Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:扫雷游戏完整开发指南
扫雷(Minesweeper)是经典的单人益智游戏,考验玩家的逻辑推理和运气。本文将详细介绍如何使用Flutter for OpenHarmony框架开发一款功能完整的扫雷游戏。文章涵盖了地雷生成算法、洪水填充算法、游戏状态管理、难度设计等核心技术点。通过本文学习,读者将掌握Flutter在鸿蒙平台上开发网格类游戏的完整流程,了解递归算法在游戏开发中的应用。目标:找出所有非地雷格子规则点击格子揭开
·
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:扫雷游戏完整开发指南
摘要
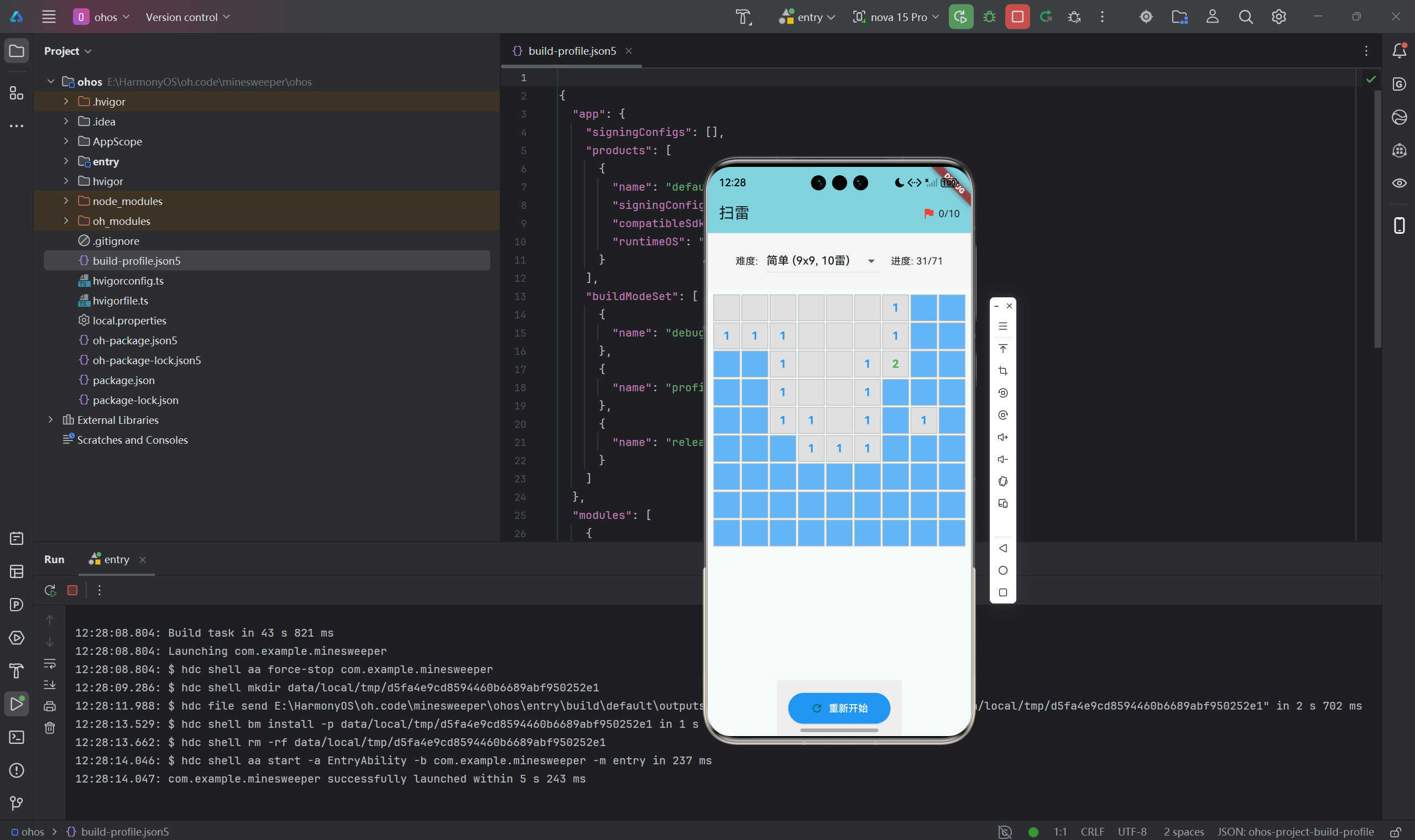
扫雷(Minesweeper)是经典的单人益智游戏,考验玩家的逻辑推理和运气。本文将详细介绍如何使用Flutter for OpenHarmony框架开发一款功能完整的扫雷游戏。文章涵盖了地雷生成算法、洪水填充算法、游戏状态管理、难度设计等核心技术点。通过本文学习,读者将掌握Flutter在鸿蒙平台上开发网格类游戏的完整流程,了解递归算法在游戏开发中的应用。
一、项目背景与功能概述
1.1 扫雷游戏介绍
扫雷是由微软在1990年代推广的经典游戏:
- 目标:找出所有非地雷格子
- 规则:
- 点击格子揭开
- 数字表示周围8格的地雷数
- 长按标记地雷
- 点到地雷则失败
1.2 应用功能规划
| 功能模块 | 具体功能 |
|---|---|
| 难度选择 | 简单(9x9)、中等(16x16)、困难(16x30) |
| 地雷生成 | 随机分布地雷 |
| 数字显示 | 显示相邻地雷数量 |
| 洪水填充 | 自动揭开空白区域 |
| 标记功能 | 长按标记/取消标记 |
| 胜负判断 | 踩雷失败、排完胜利 |
| 进度显示 | 剩余安全格子数 |
1.3 难度设置
| 难度 | 网格大小 | 地雷数 | 地雷密度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 简单 | 9×9 | 10 | 12.3% |
| 中等 | 16×16 | 40 | 15.6% |
| 困难 | 16×30 | 99 | 20.6% |
二、数据模型设计
2.1 单元格状态
enum CellState {
hidden, // 未揭开
revealed, // 已揭开
flagged, // 已标记
}
2.2 单元格类
class Cell {
final int x; // x坐标
final int y; // y坐标
final bool isMine; // 是否是地雷
final int adjacentMines; // 相邻地雷数
CellState state; // 格子状态
Cell({
required this.x,
required this.y,
required this.isMine,
required this.adjacentMines,
this.state = CellState.hidden,
});
// 复制格子
Cell copyWith({CellState? state}) {
return Cell(
x: x,
y: y,
isMine: isMine,
adjacentMines: adjacentMines,
state: state ?? this.state,
);
}
}
2.3 游戏配置
enum Difficulty {
easy, // 9x9, 10雷
medium, // 16x16, 40雷
hard, // 16x30, 99雷
}
class GameConfig {
final int rows;
final int cols;
final int totalMines;
GameConfig({required this.rows, required this.cols, required this.totalMines});
factory GameConfig.fromDifficulty(Difficulty difficulty) {
switch (difficulty) {
case Difficulty.easy:
return GameConfig(rows: 9, cols: 9, totalMines: 10);
case Difficulty.medium:
return GameConfig(rows: 16, cols: 16, totalMines: 40);
case Difficulty.hard:
return GameConfig(rows: 16, cols: 30, totalMines: 99);
}
}
int get totalCells => rows * cols;
int get safeCells => totalCells - totalMines;
double get mineDensity => totalMines / totalCells;
}
三、地雷生成算法
3.1 随机放置算法
void _placeMines() {
int placed = 0;
while (placed < _totalMines) {
final x = _random.nextInt(_cols);
final y = _random.nextInt(_rows);
if (!_grid[y][x].isMine) {
_grid[y][x] = Cell(
x: x,
y: y,
isMine: true,
adjacentMines: _grid[y][x].adjacentMines,
);
placed++;
}
}
}
3.2 避免首次踩雷
改进算法,确保第一次点击不会踩雷:
Point? _firstClick;
void _revealCell(int x, int y) {
// 如果是第一次点击,先放置地雷
if (_firstClick == null) {
_firstClick = Point(x, y);
_placeMinesAvoiding(x, y);
_calculateAdjacentMines();
}
// 正常揭开逻辑...
}
void _placeMinesAvoiding(int safeX, int safeY) {
int placed = 0;
while (placed < _totalMines) {
final x = _random.nextInt(_cols);
final y = _random.nextInt(_rows);
// 跳过首次点击位置及其周围8格
if ((x - safeX).abs() <= 1 && (y - safeY).abs() <= 1) {
continue;
}
if (!_grid[y][x].isMine) {
_grid[y][x] = Cell(
x: x,
y: y,
isMine: true,
adjacentMines: _grid[y][x].adjacentMines,
);
placed++;
}
}
}
3.3 保证可解性
更高级的地雷生成算法,确保有解:
void _placeMinesGuaranteedSolvable() {
// 1. 先放置地雷
_placeMines();
// 2. 计算每个格子的"安全度"
final safeZones = _findSafeZones();
// 3. 如果没有足够的起始安全区,重新生成
if (safeZones.length < 3) {
_initGame();
return;
}
}
List<Point> _findSafeZones() {
final safe = <Point>[];
for (int y = 0; y < _rows; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < _cols; x++) {
if (!_grid[y][x].isMine && _grid[y][x].adjacentMines == 0) {
safe.add(Point(x, y));
}
}
}
return safe;
}
四、相邻地雷计算
4.1 8方向检查
void _calculateAdjacentMines() {
for (int y = 0; y < _rows; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < _cols; x++) {
if (_grid[y][x].isMine) continue;
int count = 0;
// 检查8个方向
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
final nx = x + dx;
final ny = y + dy;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < _cols && ny >= 0 && ny < _rows) {
if (_grid[ny][nx].isMine) {
count++;
}
}
}
}
_grid[y][x] = Cell(
x: x,
y: y,
isMine: false,
adjacentMines: count,
state: _grid[y][x].state,
);
}
}
}
4.2 方向数组优化
// 8个方向的偏移量
static const List<List<int>> _directions = [
[-1, -1], [-1, 0], [-1, 1],
[0, -1], [0, 1],
[1, -1], [1, 0], [1, 1],
];
int _countAdjacentMines(int x, int y) {
int count = 0;
for (final dir in _directions) {
final nx = x + dir[0];
final ny = y + dir[1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < _cols && ny >= 0 && ny < _rows) {
if (_grid[ny][nx].isMine) {
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
五、洪水填充算法
5.1 递归实现
void _revealCell(int x, int y) {
// 边界检查
if (x < 0 || x >= _cols || y < 0 || y >= _rows) return;
final cell = _grid[y][x];
// 只处理未揭开的格子
if (cell.state != CellState.hidden) return;
// 踩到地雷
if (cell.isMine) {
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.revealed);
_gameOver = true;
_revealAllMines();
return;
}
// 揭开当前格子
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.revealed);
_revealedCount++;
// 如果是空白格子,递归揭开周围
if (cell.adjacentMines == 0) {
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
_revealCell(x + dx, y + dy);
}
}
}
}
5.2 迭代实现(避免栈溢出)
void _revealCellIterative(int startX, int startY) {
final queue = <Point>[];
final visited = <Point>{};
queue.add(Point(startX, startY));
while (queue.isNotEmpty) {
final point = queue.removeAt(0);
if (visited.contains(point)) continue;
visited.add(point);
final x = point.x;
final y = point.y;
// 边界检查
if (x < 0 || x >= _cols || y < 0 || y >= _rows) continue;
final cell = _grid[y][x];
// 只处理未揭开的格子
if (cell.state != CellState.hidden) continue;
// 踩到地雷
if (cell.isMine) {
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.revealed);
_gameOver = true;
_revealAllMines();
return;
}
// 揭开当前格子
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.revealed);
_revealedCount++;
// 如果是空白格子,将周围格子加入队列
if (cell.adjacentMines == 0) {
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
final neighbor = Point(x + dx, y + dy);
if (!visited.contains(neighbor)) {
queue.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
}
}
5.3 洪水填充可视化
// 延迟显示揭开动画
Future<void> _revealCellAnimated(int x, int y) async {
final toReveal = <Point>[];
final visited = <Point>{};
_collectCellsToReveal(x, y, toReveal, visited);
// 按距离分层揭开
final layers = <List<Point>>[];
while (toReveal.isNotEmpty) {
layers.add([...toReveal]);
toReveal.clear();
}
for (final layer in layers) {
for (final point in layer) {
if (!_grid[point.y][point.x].isMine) {
_grid[point.y][point.x] = _grid[point.y][point.x].copyWith(
state: CellState.revealed,
);
_revealedCount++;
}
}
setState(() {});
await Future.delayed(const Duration(milliseconds: 50));
}
}
六、UI界面实现
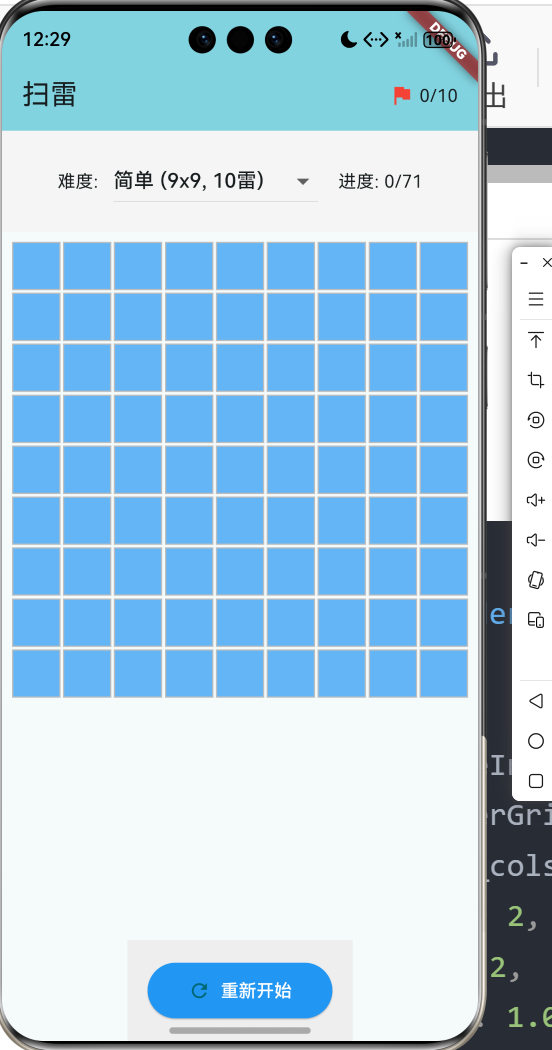
6.1 网格构建

Widget _buildGrid() {
return GridView.builder(
shrinkWrap: true,
primary: true,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
gridDelegate: SliverGridDelegateWithFixedCrossAxisCount(
crossAxisCount: _cols,
crossAxisSpacing: 2,
mainAxisSpacing: 2,
childAspectRatio: 1.0,
),
itemCount: _rows * _cols,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final x = index % _cols;
final y = index ~/ _cols;
return _buildCell(x, y);
},
);
}
6.2 单元格UI

Widget _buildCell(int x, int y) {
final cell = _grid[y][x];
Color backgroundColor;
Color textColor;
String text;
switch (cell.state) {
case CellState.hidden:
backgroundColor = Colors.blue.shade300;
textColor = Colors.transparent;
text = '';
break;
case CellState.flagged:
backgroundColor = Colors.blue.shade300;
textColor = Colors.red;
text = '🚩';
break;
case CellState.revealed:
if (cell.isMine) {
backgroundColor = Colors.red;
textColor = Colors.white;
text = '💣';
} else if (cell.adjacentMines == 0) {
backgroundColor = Colors.grey.shade300;
textColor = Colors.transparent;
text = '';
} else {
backgroundColor = Colors.grey.shade300;
textColor = _getNumberColor(cell.adjacentMines);
text = '${cell.adjacentMines}';
}
break;
}
return GestureDetector(
onTap: () => _onCellTap(x, y),
onLongPress: () => _onCellLongPress(x, y),
child: Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: backgroundColor,
border: Border.all(color: Colors.grey.shade400),
),
child: Center(
child: Text(
text,
style: TextStyle(
color: textColor,
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
),
),
);
}
6.3 数字颜色映射
Color _getNumberColor(int number) {
final colors = [
Colors.blue, // 1
Colors.green, // 2
Colors.red, // 3
Colors.purple, // 4
Colors.brown, // 5
Colors.cyan, // 6
Colors.black, // 7
Colors.grey, // 8
];
return colors[(number - 1) % colors.length];
}
七、游戏逻辑实现
7.1 点击处理
void _onCellTap(int x, int y) {
if (_gameOver || _gameWon) return;
if (_grid[y][x].state != CellState.hidden) return;
_revealCell(x, y);
setState(() {});
_checkGameState();
}
7.2 长按标记
void _onCellLongPress(int x, int y) {
if (_gameOver || _gameWon) return;
if (_grid[y][x].state != CellState.hidden) return;
setState(() {
final cell = _grid[y][x];
if (cell.state == CellState.hidden) {
// 添加标记
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.flagged);
_flagCount++;
} else if (cell.state == CellState.flagged) {
// 取消标记
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.hidden);
_flagCount--;
}
});
}
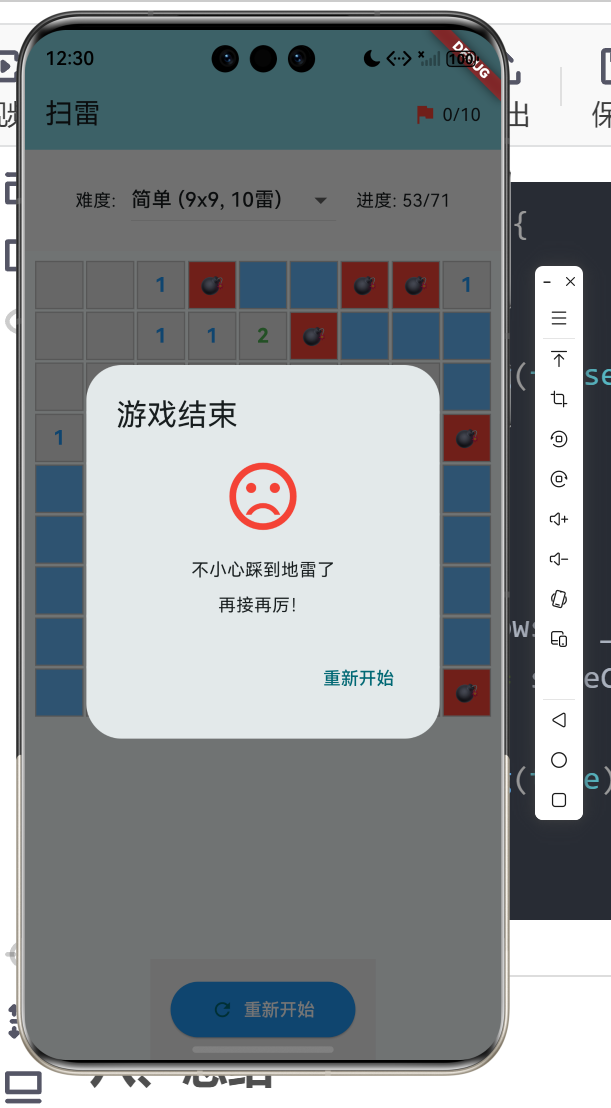
7.3 胜负判断
void _checkGameState() {
// 失败判断
if (_gameOver) {
_showGameOverDialog(false);
return;
}
// 胜利判断
final safeCells = _rows * _cols - _totalMines;
if (_revealedCount == safeCells) {
_gameWon = true;
_showGameOverDialog(true);
}
}
八、总结
本文详细介绍了使用Flutter for OpenHarmony开发扫雷游戏的完整过程,涵盖了以下核心技术点:
- 数据模型:单元格状态、游戏配置
- 地雷生成:随机算法、避免首次踩雷
- 相邻计算:8方向检查、数字显示
- 洪水填充:递归实现、迭代优化
- UI实现:网格构建、单元格渲染
- 交互设计:点击揭开、长按标记
- 胜负判断:游戏状态检测
这个项目展示了Flutter在网格类游戏开发中的完整流程。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区: 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献16条内容
已为社区贡献16条内容







所有评论(0)