Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:甘特图(Gantt Chart)组件
在移动开发领域,我们总是面临着选择与适配。今天,你的Flutter应用在Android和iOS上跑得正欢,明天可能就需要考虑一个新的平台:HarmonyOS(鸿蒙)。这不是一道选答题,而是很多团队正在面对的现实。Flutter的优势很明确——写一套代码,就能在两个主要平台上运行,开发体验流畅。而鸿蒙代表的是下一个时代的互联生态,它不仅仅是手机系统,更着眼于未来全场景的体验。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区: https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net
目录
前言:跨生态开发的新机遇
在移动开发领域,我们总是面临着选择与适配。今天,你的Flutter应用在Android和iOS上跑得正欢,明天可能就需要考虑一个新的平台:HarmonyOS(鸿蒙)。这不是一道选答题,而是很多团队正在面对的现实。
Flutter的优势很明确——写一套代码,就能在两个主要平台上运行,开发体验流畅。而鸿蒙代表的是下一个时代的互联生态,它不仅仅是手机系统,更着眼于未来全场景的体验。将现有的Flutter应用适配到鸿蒙,听起来像是一个“跨界”任务,但它本质上是一次有价值的技术拓展:让产品触达更多用户,也让技术栈覆盖更广。
不过,这条路走起来并不像听起来那么简单。Flutter和鸿蒙,从底层的架构到上层的工具链,都有着各自的设计逻辑。会遇到一些具体的问题:代码如何组织?原有的功能在鸿蒙上如何实现?那些平台特有的能力该怎么调用?更实际的是,从编译打包到上架部署,整个流程都需要重新摸索。
这篇文章想做的,就是把这些我们趟过的路、踩过的坑,清晰地摊开给你看。我们不会只停留在“怎么做”,还会聊到“为什么得这么做”,以及“如果出了问题该往哪想”。这更像是一份实战笔记,源自真实的项目经验,聚焦于那些真正卡住过我们的环节。
无论你是在为一个成熟产品寻找新的落地平台,还是从一开始就希望构建能面向多端的应用,这里的思路和解决方案都能提供直接的参考。理解了两套体系之间的异同,掌握了关键的衔接技术,不仅能完成这次迁移,更能积累起应对未来技术变化的能力。
混合工程结构深度解析
项目目录架构
当Flutter项目集成鸿蒙支持后,典型的项目结构会发生显著变化。以下是经过ohos_flutter插件初始化后的项目结构:
my_flutter_harmony_app/
├── lib/ # Flutter业务代码(基本不变)
│ ├── main.dart # 应用入口
│ ├── components/ # 组件目录
│ │ └── gantt_chart.dart # 甘特图组件
│ └── utils/ # 工具类目录
├── pubspec.yaml # Flutter依赖配置
├── ohos/ # 鸿蒙原生层(核心适配区)
│ ├── entry/ # 主模块
│ │ └── src/main/
│ │ ├── ets/ # ArkTS代码
│ │ │ ├── MainAbility/
│ │ │ │ ├── MainAbility.ts # 主Ability
│ │ │ │ └── MainAbilityContext.ts
│ │ │ └── pages/
│ │ │ ├── Index.ets # 主页面
│ │ │ └── Splash.ets # 启动页
│ │ ├── resources/ # 鸿蒙资源文件
│ │ │ ├── base/
│ │ │ │ ├── element/ # 字符串等
│ │ │ │ ├── media/ # 图片资源
│ │ │ │ └── profile/ # 配置文件
│ │ │ └── en_US/ # 英文资源
│ │ └── config.json # 应用核心配置
│ ├── ohos_test/ # 测试模块
│ ├── build-profile.json5 # 构建配置
│ └── oh-package.json5 # 鸿蒙依赖管理
└── README.md
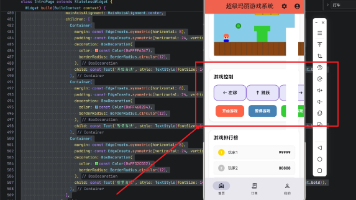
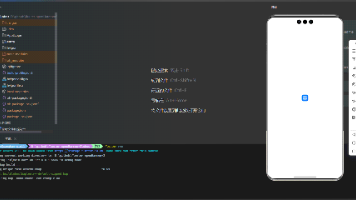
展示效果图片
flutter 实时预览 效果展示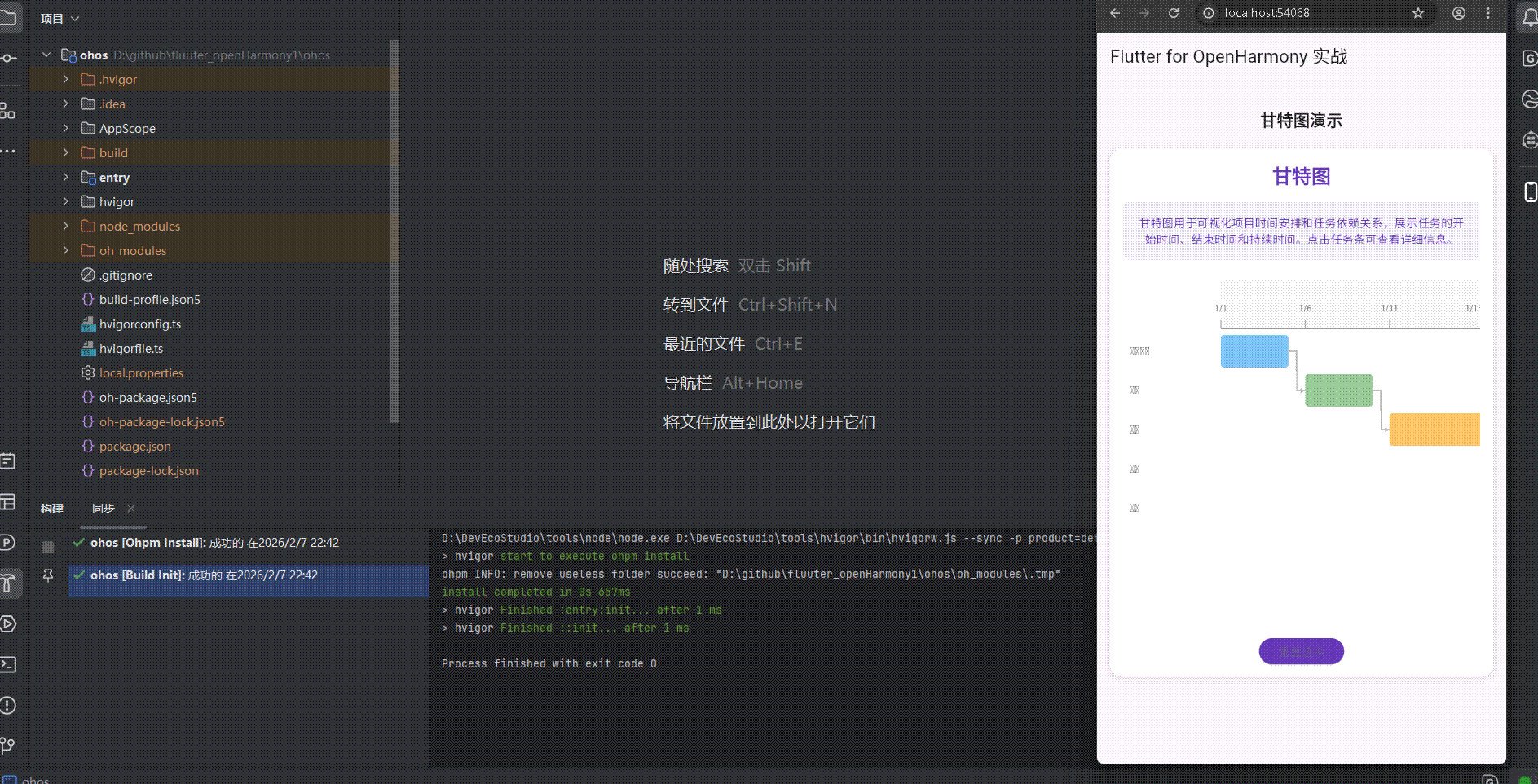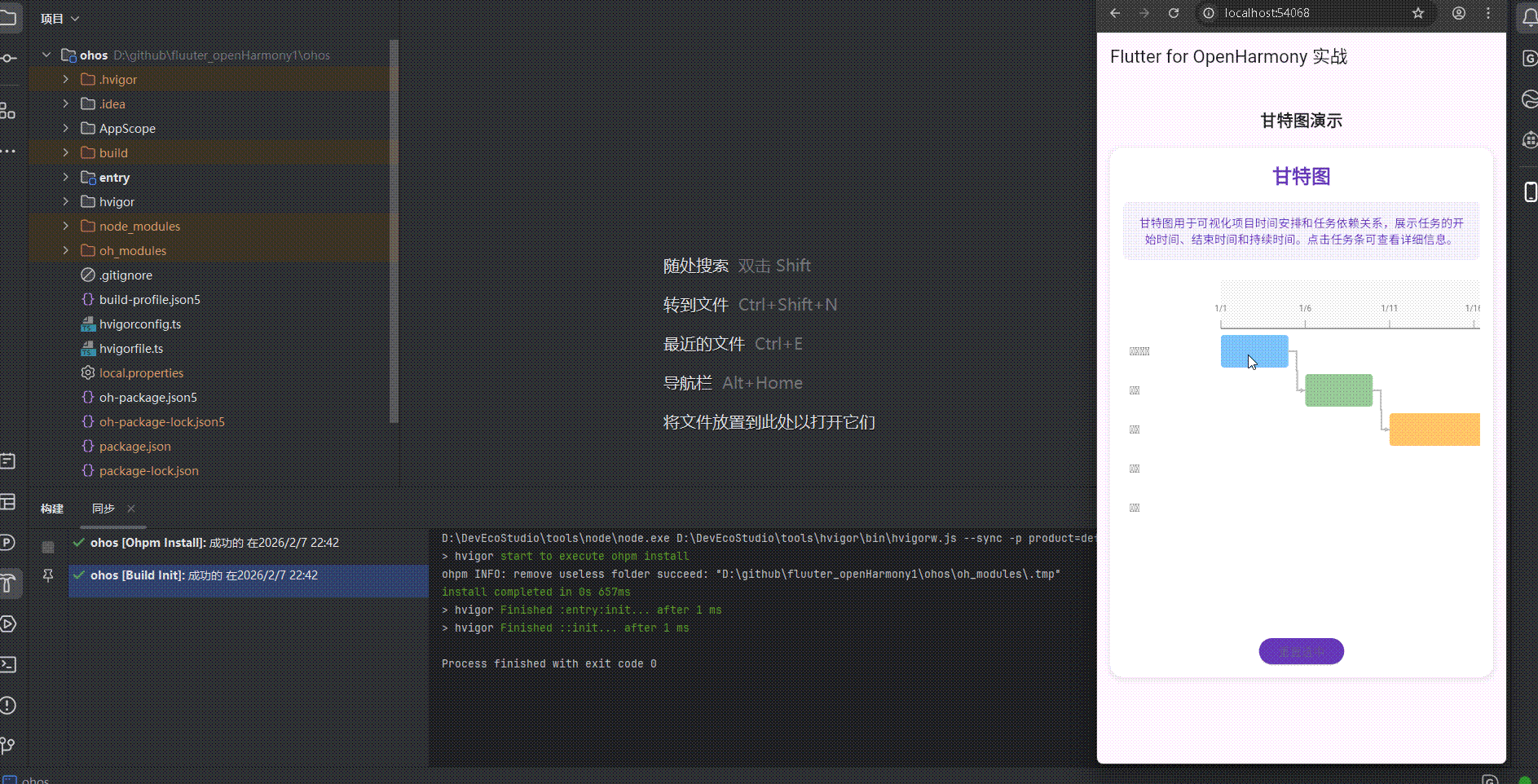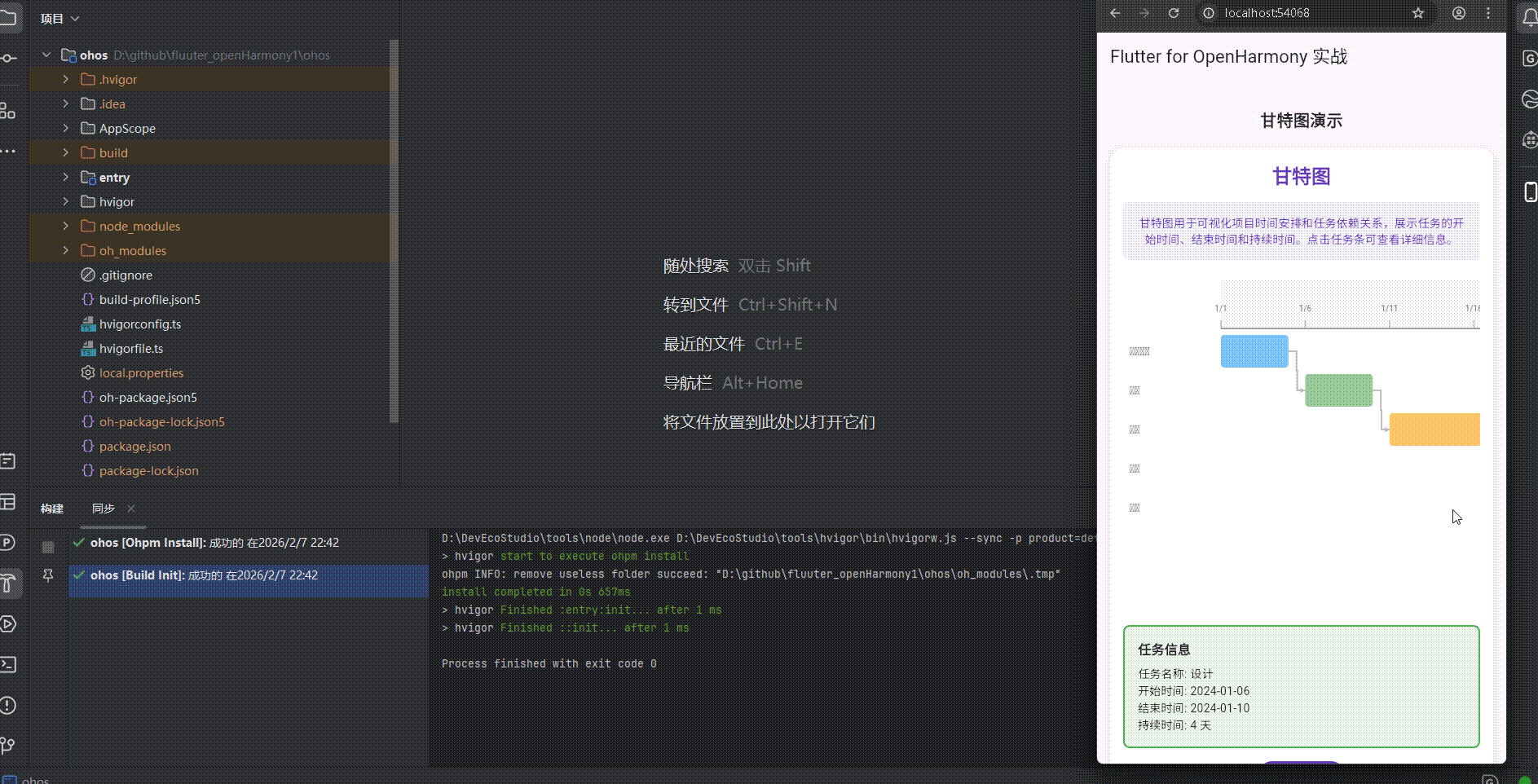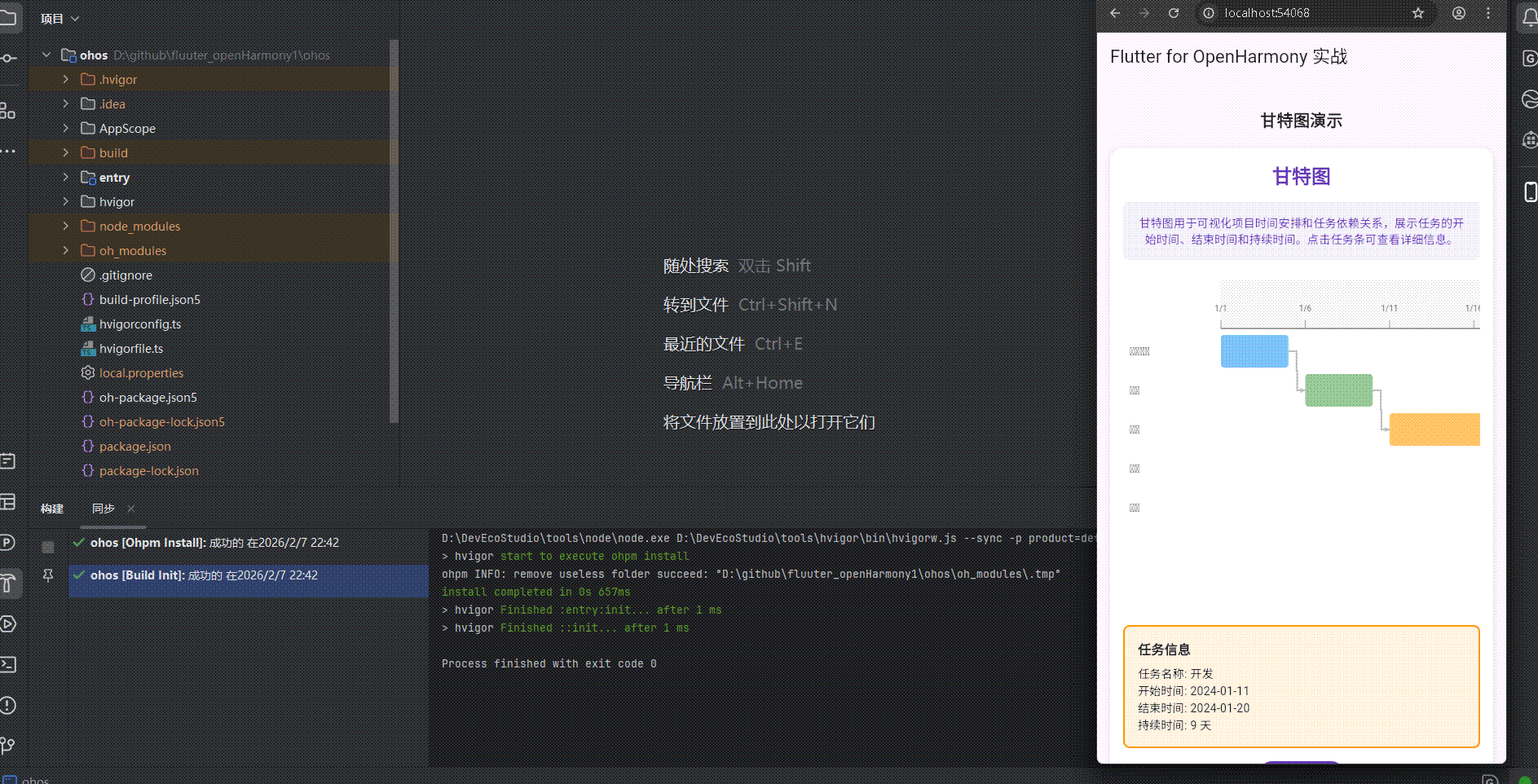
运行到鸿蒙虚拟设备中效果展示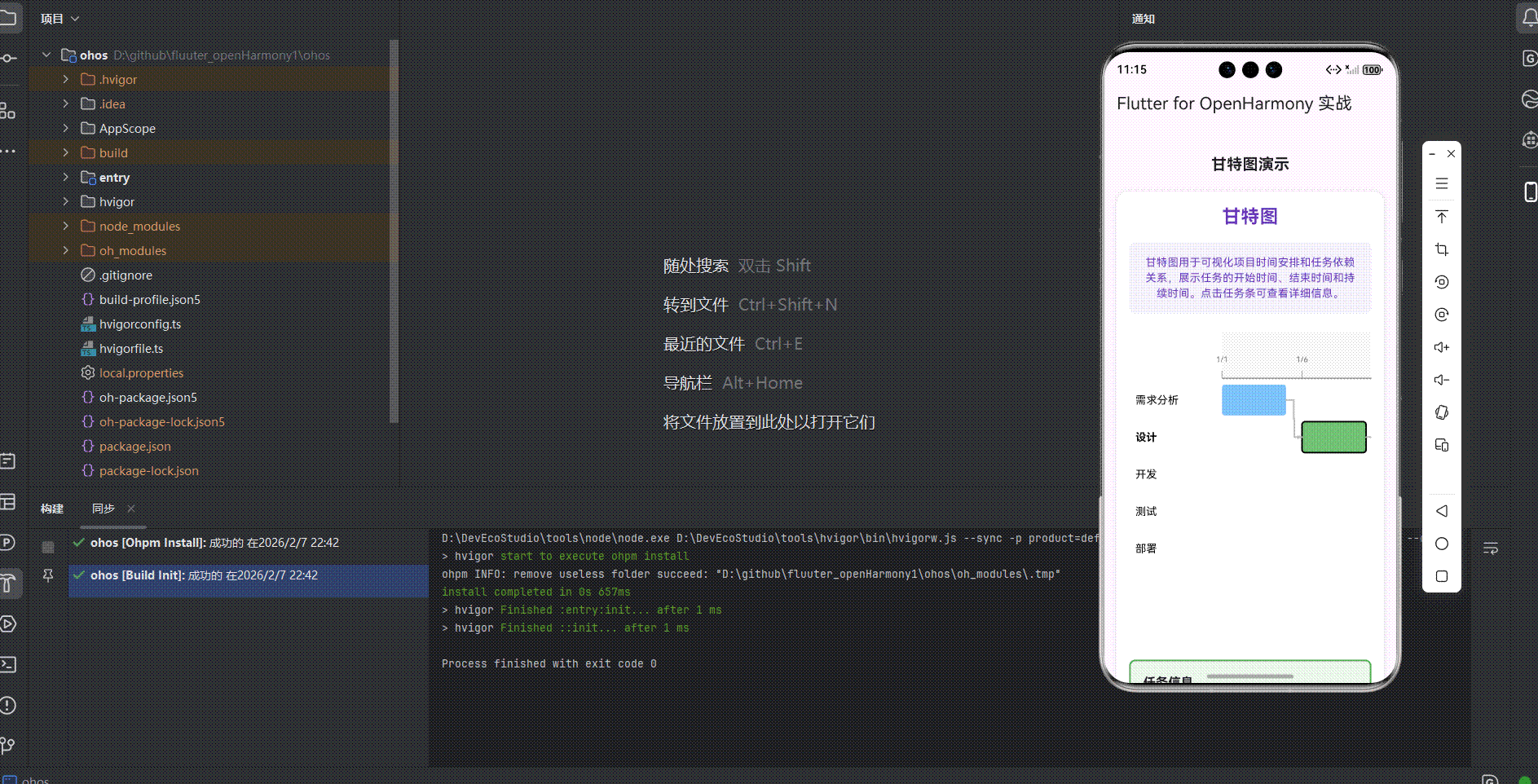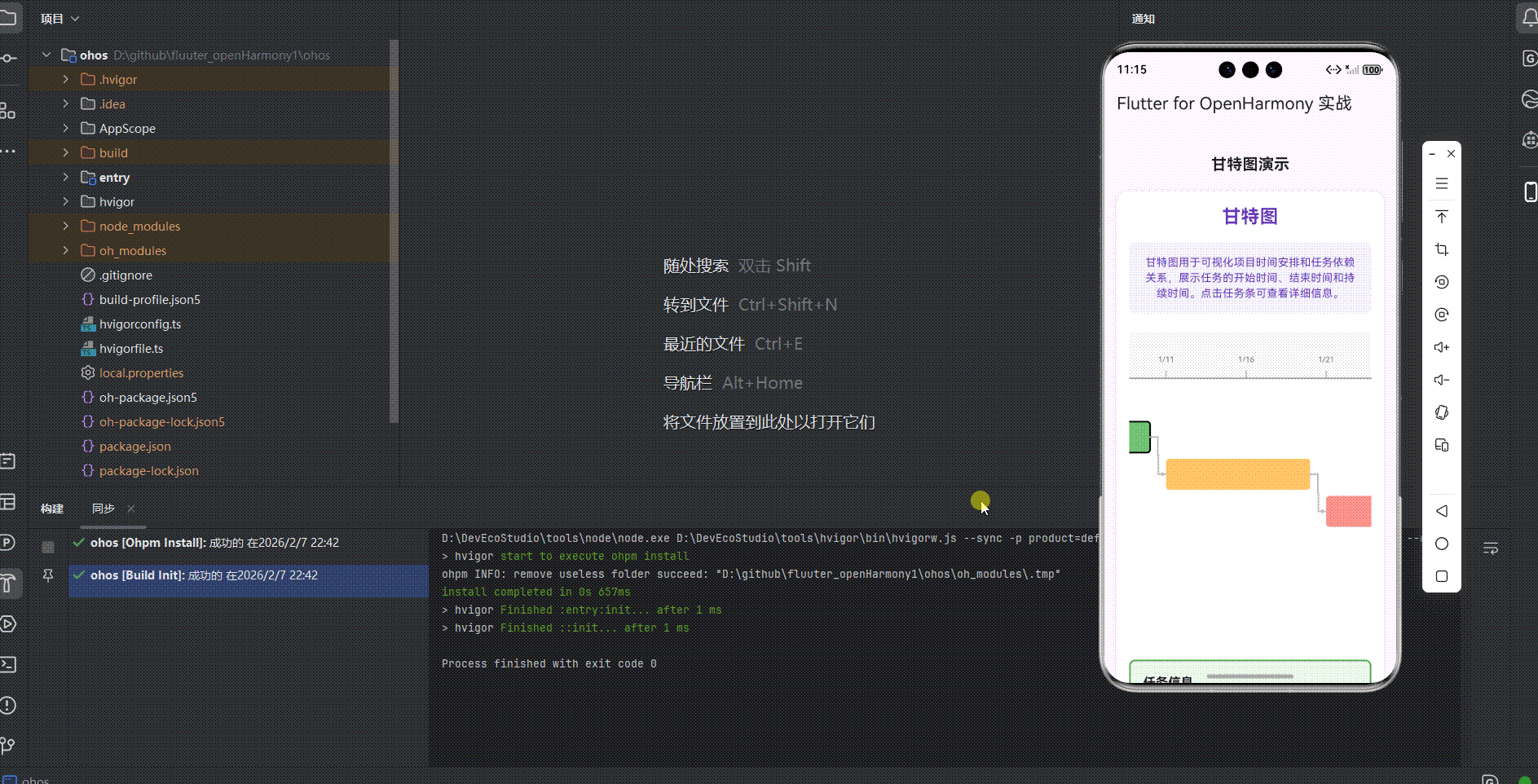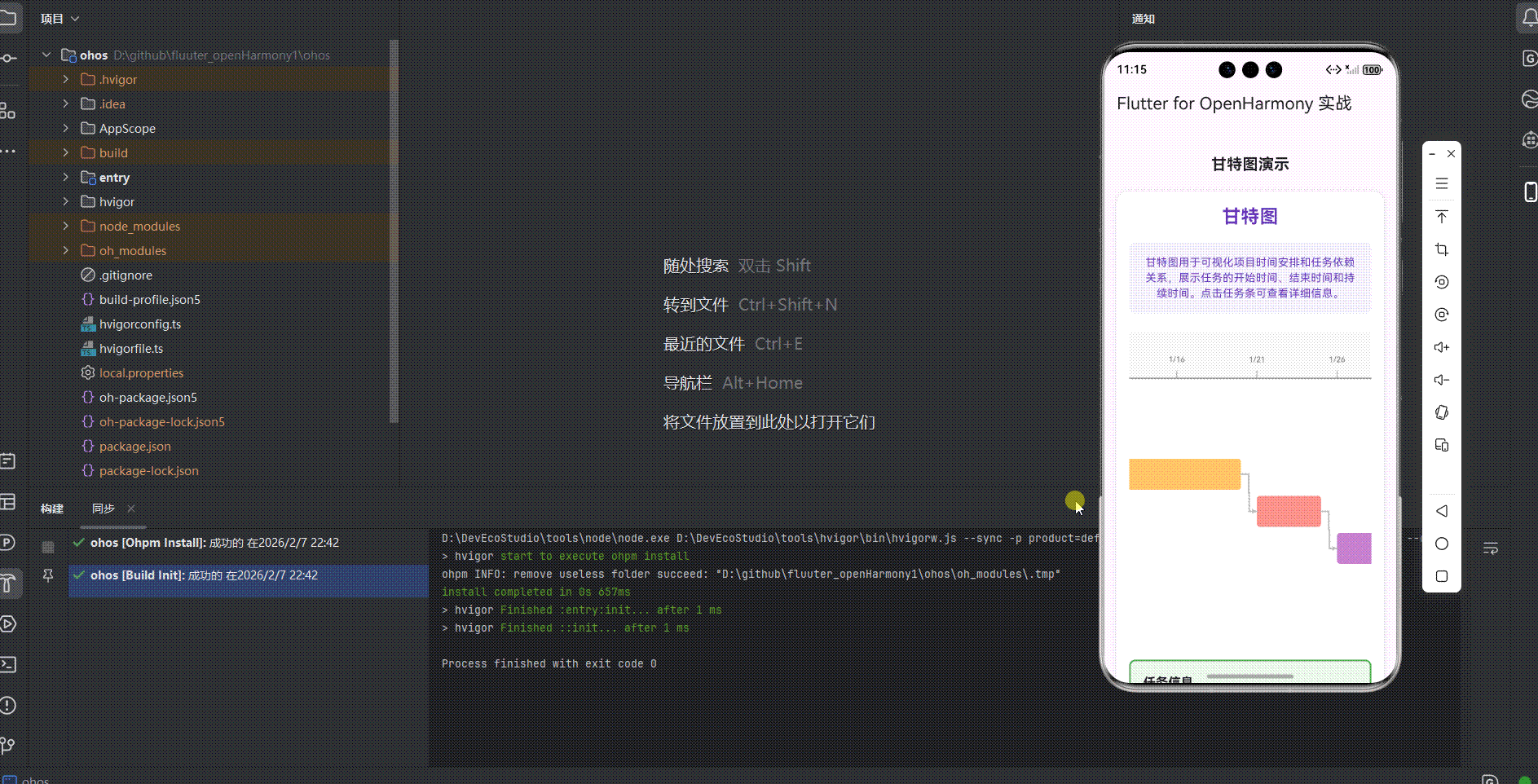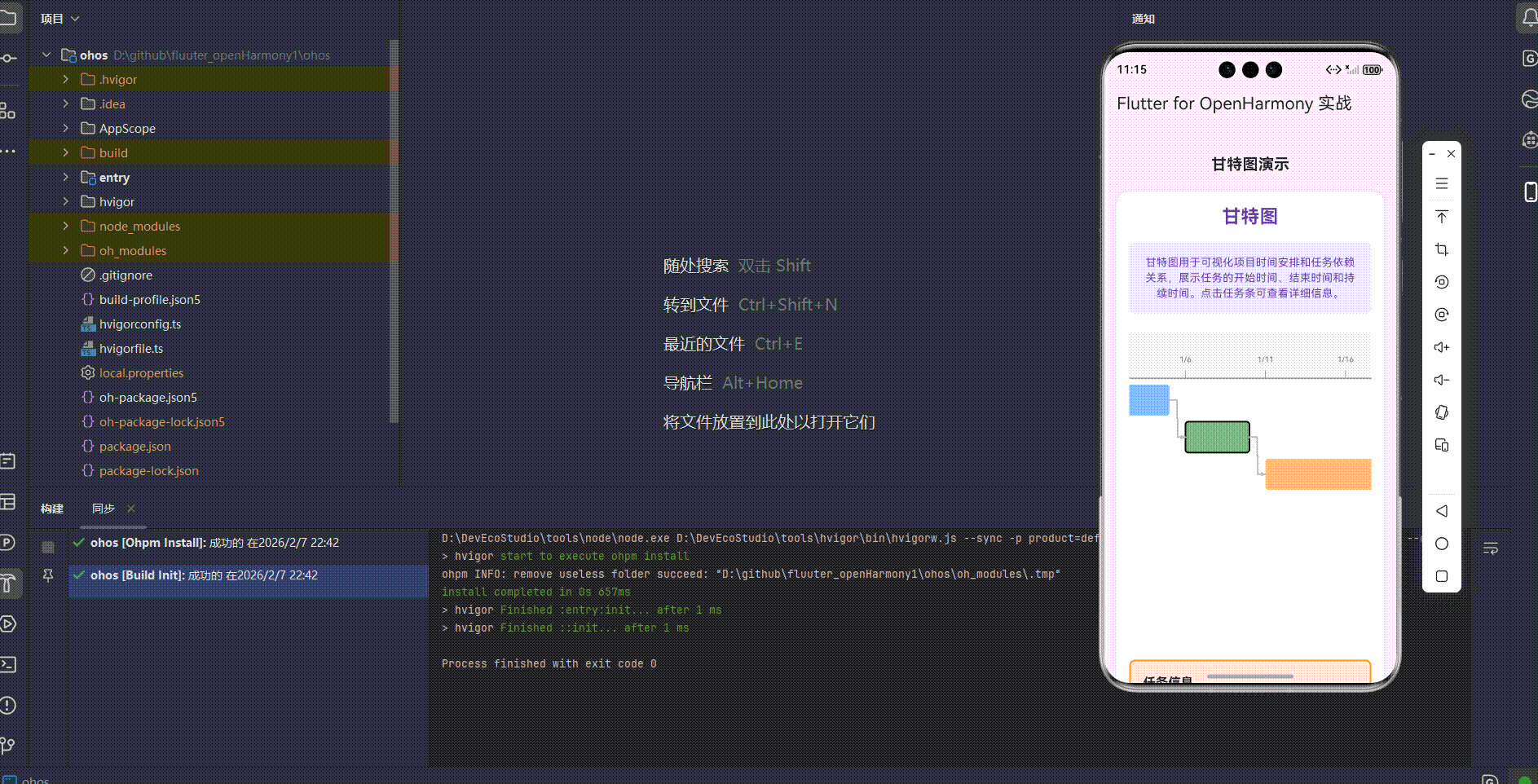
功能代码实现
甘特图组件设计与实现
1. 数据模型设计
甘特图组件的核心是数据模型,我们需要设计两个主要的模型:GanttTask(任务)和GanttDependency(任务依赖关系)。
// 甘特图任务模型
class GanttTask {
final String id;
final String name;
final DateTime startDate;
final DateTime endDate;
final Color color;
bool isSelected;
GanttTask({
required this.id,
required this.name,
required this.startDate,
required this.endDate,
this.color = Colors.blue,
this.isSelected = false,
});
Duration get duration => endDate.difference(startDate);
}
// 任务依赖关系模型
class GanttDependency {
final String sourceId;
final String targetId;
GanttDependency({
required this.sourceId,
required this.targetId,
});
}
2. 甘特图组件实现
甘特图组件使用StatefulWidget实现,因为它需要管理任务的选中状态。
// 甘特图组件
class GanttChartComponent extends StatefulWidget {
const GanttChartComponent({super.key});
State<GanttChartComponent> createState() => _GanttChartComponentState();
}
class _GanttChartComponentState extends State<GanttChartComponent> {
// 示例数据
final List<GanttTask> _tasks = [
GanttTask(
id: '1',
name: '需求分析',
startDate: DateTime(2024, 1, 1),
endDate: DateTime(2024, 1, 5),
color: Colors.blue,
),
// 其他任务...
];
// 任务依赖关系
final List<GanttDependency> _dependencies = [
GanttDependency(sourceId: '1', targetId: '2'),
// 其他依赖关系...
];
// 布局参数
final double _taskHeight = 40;
final double _taskPadding = 8;
final double _chartWidth = 600;
final double _chartHeight = 300;
final double _taskNameWidth = 120;
final double _timeAxisHeight = 60;
// 选中状态
GanttTask? _selectedTask;
// 计算时间范围
DateTime get _minDate {
return _tasks.map((task) => task.startDate).reduce((a, b) => a.isBefore(b) ? a : b);
}
DateTime get _maxDate {
return _tasks.map((task) => task.endDate).reduce((a, b) => a.isAfter(b) ? a : b);
}
// 处理任务点击
void _selectTask(GanttTask task) {
setState(() {
if (_selectedTask == task) {
_selectedTask = null;
task.isSelected = false;
} else {
if (_selectedTask != null) {
_selectedTask!.isSelected = false;
}
_selectedTask = task;
task.isSelected = true;
}
});
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.white,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(16),
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: Colors.grey.withAlpha(51),
spreadRadius: 2,
blurRadius: 5,
offset: const Offset(0, 2),
),
],
),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.stretch,
children: [
// 标题
const Text(
'甘特图',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.deepPurple,
),
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
// 说明文字
Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.deepPurple.withAlpha(20),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(8),
),
child: const Text(
'甘特图用于可视化项目时间安排和任务依赖关系,展示任务的开始时间、结束时间和持续时间。点击任务条可查看详细信息。',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.deepPurple,
),
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 24),
// 甘特图
Center(
child: Container(
width: _chartWidth + _taskNameWidth + 40,
height: _chartHeight + _timeAxisHeight + 40,
child: SingleChildScrollView(
scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal,
child: Container(
width: _chartWidth + _taskNameWidth + 40,
child: CustomPaint(
painter: GanttChartPainter(
tasks: _tasks,
dependencies: _dependencies,
minDate: _minDate,
maxDate: _maxDate,
taskHeight: _taskHeight,
taskPadding: _taskPadding,
chartWidth: _chartWidth,
taskNameWidth: _taskNameWidth,
timeAxisHeight: _timeAxisHeight,
onTaskTap: _selectTask,
),
),
),
),
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 24),
// 选中信息
if (_selectedTask != null)
Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: _selectedTask!.color.withAlpha(30),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(8),
border: Border.all(
color: _selectedTask!.color,
width: 2,
),
),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
const Text(
'任务信息',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
Text('任务名称: ${_selectedTask!.name}'),
Text('开始时间: ${_selectedTask!.startDate.toString().split(' ')[0]}'),
Text('结束时间: ${_selectedTask!.endDate.toString().split(' ')[0]}'),
Text('持续时间: ${_selectedTask!.duration.inDays} 天'),
],
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
// 操作按钮
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
setState(() {
if (_selectedTask != null) {
_selectedTask!.isSelected = false;
_selectedTask = null;
}
for (final task in _tasks) {
task.isSelected = false;
}
});
},
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
backgroundColor: Colors.deepPurple,
),
child: const Text('重置选中'),
),
],
),
],
),
);
}
}
3. 甘特图画布绘制器
甘特图的可视化部分使用CustomPaint和CustomPainter实现,我们需要创建一个GanttChartPainter类来处理绘制逻辑。
// 甘特图画布绘制器
class GanttChartPainter extends CustomPainter {
final List<GanttTask> tasks;
final List<GanttDependency> dependencies;
final DateTime minDate;
final DateTime maxDate;
final double taskHeight;
final double taskPadding;
final double chartWidth;
final double taskNameWidth;
final double timeAxisHeight;
final Function(GanttTask) onTaskTap;
// 记录上次点击的任务,防止重复触发
GanttTask? _lastTappedTask;
GanttChartPainter({
required this.tasks,
required this.dependencies,
required this.minDate,
required this.maxDate,
required this.taskHeight,
required this.taskPadding,
required this.chartWidth,
required this.taskNameWidth,
required this.timeAxisHeight,
required this.onTaskTap,
});
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
// 绘制时间轴
_drawTimeAxis(canvas, size);
// 绘制任务名称和任务条
_drawTasks(canvas, size);
// 绘制依赖关系
_drawDependencies(canvas, size);
}
// 绘制时间轴
void _drawTimeAxis(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
final paint = Paint()
..color = Colors.grey
..strokeWidth = 1;
// 绘制时间轴背景
canvas.drawRect(
Rect.fromLTWH(taskNameWidth, 0, chartWidth, timeAxisHeight),
Paint()..color = Colors.grey.withAlpha(20),
);
// 绘制时间轴刻度和标签
final totalDays = maxDate.difference(minDate).inDays;
const interval = 5; // 每5天一个刻度
for (int i = 0; i <= totalDays; i += interval) {
final x = taskNameWidth + (i / totalDays) * chartWidth;
final date = minDate.add(Duration(days: i));
// 绘制刻度线
canvas.drawLine(
Offset(x, timeAxisHeight - 10),
Offset(x, timeAxisHeight),
paint,
);
// 绘制日期标签
final textPainter = TextPainter(
text: TextSpan(
text: '${date.month}/${date.day}',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 10,
color: Colors.grey[600],
),
),
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
)..layout();
textPainter.paint(
canvas,
Offset(x - textPainter.width / 2, timeAxisHeight - 30),
);
}
// 绘制时间轴底部边框
canvas.drawLine(
Offset(taskNameWidth, timeAxisHeight),
Offset(taskNameWidth + chartWidth, timeAxisHeight),
Paint()..color = Colors.grey..strokeWidth = 2,
);
}
// 绘制任务名称和任务条
void _drawTasks(canvas, size) {
for (int i = 0; i < tasks.length; i++) {
final task = tasks[i];
final y = timeAxisHeight + i * (taskHeight + taskPadding) + taskPadding;
// 绘制任务名称
final textPainter = TextPainter(
text: TextSpan(
text: task.name,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.black,
fontWeight: task.isSelected ? FontWeight.bold : FontWeight.normal,
),
),
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
maxLines: 1,
ellipsis: '...',
)..layout(maxWidth: taskNameWidth - 16);
textPainter.paint(
canvas,
Offset(8, y + (taskHeight - textPainter.height) / 2),
);
// 计算任务条位置和宽度
final totalDays = maxDate.difference(minDate).inDays;
final taskStartDays = task.startDate.difference(minDate).inDays;
final taskDurationDays = task.duration.inDays;
final x = taskNameWidth + (taskStartDays / totalDays) * chartWidth;
final width = (taskDurationDays / totalDays) * chartWidth;
// 绘制任务条
final taskPaint = Paint()
..color = task.isSelected ? task.color.withAlpha(200) : task.color.withAlpha(150);
final taskRect = Rect.fromLTWH(x, y, width, taskHeight);
canvas.drawRRect(
RRect.fromRectAndRadius(taskRect, Radius.circular(4)),
taskPaint,
);
// 绘制任务条边框
if (task.isSelected) {
canvas.drawRRect(
RRect.fromRectAndRadius(taskRect, Radius.circular(4)),
Paint()
..color = Colors.black
..strokeWidth = 2
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke,
);
}
}
}
// 绘制依赖关系
void _drawDependencies(canvas, size) {
final paint = Paint()
..color = Colors.grey[400]!
..strokeWidth = 2
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeCap = StrokeCap.round;
for (final dependency in dependencies) {
final sourceTask = tasks.firstWhere(
(task) => task.id == dependency.sourceId,
orElse: () => tasks[0],
);
final targetTask = tasks.firstWhere(
(task) => task.id == dependency.targetId,
orElse: () => tasks[0],
);
final sourceIndex = tasks.indexOf(sourceTask);
final targetIndex = tasks.indexOf(targetTask);
if (sourceIndex != -1 && targetIndex != -1) {
final totalDays = maxDate.difference(minDate).inDays;
final sourceEndX = taskNameWidth +
((sourceTask.endDate.difference(minDate).inDays) / totalDays) * chartWidth;
final targetStartX = taskNameWidth +
((targetTask.startDate.difference(minDate).inDays) / totalDays) * chartWidth;
final sourceY = timeAxisHeight +
sourceIndex * (taskHeight + taskPadding) +
taskPadding +
taskHeight / 2;
final targetY = timeAxisHeight +
targetIndex * (taskHeight + taskPadding) +
taskPadding +
taskHeight / 2;
// 绘制连接线
final path = Path();
path.moveTo(sourceEndX, sourceY);
path.lineTo(sourceEndX + 10, sourceY);
path.lineTo(sourceEndX + 10, (sourceY + targetY) / 2);
path.lineTo(targetStartX - 10, (sourceY + targetY) / 2);
path.lineTo(targetStartX - 10, targetY);
path.lineTo(targetStartX, targetY);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
// 绘制箭头
final arrowPath = Path();
arrowPath.moveTo(targetStartX, targetY);
arrowPath.lineTo(targetStartX - 6, targetY - 3);
arrowPath.lineTo(targetStartX - 6, targetY + 3);
arrowPath.close();
canvas.drawPath(arrowPath, Paint()..color = Colors.grey[400]!);
}
}
}
bool shouldRepaint(covariant CustomPainter oldDelegate) {
// 只有当旧绘制器的数据与当前不同时才重绘
if (oldDelegate is GanttChartPainter) {
// 检查任务列表是否相同
if (oldDelegate.tasks.length != tasks.length) return true;
// 检查任务是否有变化
for (int i = 0; i < tasks.length; i++) {
if (oldDelegate.tasks[i].isSelected != tasks[i].isSelected) {
return true;
}
}
// 其他数据检查...
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool hitTest(Offset position) {
// 检查是否点击了任务条
for (int i = 0; i < tasks.length; i++) {
final task = tasks[i];
final y = timeAxisHeight + i * (taskHeight + taskPadding) + taskPadding;
final totalDays = maxDate.difference(minDate).inDays;
final taskStartDays = task.startDate.difference(minDate).inDays;
final taskDurationDays = task.duration.inDays;
final x = taskNameWidth + (taskStartDays / totalDays) * chartWidth;
final width = (taskDurationDays / totalDays) * chartWidth;
final taskRect = Rect.fromLTWH(x, y, width, taskHeight);
if (taskRect.contains(position)) {
// 只有当点击的任务与上次不同时才触发回调
if (_lastTappedTask != task) {
_lastTappedTask = task;
onTaskTap(task);
}
return true;
}
}
// 如果没有点击任务条,重置上次点击的任务
_lastTappedTask = null;
return false;
}
}
4. 主页面集成
在主页面中,我们需要导入并使用甘特图组件。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'components/gantt_chart.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter for openHarmony',
theme: ThemeData(
colorScheme: ColorScheme.fromSeed(seedColor: Colors.deepPurple),
useMaterial3: true,
),
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
home: const MyHomePage(title: 'Flutter for openHarmony'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
final String title;
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战'),
),
body: SingleChildScrollView(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
child: Column(
children: [
const SizedBox(height: 20),
const Text(
'甘特图演示',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 20),
const GanttChartComponent(),
const SizedBox(height: 40),
],
),
),
);
}
}
本次开发中容易遇到的问题
1. 点击焦点闪烁问题
问题描述
在开发甘特图组件时,点击任务条会出现焦点闪烁的现象,影响用户体验。
原因分析
- 点击事件被重复触发,导致任务的选中状态在选中和未选中之间快速切换。
- 每次点击都会触发组件的重绘,即使数据没有变化。
解决方案
- 在
GanttChartPainter类中添加_lastTappedTask变量,记录上次点击的任务,防止重复触发点击事件。 - 优化
shouldRepaint方法,只有当任务的选中状态发生变化时才重绘组件,减少不必要的重绘。
2. 任务依赖关系绘制问题
问题描述
任务依赖关系的连接线绘制不正确,特别是当任务之间的时间间隔较大时。
原因分析
- 依赖关系的计算逻辑没有考虑到任务的实际时间范围。
- 连接线的路径绘制不够平滑,影响视觉效果。
解决方案
- 正确计算任务的开始和结束位置,确保连接线能够准确连接两个任务。
- 使用
Path类绘制平滑的连接线,并添加箭头指示依赖方向。
3. 时间轴刻度计算问题
问题描述
时间轴的刻度计算不正确,导致任务条的位置和宽度与实际时间不符。
原因分析
- 时间轴的总宽度计算错误,没有考虑到任务的实际时间范围。
- 刻度间隔设置不合理,导致时间标签显示不清晰。
解决方案
- 正确计算任务的时间范围,确保时间轴能够覆盖所有任务的开始和结束时间。
- 设置合理的刻度间隔,确保时间标签显示清晰易读。
4. 组件性能优化问题
问题描述
当任务数量较多时,甘特图组件的性能会下降,特别是在滚动和点击操作时。
原因分析
- 每次操作都会触发整个组件的重绘,即使只有部分内容需要更新。
- 绘制逻辑不够高效,没有利用缓存机制。
解决方案
- 优化
shouldRepaint方法,只有当数据发生变化时才重绘组件。 - 考虑使用
RepaintBoundary包裹组件,减少不必要的重绘。 - 对于大量任务的场景,可以考虑使用虚拟化技术,只绘制可见区域的任务。
总结本次开发中用到的技术点
1. Flutter核心技术
1.1 自定义组件开发
- 使用
StatefulWidget和StatelessWidget构建组件 - 利用
CustomPaint和CustomPainter实现自定义绘制 - 掌握组件的生命周期管理和状态管理
1.2 布局与滚动
- 使用
SingleChildScrollView实现横向滚动 - 利用
Container、Column、Row等布局组件构建界面 - 掌握
BoxDecoration实现组件的样式美化
1.3 手势与交互
- 实现
hitTest方法处理点击事件 - 利用
setState更新组件状态 - 掌握手势检测和事件处理机制
2. 图形绘制技术
2.1 Canvas绘制
- 使用
Canvas绘制任务条、时间轴和依赖关系 - 掌握
Paint、Path、Rect等绘制类的使用 - 实现文本绘制和样式设置
2.2 坐标计算
- 实现时间到坐标的转换
- 计算任务条的位置和宽度
- 处理依赖关系的连接线坐标
3. 数据模型设计
3.1 任务模型
- 设计
GanttTask类表示任务 - 实现任务的开始时间、结束时间和持续时间计算
- 管理任务的选中状态
3.2 依赖关系模型
- 设计
GanttDependency类表示任务依赖关系 - 实现依赖关系的可视化绘制
4. 性能优化技术
4.1 重绘优化
- 优化
shouldRepaint方法,减少不必要的重绘 - 实现点击事件的防重复触发机制
4.2 计算优化
- 缓存时间范围计算结果
- 优化绘制逻辑,提高绘制效率
5. 鸿蒙平台适配
5.1 项目结构适配
- 了解Flutter项目集成鸿蒙支持后的目录结构
- 掌握鸿蒙原生层的配置和开发
5.2 平台特性适配
- 确保组件在鸿蒙平台上的显示效果与Flutter一致
- 处理平台特有的手势和交互差异
6. 开发工具与实践
6.1 代码组织
- 采用模块化的代码组织方式
- 将组件抽离为独立的文件,提高代码复用性
6.2 调试技巧
- 利用Flutter的热重载功能快速调试
- 使用
print语句和调试工具定位问题
6.3 最佳实践
- 遵循Flutter的代码风格和最佳实践
- 编写清晰、可维护的代码
- 提供详细的注释和文档
通过本次开发,我们成功实现了一个功能完整、交互友好的甘特图组件,并且掌握了一系列Flutter开发和鸿蒙平台适配的技术点。这些技术点不仅适用于甘特图组件的开发,也可以应用于其他类似的可视化组件开发中。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区: https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献8条内容
已为社区贡献8条内容







所有评论(0)