Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:provider 经典状态管理的高效应用
摘要 Flutter 状态管理插件 provider 凭借其简单易用、性能优异的特点,成为 HarmonyOS NEXT 商业项目开发的首选方案。本文深入剖析 provider 的核心优势:数据驱动UI的闭环逻辑、注入式依赖管理以及出色的性能表现。通过底层技术分析,揭示 provider 相比原生 InheritedWidget 的效率提升机制。文章提供完整的集成指南,并展示如何在鸿蒙项目中实现细
Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:provider 经典状态管理的高效应用

前言
在 Flutter 开发的长河中,provider 无疑是普及率、社区支持度最高的状态管理插件。虽然近年来有 Riverpod 等新秀出现,但在追求稳定交付、团队上手成本优先的 HarmonyOS NEXT 商业项目开发中,provider 依然是许多中大型 App 的中流砥柱。
本文将演示如何在鸿蒙环境下,利用 provider 构建响应式的高性能业务架构。
一、 Provider 的核心哲学:为什么它能经久不衰?
1.1 数据驱动 UI 的闭环逻辑
通过封装 ChangeNotifier,provider 实现了一种高度解耦的发布订阅模式。业务逻辑(Model)只需要专注于数据的自增或修改,并通过 notifyListeners() 告知外部。这种架构让 HarmonyOS NEXT 的开发者能从繁琐的 setState 地狱中解脱,让 UI 真正成为数据的“映射”。
1.2 注入式依赖管理(Dependency Injection)
它基于 Flutter 最底层的 InheritedWidget 工作,提供了一套优雅的注入语法。相比全局变量,provider 保证了状态的生命周期与 Widget 树绑定,能随着页面的销毁自动释放内存,这在对内存管控极其严格的鸿蒙生态中至关重要。
1.3 极简的上手门槛与极高的上限
无论是初入鸿蒙开发领域的萌新,还是构建数十万行代码的大型 App,provider 提供的 MultiProvider 和 ProxyProvider 都能满足从简单属性共享到复杂依赖链路的需求。
二、 技术内幕:拆解 Provider 的底层分发效率
2.1 为什么它比 InheritedWidget 更快?
传统的 InheritedWidget 在更新时会通知其下所有的子 Widget。而 provider 通过 SelectiveUpdate 机制以及 Selector 控件,实现了“外科手术式”的重绘。它对比数据前后的 hash 值,只有当真正需要更新的属性发生偏移时,才会触发对应的 Element.markNeedsBuild()。
2.2 树遍历的 O(1) 效率
在鸿蒙端处理超长 Widget 树时,寻找 Provider 的开销几乎可以忽略不计。它利用了 BuildContext 提供的 getElementForInheritedWidgetOfExactType() 缓存,确保了无论层级多深,状态获取的复杂度始终为 O(1)。
三、 集成指南
2.1 添加依赖
dependencies:
provider: ^6.1.5
四、 实战:构建高度复杂的鸿蒙业务模型
4.1 使用 Selector 实现细粒度更新
在鸿蒙首页中,如果只需更新用户的“积分”,不需要更新“用户名”:
// 💡 实战技巧:只有当 score 改变时才触发重绘
Selector<UserStore, int>(
selector: (_, store) => store.score,
builder: (context, score, _) {
return Text('鸿蒙积分: $score');
},
);
4.2 ProxyProvider:处理具有依赖关系的 Provider
处理鸿蒙登录鉴权后自动注入 Token 的场景:
MultiProvider(
providers: [
ChangeNotifierProvider(create: (_) => AuthStore()),
// 💡 亮点:APIClient 依赖于 AuthStore 中的 token
ProxyProvider<AuthStore, ApiClient>(
update: (_, auth, __) => ApiClient(auth.token),
),
],
child: const MyApp(),
);
四、 鸿蒙平台的性能调优
4.1 避免全局 Rebuild
鸿蒙设备通常具有极佳的刷新率。在繁杂的 UI 中,务必使用 context.select 提取需要的细粒度属性,或者使用 Consumer 包裹最小的 Widget,防止点击一个开关导致整个鸿蒙首页重新渲染。
4.2 静态数据获取
如果仅仅是为了调用方法而不需要监听数据变化,请务必使用 read 而非 watch。
// 💡 提示:在鸿蒙端性能优化中,read 不会注册监听,节省 CPU 资源
Provider.of<SettingsStore>(context, listen: false).toggleTheme();
// 推荐写法:
context.read<SettingsStore>().toggleTheme();
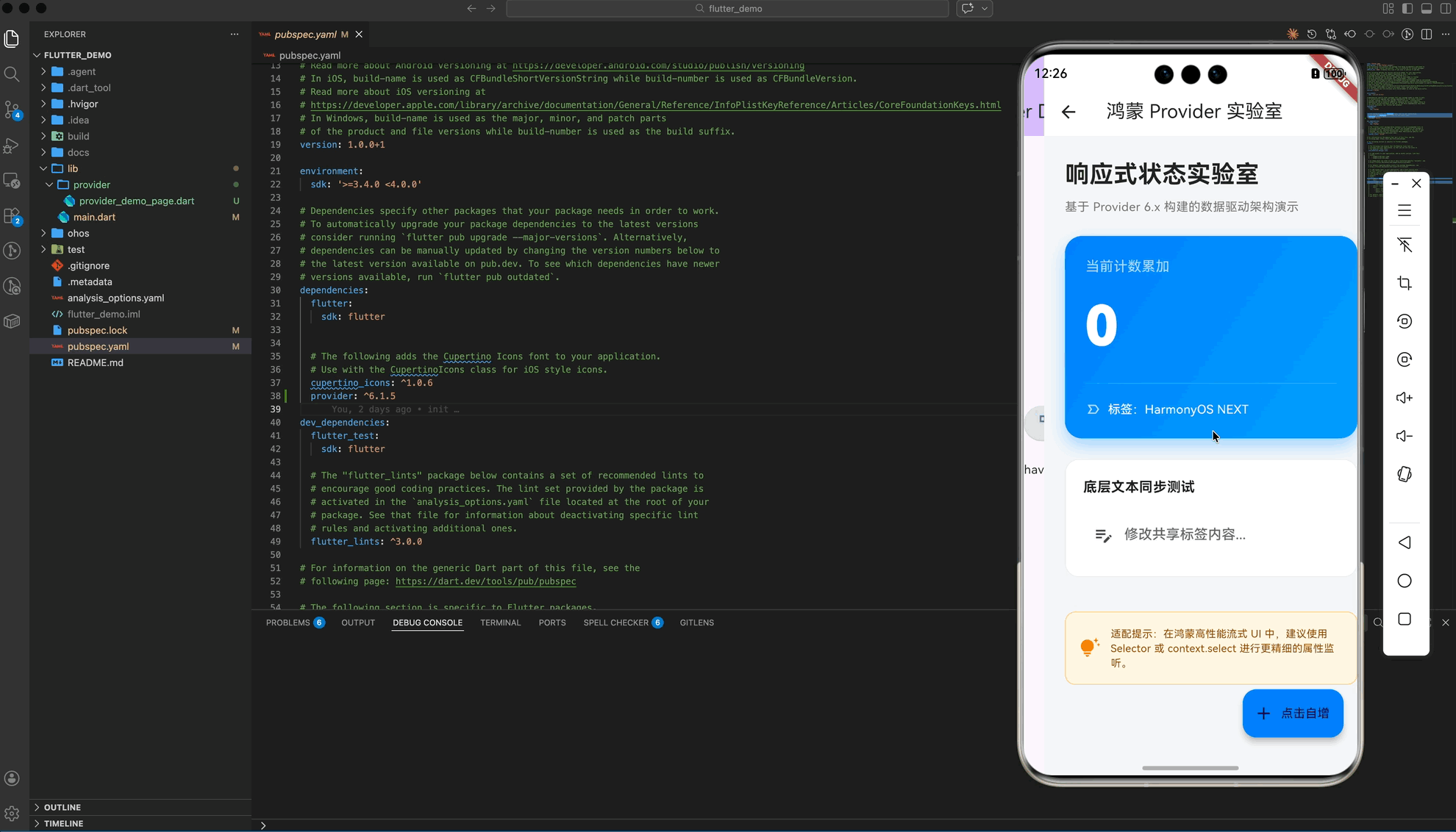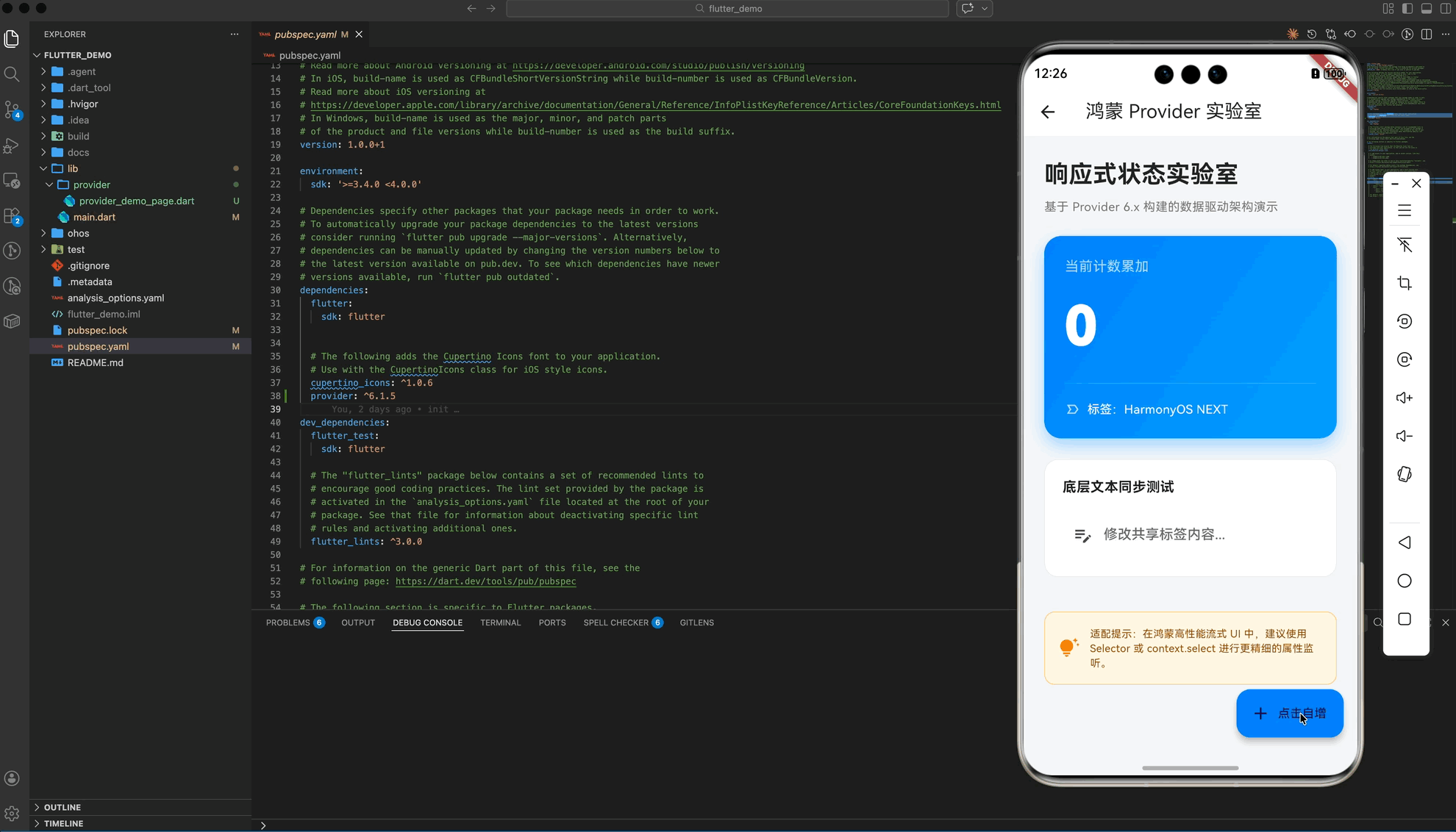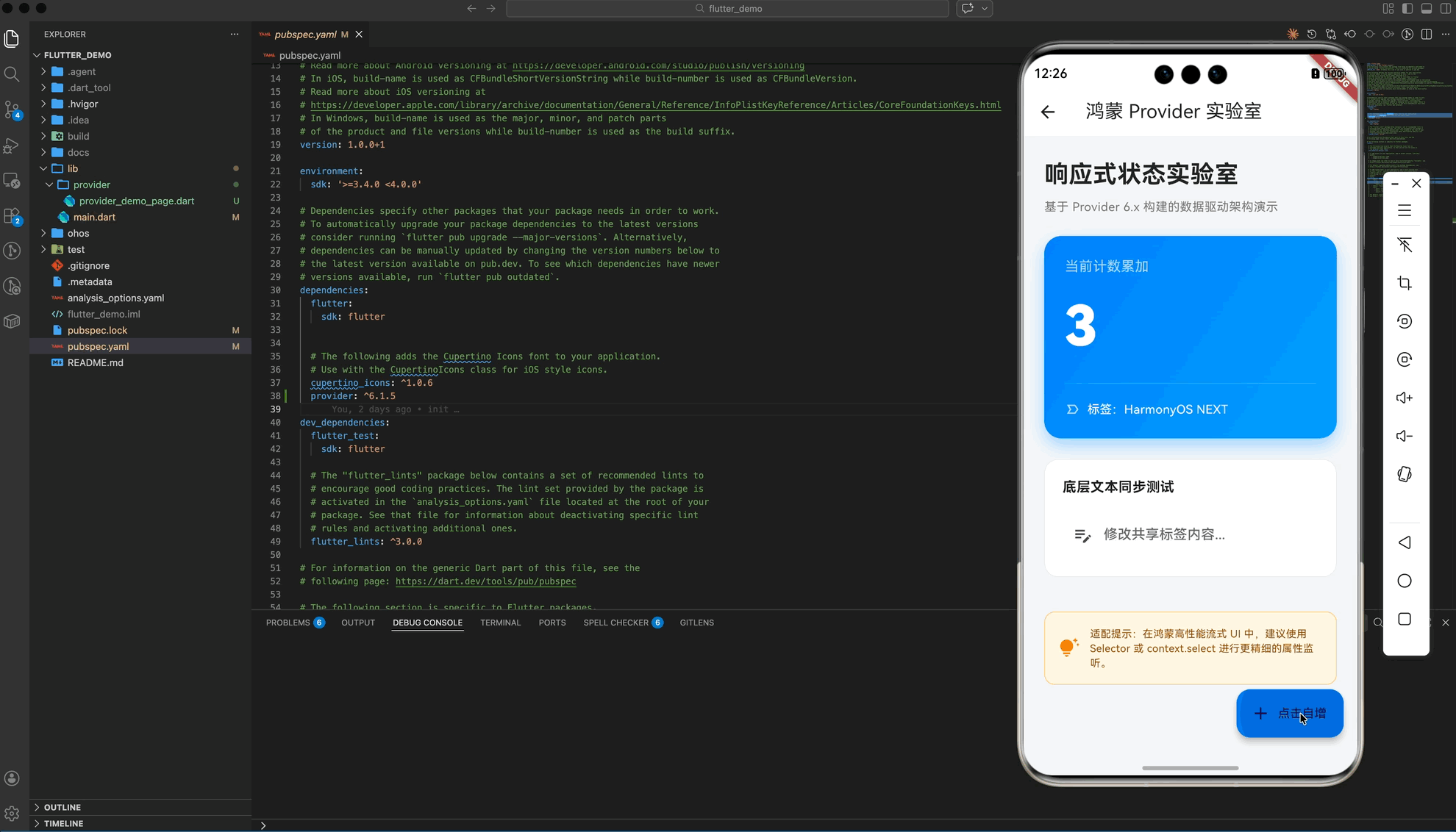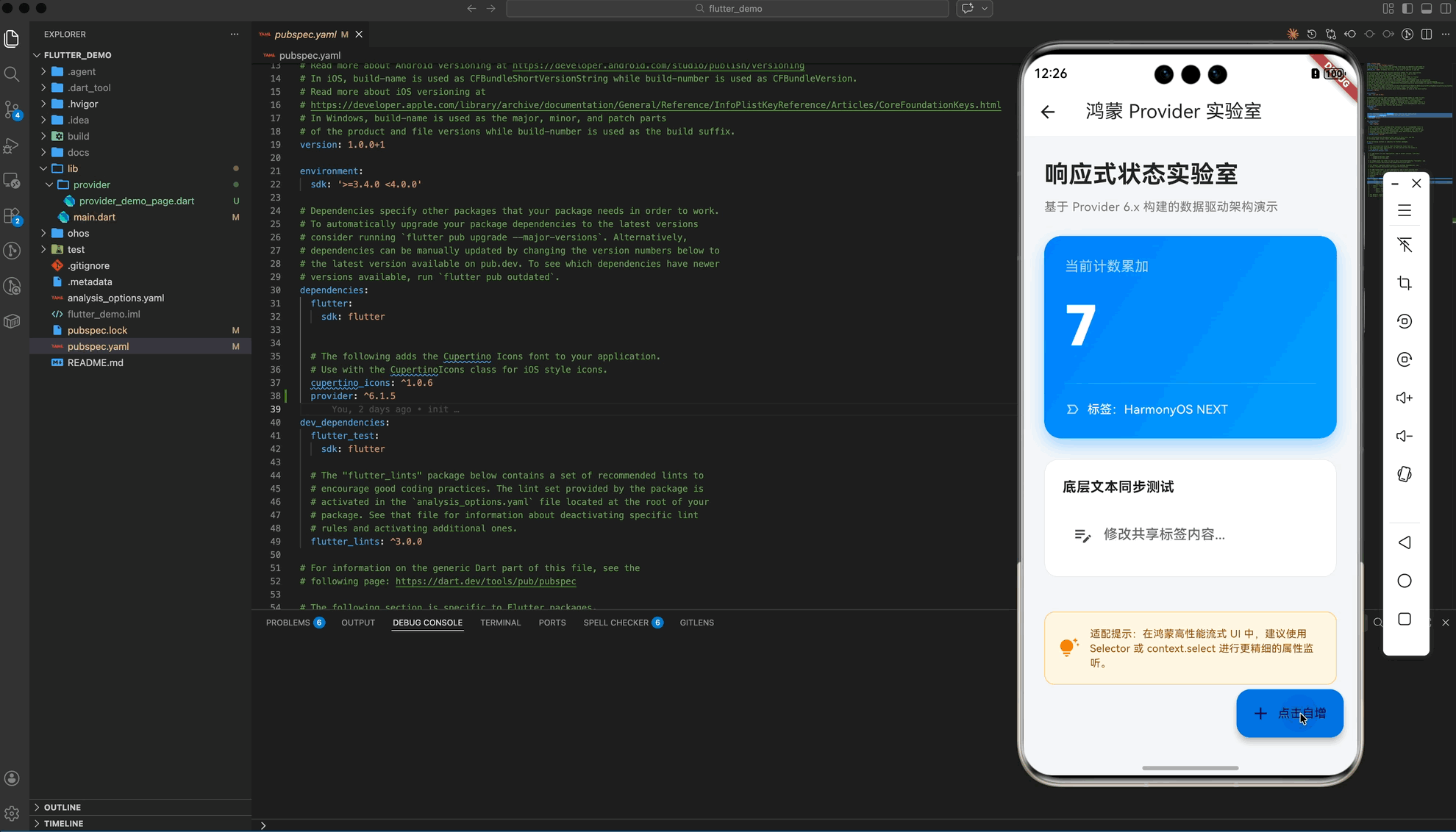
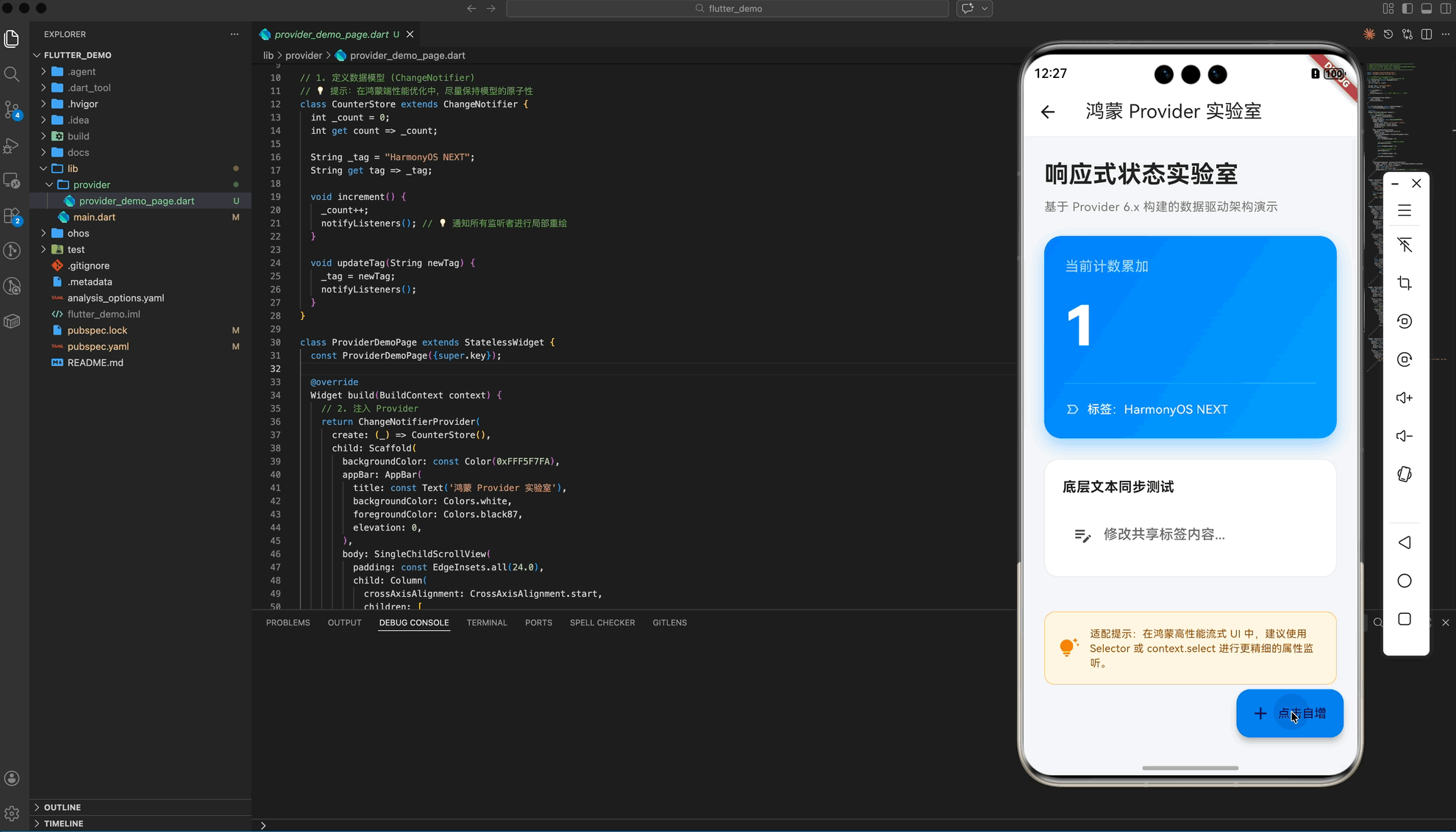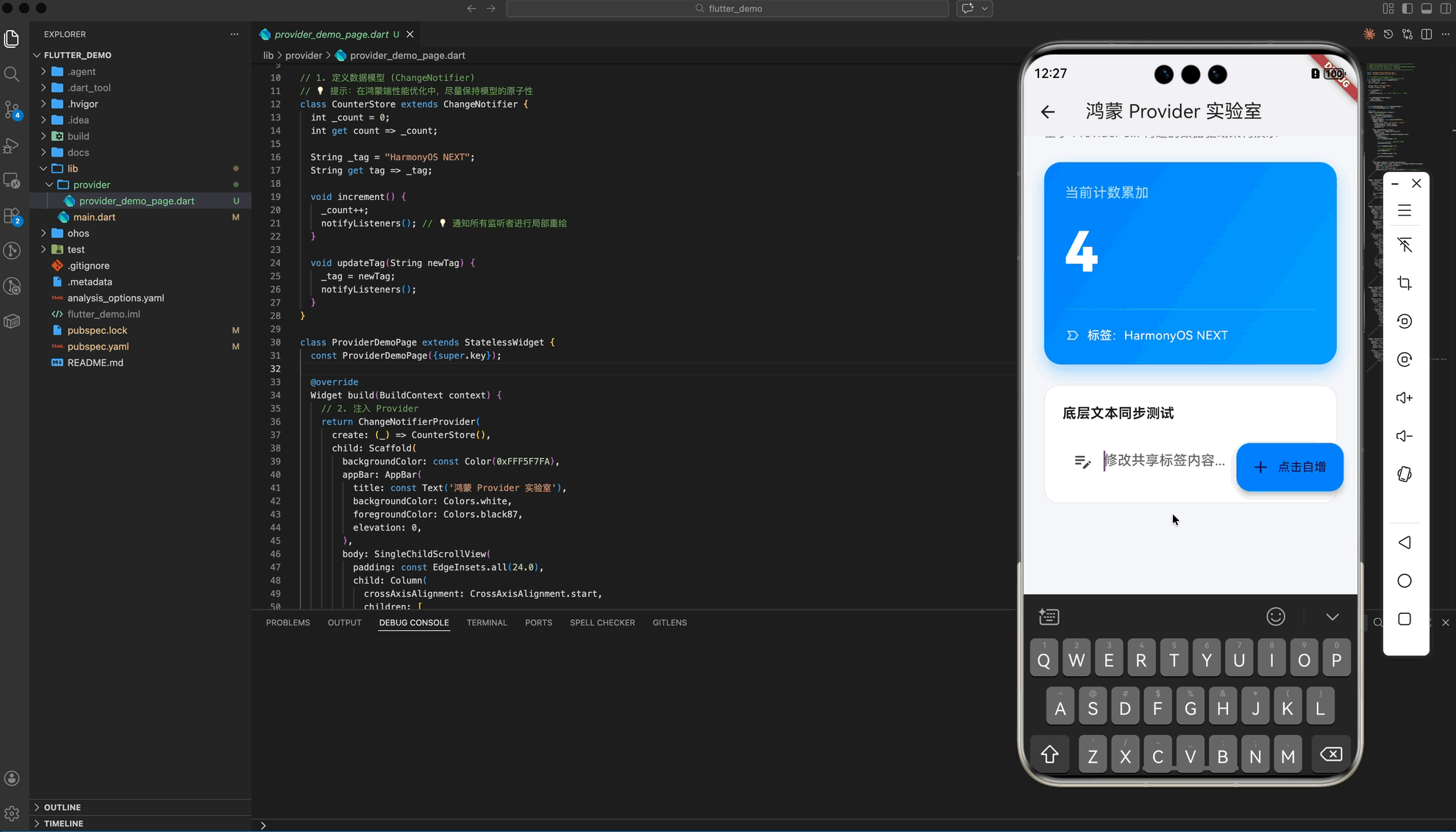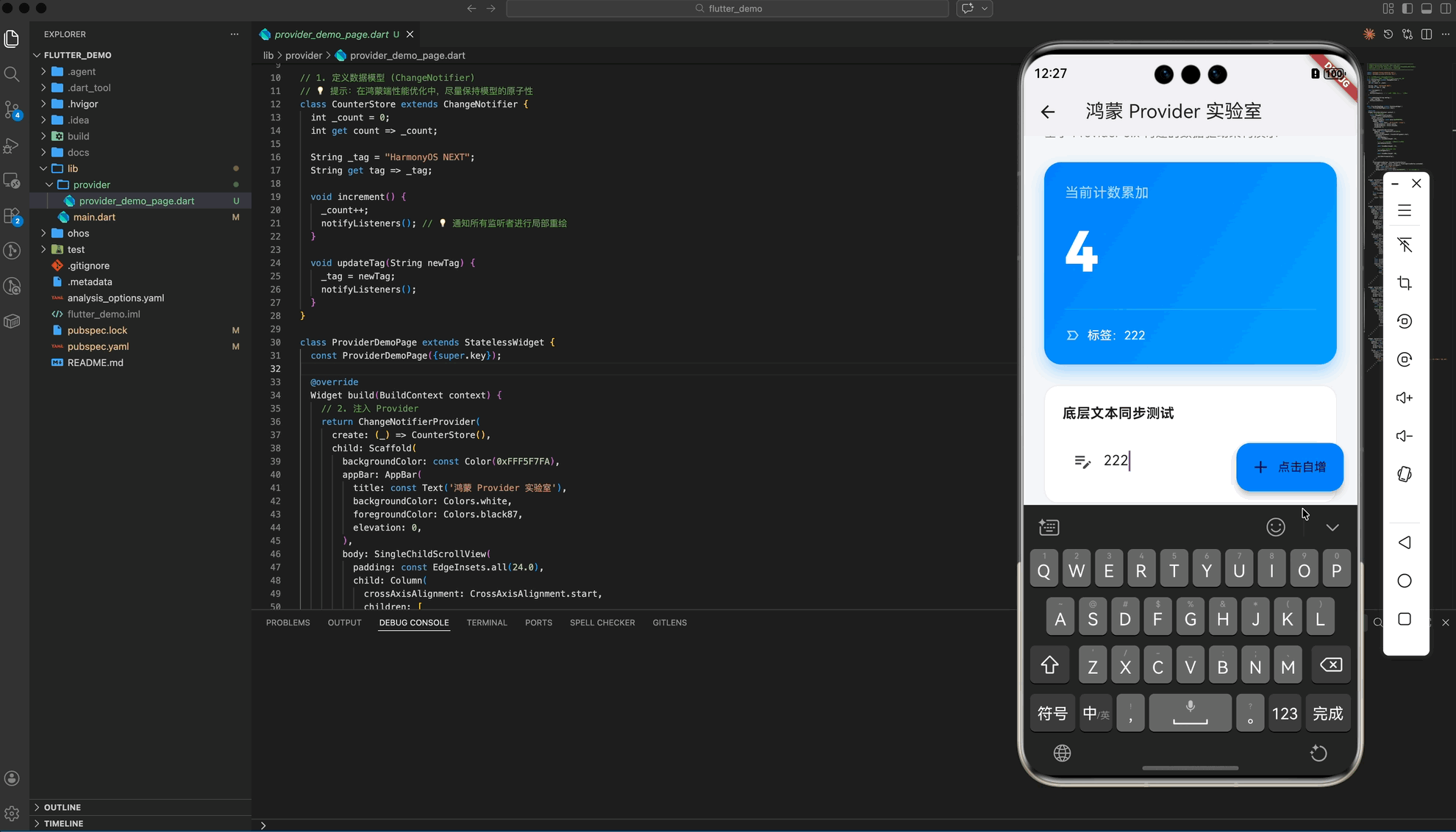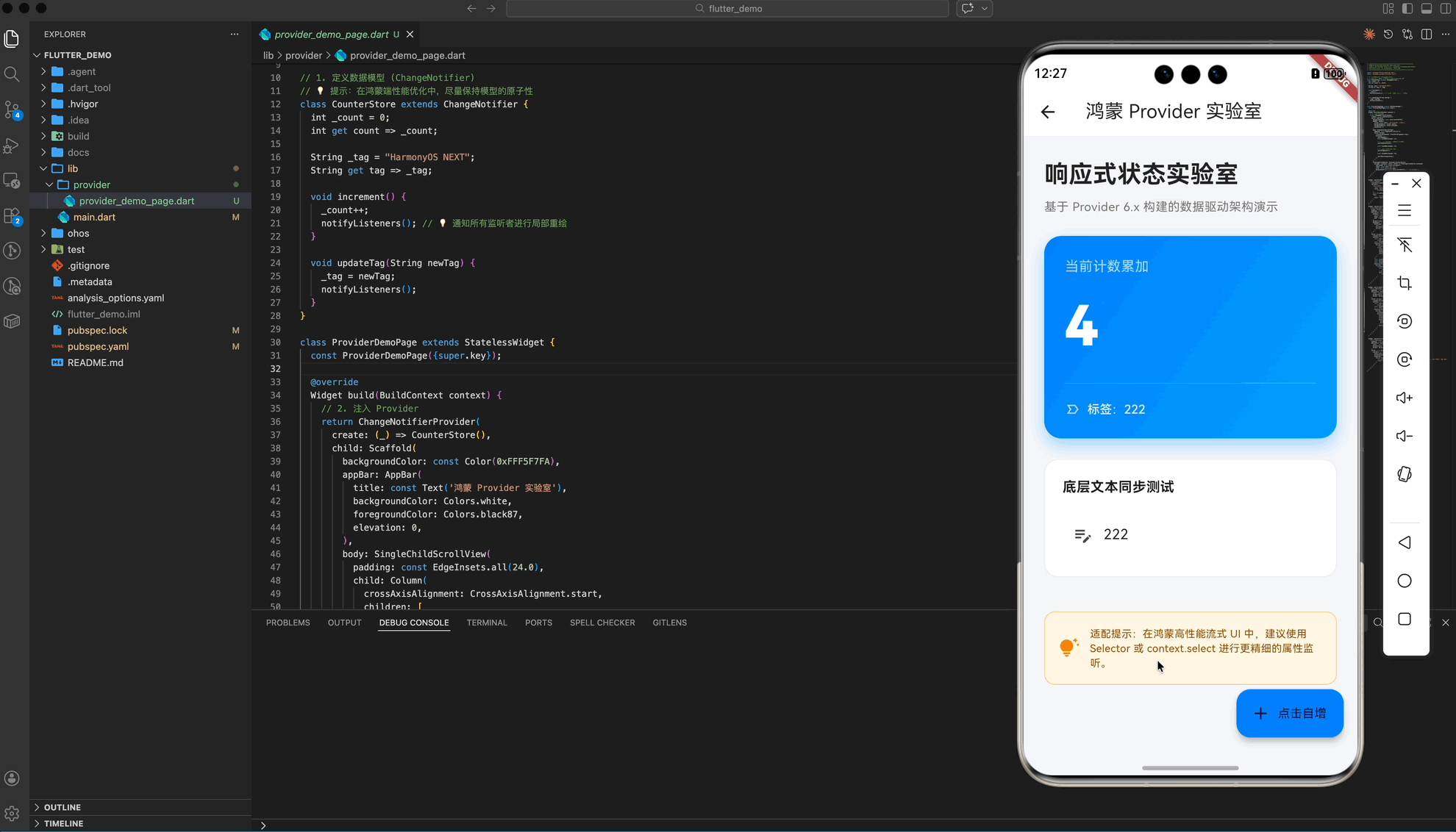
五、 实战示例:构建“鸿蒙状态管理实验室”
以下演示了一个具备 Premium UI 视觉规范的综合案例,展示了计数器自增与文本实时同步的双重逻辑:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:provider/provider.dart';
// 1. 定义数据模型 (ChangeNotifier)
// 💡 提示:在鸿蒙端性能优化中,尽量保持模型的原子性
class CounterStore extends ChangeNotifier {
int _count = 0;
int get count => _count;
String _tag = "HarmonyOS NEXT";
String get tag => _tag;
void increment() {
_count++;
notifyListeners(); // 💡 通知所有监听者进行局部重绘
}
void updateTag(String newTag) {
_tag = newTag;
notifyListeners();
}
}
class ProviderDemoPage extends StatelessWidget {
const ProviderDemoPage({super.key});
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// 2. 注入 Provider
return ChangeNotifierProvider(
create: (_) => CounterStore(),
child: Scaffold(
backgroundColor: const Color(0xFFF5F7FA),
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('鸿蒙 Provider 实验室'),
backgroundColor: Colors.white,
foregroundColor: Colors.black87,
elevation: 0,
),
body: SingleChildScrollView(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(24.0),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
_buildHeader(),
const SizedBox(height: 24),
// 3. 使用 Consumer 实现响应式仪表盘
_buildCounterCard(),
const SizedBox(height: 24),
// 4. 展示 TextField 同步
_buildTagEditor(),
const SizedBox(height: 40),
_buildPerformanceTip(),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: Consumer<CounterStore>(
builder: (context, store, child) => FloatingActionButton.extended(
onPressed: () => store.increment(),
label: const Text('点击自增'),
icon: const Icon(Icons.add),
backgroundColor: const Color(0xFF007DFF), // 华为经典星空蓝
),
),
),
);
}
Widget _buildHeader() {
return Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
const Text(
"响应式状态实验室",
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 28, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold, color: Colors.black87),
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
Text(
"基于 Provider 6.x 构建的数据驱动架构演示",
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 14, color: Colors.grey[600]),
),
],
);
}
Widget _buildCounterCard() {
return Container(
width: double.infinity,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(24),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
gradient: const LinearGradient(
colors: [Color(0xFF007DFF), Color(0xFF409EFF)],
begin: Alignment.topLeft,
end: Alignment.bottomRight,
),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(20),
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: const Color(0xFF007DFF).withOpacity(0.3),
blurRadius: 15,
offset: const Offset(0, 8),
),
],
),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
const Text("当前计数累加",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white70, fontSize: 16)),
const SizedBox(height: 12),
Consumer<CounterStore>(
builder: (context, store, _) => Text(
"${store.count}",
style: const TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 64,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w900,
letterSpacing: -2,
),
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 12),
const Divider(color: Colors.white24),
const SizedBox(height: 12),
Consumer<CounterStore>(
builder: (context, store, _) => Row(
children: [
const Icon(Icons.label_important_outline,
color: Colors.white70, size: 18),
const SizedBox(width: 8),
Text("标签:${store.tag}",
style: const TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 14)),
],
),
),
],
),
);
}
Widget _buildTagEditor() {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.white,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(16),
border: Border.all(color: Colors.grey[200]!),
),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
const Text("底层文本同步测试",
style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold, fontSize: 16)),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
// 💡 亮点:演示 context.read 的非监听获取方式
Consumer<CounterStore>(
builder: (context, store, _) => TextField(
onChanged: (val) => store.updateTag(val),
decoration: InputDecoration(
hintText: "修改共享标签内容...",
filled: true,
fillColor: Colors.grey[50],
border: OutlineInputBorder(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
borderSide: BorderSide.none,
),
prefixIcon: const Icon(Icons.edit_note),
),
),
),
],
),
);
}
Widget _buildPerformanceTip() {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: const Color(0xFFFFF7E6),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
border: Border.all(color: const Color(0xFFFFD591)),
),
child: const Row(
children: [
Icon(Icons.tips_and_updates, color: Color(0xFFFA8C16)),
SizedBox(width: 12),
Expanded(
child: Text(
"适配提示:在鸿蒙高性能流式 UI 中,建议使用 Selector 或 context.select 进行更精细的属性监听。",
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 12, color: Color(0xFF874D00)),
),
),
],
),
);
}
}
七、 总结
provider 虽然没有花哨的流式编程,但其胜在清晰与稳定。在追求开发效率与商业交付的鸿蒙生态初期,它是构建中小型应用逻辑层最稳健的基石。理解“精准通知”与“颗粒度控制”,你就能在 HarmonyOS NEXT 上跑出丝滑般的状态流转效果。
🔗 相关阅读推荐:
🌐 欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献10条内容
已为社区贡献10条内容









所有评论(0)