正确
processed_boxes = []
for bbox_list in boxes:
# 每个边界框应该是4个整数
normalized_bboxes = []
for bbox in bbox_list:
if len(bbox) == 4:
normalized_bboxes.append([int(coord) for coord in bbox])
else:
# 如果格式不对,使用默认值
normalized_bboxes.append([0, 0, 1000, 1000])
processed_boxes.append(normalized_bboxes)
# 调用tokenizer
tokenized_inputs = tokenizer(
text=texts,
boxes=processed_boxes,
padding=padding,
truncation=True,
return_overflowing_tokens=True,
)
labels = []
bboxes = []
images = []
for batch_index in range(len(tokenized_inputs["input_ids"])):
word_ids = tokenized_inputs.word_ids(batch_index=batch_index)
org_batch_index = tokenized_inputs["overflow_to_sample_mapping"][batch_index]
label = examples[label_column_name][org_batch_index]
bbox = examples["bboxes"][org_batch_index]
image = examples["image"][org_batch_index]
previous_word_idx = None
label_ids = []
bbox_inputs = []
for word_idx in word_ids:
# Special tokens have a word id that is None. We set the label to -100 so they are automatically
# ignored in the loss function.
if word_idx is None:
label_ids.append(-100)
bbox_inputs.append([0, 0, 0, 0])
# We set the label for the first token of each word.
elif word_idx != previous_word_idx:
label_ids.append(label_to_id[label[word_idx]])
bbox_inputs.append(bbox[word_idx])
# For the other tokens in a word, we set the label to either the current label or -100, depending on
# the label_all_tokens flag.
else:
label_ids.append(label_to_id[label[word_idx]] if data_args.label_all_tokens else -100)
bbox_inputs.append(bbox[word_idx])
previous_word_idx = word_idx
labels.append(label_ids)
bboxes.append(bbox_inputs)
images.append(image)
tokenized_inputs["labels"] = labels
tokenized_inputs["bbox"] = bboxes
tokenized_inputs["image"] = images
return tokenized_inputs
if training_args.do_train:
if "train" not in datasets:
raise ValueError("--do_train requires a train dataset")
train_dataset = datasets["train"]
if data_args.max_train_samples is not None:
train_dataset = train_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_train_samples))
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(
tokenize_and_align_labels,
batched=True,
remove_columns=remove_columns,
num_proc=data_args.preprocessing_num_workers,
load_from_cache_file=not data_args.overwrite_cache,
)
if training_args.do_eval:
if "validation" not in datasets:
raise ValueError("--do_eval requires a validation dataset")
eval_dataset = datasets["validation"]
if data_args.max_val_samples is not None:
eval_dataset = eval_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_val_samples))
eval_dataset = eval_dataset.map(
tokenize_and_align_labels,
batched=True,
remove_columns=remove_columns,
num_proc=data_args.preprocessing_num_workers,
load_from_cache_file=not data_args.overwrite_cache,
)
if training_args.do_predict:
if "test" not in datasets:
raise ValueError("--do_predict requires a test dataset")
test_dataset = datasets["test"]
if data_args.max_test_samples is not None:
test_dataset = test_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_test_samples))
test_dataset = test_dataset.map(
tokenize_and_align_labels,
batched=True,
remove_columns=remove_columns,
num_proc=data_args.preprocessing_num_workers,
load_from_cache_file=not data_args.overwrite_cache,
)
# Data collator
data_collator = DataCollatorForKeyValueExtraction(
tokenizer,
pad_to_multiple_of=8 if training_args.fp16 else None,
padding=padding,
max_length=512,
)
# Metrics - 使用简化的评估函数
def compute_metrics(p):
predictions, labels = p
predictions = np.argmax(predictions, axis=2)
# Remove ignored index (special tokens)
true_predictions = [
[label_list[p] for (p, l) in zip(prediction, label) if l != -100]
for prediction, label in zip(predictions, labels)
]
true_labels = [
[label_list[l] for (p, l) in zip(prediction, label) if l != -100]
for prediction, label in zip(predictions, labels)
]
# 计算简单准确率
correct = 0
total = 0
for pred_line, label_line in zip(true_predictions, true_labels):
for p_token, l_token in zip(pred_line, label_line):
total += 1
if p_token == l_token:
correct += 1
accuracy = correct / total if total > 0 else 0.0
return {
"accuracy": accuracy,
"precision": accuracy,
"recall": accuracy,
"f1": accuracy,
}
# 创建自定义Trainer来确保数据在正确的设备上
class NPUTrainer(Trainer):
def _wrap_model(self, model, training=True, dataloader=None):
# 直接返回模型,不进行数据并行包装
# 接受training参数以适应新版本的transformers
return model.to(device) if device else model
def _prepare_inputs(self, inputs):
# 确保所有输入张量都在正确的设备上
prepared_inputs = {}
for k, v in inputs.items():
if isinstance(v, torch.Tensor):
prepared_inputs[k] = v.to(device)
else:
prepared_inputs[k] = v
return prepared_inputs
# Initialize our Trainer
trainer = NPUTrainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=train_dataset if training_args.do_train else None,
eval_dataset=eval_dataset if training_args.do_eval else None,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
data_collator=data_collator,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
)
# Training
if training_args.do_train:
checkpoint = last_checkpoint if last_checkpoint else None
train_result = trainer.train(resume_from_checkpoint=checkpoint)
metrics = train_result.metrics
trainer.save_model() # Saves the tokenizer too for easy upload
max_train_samples = (
data_args.max_train_samples if data_args.max_train_samples is not None else len(train_dataset)
)
metrics["train_samples"] = min(max_train_samples, len(train_dataset))
trainer.log_metrics("train", metrics)
trainer.save_metrics("train", metrics)
trainer.save_state()
# Evaluation
if training_args.do_eval:
logger.info("*** Evaluate ***")
metrics = trainer.evaluate()
max_val_samples = data_args.max_val_samples if data_args.max_val_samples is not None else len(eval_dataset)
metrics["eval_samples"] = min(max_val_samples, len(eval_dataset))
trainer.log_metrics("eval", metrics)
trainer.save_metrics("eval", metrics)
# Predict
if training_args.do_predict:
logger.info("*** Predict ***")
predictions, labels, metrics = trainer.predict(test_dataset)
predictions = np.argmax(predictions, axis=2)
# Remove ignored index (special tokens)
true_predictions = [
[label_list[p] for (p, l) in zip(prediction, label) if l != -100]
for prediction, label in zip(predictions, labels)
]
trainer.log_metrics("test", metrics)
trainer.save_metrics("test", metrics)
# Save predictions
output_test_predictions_file = os.path.join(training_args.output_dir, "test_predictions.txt")
if trainer.is_world_process_zero():
with open(output_test_predictions_file, "w") as writer:
for prediction in true_predictions:
writer.write(" ".join(prediction) + "\n")
def _mp_fn(index):
# For xla_spawn (TPUs)
main()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)