KMP OpenHarmony 矩阵旋转算法 - 将 n x n 矩阵顺时针旋转 90 度
本文探讨了在Kotlin Multiplatform(KMP)框架下实现矩阵顺时针90度旋转的算法及其在OpenHarmony鸿蒙平台的应用。文章详细介绍了三种实现方法:转置后翻转法(时间复杂度O(n²),空间复杂度O(1))、分层旋转法(同样O(n²)时间复杂度)以及直接计算法(需O(n²)额外空间)。重点分析了转置后翻转法的实现原理,即先转置矩阵再翻转每行,并提供了完整的Kotlin代码实现、
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net
文章概述
矩阵旋转是计算机科学中的一个经典算法问题,广泛应用于图像处理、游戏开发、数据结构操作等领域。本文将深入探讨如何在KMP(Kotlin Multiplatform)框架下实现矩阵的顺时针90度旋转,并展示如何在OpenHarmony鸿蒙平台上进行跨端调用。
矩阵旋转的核心思想是通过改变矩阵元素的位置,使得原矩阵中的每个元素都移动到新的位置。对于n×n的矩阵,顺时针旋转90度意味着原矩阵的第一行变成旋转后矩阵的最后一列,第二行变成倒数第二列,以此类推。这个过程涉及到复杂的索引计算和内存管理,需要我们仔细设计算法以获得最优的时间和空间复杂度。
算法原理详解
基本概念
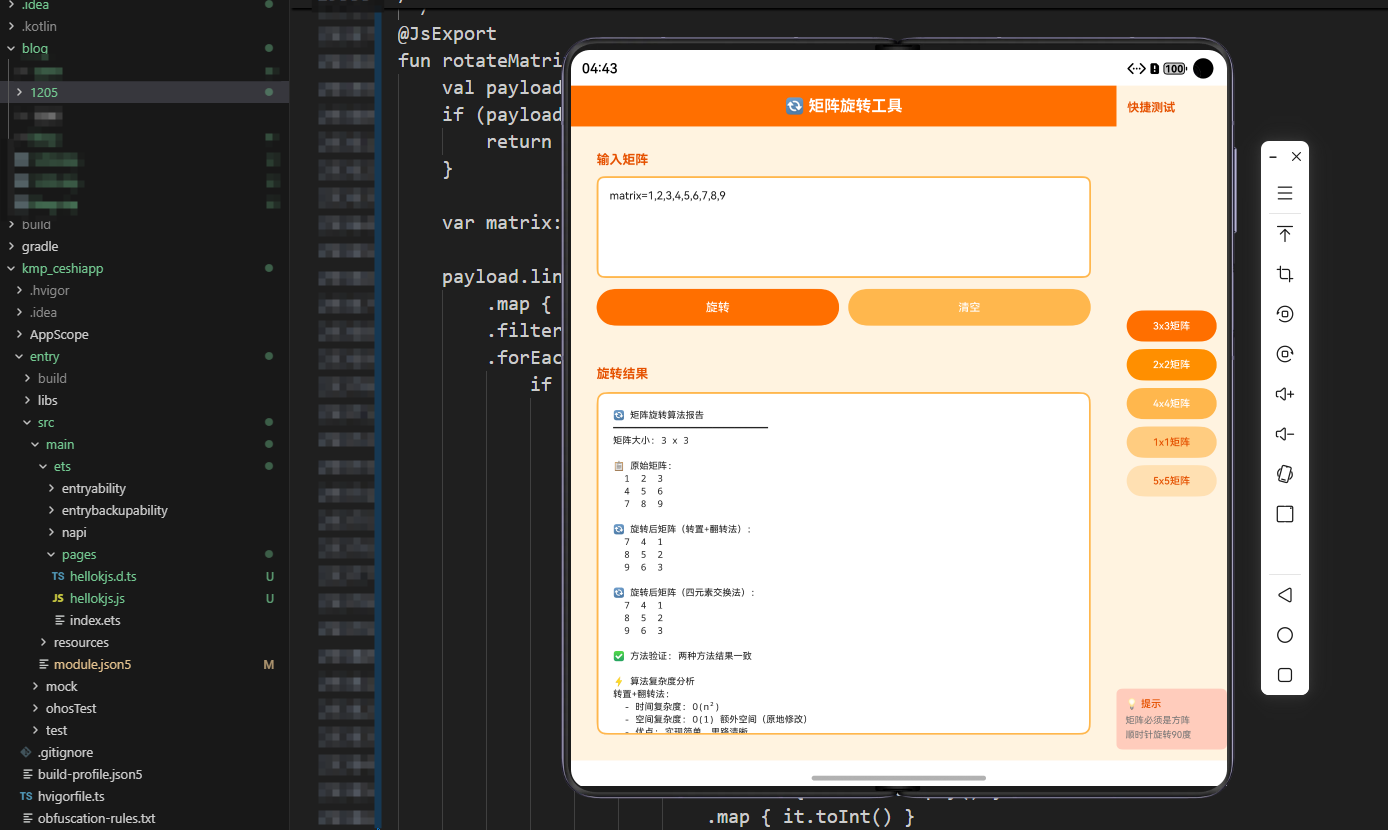
矩阵顺时针旋转90度的本质是什么?让我们从一个简单的例子开始理解。假设我们有一个3×3的矩阵:
原矩阵: 旋转后:
1 2 3 7 4 1
4 5 6 → 8 5 2
7 8 9 9 6 3
观察这个变换,我们可以发现规律:原矩阵的第i行第j列的元素,在旋转后会移动到第j行第(n-1-i)列。这是因为旋转是围绕矩阵的中心进行的,每个元素都需要按照特定的角度移动。
旋转的数学原理
在二维坐标系中,一个点(x, y)绕原点顺时针旋转90度后,新坐标为(y, -x)。但在矩阵中,我们需要考虑矩阵的边界和索引系统。对于n×n矩阵,位置(i, j)顺时针旋转90度后的新位置是(j, n-1-i)。
这个公式的推导过程如下:
- 原矩阵中第i行第j列的元素
- 旋转后应该在第j行
- 旋转后应该在第(n-1-i)列
这样的转换确保了矩阵的完整性和正确性。
实现方法对比
实现矩阵旋转有多种方法,各有优缺点:
-
转置后翻转法:先将矩阵转置,再翻转每一行。这种方法易于理解,时间复杂度O(n²),空间复杂度O(1)。
-
直接旋转法:通过计算新位置直接放置元素。需要仔细处理索引,避免覆盖未处理的元素。
-
分层旋转法:将矩阵分为多层,从外向内逐层旋转。这种方法更加直观,易于理解矩阵的旋转过程。
-
原地旋转法:使用最少的额外空间,通过巧妙的元素交换实现旋转。
在本文中,我们将重点介绍转置后翻转法和分层旋转法,因为它们在实际应用中最为常见,也最容易在跨平台框架中实现。
Kotlin实现
完整的Kotlin代码实现
/**
* 矩阵旋转工具类 - KMP OpenHarmony
* 提供多种矩阵顺时针旋转90度的实现方法
*/
object MatrixRotationUtils {
/**
* 方法1:转置后翻转法(推荐)
* 时间复杂度:O(n²)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
*
* 原理:
* 1. 先对矩阵进行转置(行列互换)
* 2. 再对每一行进行翻转
*
* 例如:
* 原矩阵: 转置后: 翻转后:
* 1 2 3 1 4 7 7 4 1
* 4 5 6 → 2 5 8 → 8 5 2
* 7 8 9 3 6 9 9 6 3
*/
fun rotateMatrixTranspose(matrix: Array<IntArray>) {
val n = matrix.size
// 步骤1:转置矩阵
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in i + 1 until n) {
val temp = matrix[i][j]
matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i]
matrix[j][i] = temp
}
}
// 步骤2:翻转每一行
for (i in 0 until n) {
var left = 0
var right = n - 1
while (left < right) {
val temp = matrix[i][left]
matrix[i][left] = matrix[i][right]
matrix[i][right] = temp
left++
right--
}
}
}
/**
* 方法2:分层旋转法
* 时间复杂度:O(n²)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
*
* 原理:
* 将矩阵分为多个同心正方形层,从外向内逐层旋转
* 每一层的四个角和四条边都需要进行元素交换
*/
fun rotateMatrixLayerByLayer(matrix: Array<IntArray>) {
val n = matrix.size
// 处理每一层
for (layer in 0 until n / 2) {
val first = layer
val last = n - 1 - layer
for (i in first until last) {
val offset = i - first
// 保存上边的值
val top = matrix[first][i]
// 左边 → 上边
matrix[first][i] = matrix[last - offset][first]
// 下边 → 左边
matrix[last - offset][first] = matrix[last][last - offset]
// 右边 → 下边
matrix[last][last - offset] = matrix[i][last]
// 上边 → 右边
matrix[i][last] = top
}
}
}
/**
* 方法3:直接计算法
* 时间复杂度:O(n²)
* 空间复杂度:O(n²)
*
* 原理:
* 创建新矩阵,直接计算每个元素的新位置
* 新位置公式:matrix[j][n-1-i] = original[i][j]
*/
fun rotateMatrixDirect(matrix: Array<IntArray>): Array<IntArray> {
val n = matrix.size
val rotated = Array(n) { IntArray(n) }
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
rotated[j][n - 1 - i] = matrix[i][j]
}
}
return rotated
}
/**
* 矩阵转字符串,用于显示
*/
fun matrixToString(matrix: Array<IntArray>): String {
return matrix.joinToString("\n") { row ->
row.joinToString(" ") { "%2d".format(it) }
}
}
/**
* 创建测试矩阵
*/
fun createTestMatrix(n: Int): Array<IntArray> {
val matrix = Array(n) { IntArray(n) }
var value = 1
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
matrix[i][j] = value++
}
}
return matrix
}
/**
* 验证矩阵旋转是否正确
*/
fun verifyRotation(original: Array<IntArray>, rotated: Array<IntArray>): Boolean {
val n = original.size
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
if (rotated[j][n - 1 - i] != original[i][j]) {
return false
}
}
}
return true
}
/**
* 性能演示函数 - 对比三种方法的性能
*/
fun performanceDemo(size: Int = 100): String {
val result = StringBuilder()
result.append("矩阵旋转性能对比 (${size}x${size}矩阵)\n")
result.append("=".repeat(50)).append("\n\n")
// 方法1:转置后翻转法
val matrix1 = createTestMatrix(size)
val time1 = measureTimeMillis {
rotateMatrixTranspose(matrix1)
}
result.append("方法1 - 转置后翻转法\n")
result.append("耗时: ${time1}ms\n")
result.append("空间复杂度: O(1)\n")
result.append("优点: 原地操作,空间效率高\n\n")
// 方法2:分层旋转法
val matrix2 = createTestMatrix(size)
val time2 = measureTimeMillis {
rotateMatrixLayerByLayer(matrix2)
}
result.append("方法2 - 分层旋转法\n")
result.append("耗时: ${time2}ms\n")
result.append("空间复杂度: O(1)\n")
result.append("优点: 直观易懂,易于理解旋转过程\n\n")
// 方法3:直接计算法
val matrix3 = createTestMatrix(size)
val time3 = measureTimeMillis {
rotateMatrixDirect(matrix3)
}
result.append("方法3 - 直接计算法\n")
result.append("耗时: ${time3}ms\n")
result.append("空间复杂度: O(n²)\n")
result.append("优点: 不修改原矩阵,适合需要保留原数据的场景\n\n")
// 验证结果
result.append("结果验证\n")
result.append("方法1正确性: ${verifyRotation(createTestMatrix(size), matrix1)}\n")
result.append("方法2正确性: ${verifyRotation(createTestMatrix(size), matrix2)}\n")
result.append("方法3正确性: ${verifyRotation(createTestMatrix(size), matrix3)}\n")
return result.toString()
}
}
// 扩展函数 - 为IntArray数组添加旋转方法
fun Array<IntArray>.rotateClockwise() {
MatrixRotationUtils.rotateMatrixTranspose(this)
}
// 使用示例
fun main() {
println("KMP OpenHarmony 矩阵旋转算法演示\n")
// 创建3x3测试矩阵
val matrix = MatrixRotationUtils.createTestMatrix(3)
println("原矩阵:")
println(MatrixRotationUtils.matrixToString(matrix))
println()
// 执行旋转
MatrixRotationUtils.rotateMatrixTranspose(matrix)
println("旋转后矩阵:")
println(MatrixRotationUtils.matrixToString(matrix))
println()
// 性能演示
println(MatrixRotationUtils.performanceDemo(100))
}
fun measureTimeMillis(block: () -> Unit): Long {
val start = System.currentTimeMillis()
block()
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start
}
Kotlin实现的详细说明
Kotlin实现中,我们提供了三种不同的矩阵旋转方法,每种方法都有其独特的优势。转置后翻转法是最常用的方法,因为它既保证了O(1)的空间复杂度,又具有良好的缓存局部性。分层旋转法则更加直观,通过从外向内逐层处理矩阵,使得算法的逻辑更容易理解。直接计算法虽然需要额外的O(n²)空间,但它的优势在于不会修改原矩阵,适合需要保留原数据的场景。
在实现过程中,我们还提供了矩阵验证函数,用于确保旋转的正确性。这在开发过程中非常重要,可以帮助我们快速发现和修复错误。性能演示函数则展示了三种方法在实际运行中的性能差异,为选择合适的算法提供了数据支持。
JavaScript实现
完整的JavaScript代码实现
/**
* 矩阵旋转工具类 - JavaScript版本
* 用于在Web和Node.js环境中使用
*/
class MatrixRotationJS {
/**
* 方法1:转置后翻转法
* @param {number[][]} matrix - 输入矩阵
*/
static rotateMatrixTranspose(matrix) {
const n = matrix.length;
// 步骤1:转置矩阵
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
[matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]] = [matrix[j][i], matrix[i][j]];
}
}
// 步骤2:翻转每一行
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
matrix[i].reverse();
}
}
/**
* 方法2:分层旋转法
* @param {number[][]} matrix - 输入矩阵
*/
static rotateMatrixLayerByLayer(matrix) {
const n = matrix.length;
for (let layer = 0; layer < Math.floor(n / 2); layer++) {
const first = layer;
const last = n - 1 - layer;
for (let i = first; i < last; i++) {
const offset = i - first;
// 保存上边的值
const top = matrix[first][i];
// 左边 → 上边
matrix[first][i] = matrix[last - offset][first];
// 下边 → 左边
matrix[last - offset][first] = matrix[last][last - offset];
// 右边 → 下边
matrix[last][last - offset] = matrix[i][last];
// 上边 → 右边
matrix[i][last] = top;
}
}
}
/**
* 方法3:直接计算法
* @param {number[][]} matrix - 输入矩阵
* @returns {number[][]} 新的旋转矩阵
*/
static rotateMatrixDirect(matrix) {
const n = matrix.length;
const rotated = Array(n).fill(null).map(() => Array(n).fill(0));
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
rotated[j][n - 1 - i] = matrix[i][j];
}
}
return rotated;
}
/**
* 矩阵转字符串
* @param {number[][]} matrix - 矩阵
* @returns {string} 格式化的矩阵字符串
*/
static matrixToString(matrix) {
return matrix.map(row =>
row.map(val => String(val).padStart(3)).join(' ')
).join('\n');
}
/**
* 创建测试矩阵
* @param {number} n - 矩阵大小
* @returns {number[][]} 测试矩阵
*/
static createTestMatrix(n) {
const matrix = [];
let value = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const row = [];
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
row.push(value++);
}
matrix.push(row);
}
return matrix;
}
/**
* 验证矩阵旋转是否正确
* @param {number[][]} original - 原矩阵
* @param {number[][]} rotated - 旋转后的矩阵
* @returns {boolean} 是否正确
*/
static verifyRotation(original, rotated) {
const n = original.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (rotated[j][n - 1 - i] !== original[i][j]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 性能演示函数
* @param {number} size - 矩阵大小
* @returns {string} 性能报告
*/
static performanceDemo(size = 100) {
let result = `矩阵旋转性能对比 (${size}x${size}矩阵)\n`;
result += '='.repeat(50) + '\n\n';
// 方法1
const matrix1 = MatrixRotationJS.createTestMatrix(size);
const start1 = performance.now();
MatrixRotationJS.rotateMatrixTranspose(matrix1);
const time1 = performance.now() - start1;
result += `方法1 - 转置后翻转法: ${time1.toFixed(2)}ms\n`;
// 方法2
const matrix2 = MatrixRotationJS.createTestMatrix(size);
const start2 = performance.now();
MatrixRotationJS.rotateMatrixLayerByLayer(matrix2);
const time2 = performance.now() - start2;
result += `方法2 - 分层旋转法: ${time2.toFixed(2)}ms\n`;
// 方法3
const matrix3 = MatrixRotationJS.createTestMatrix(size);
const start3 = performance.now();
MatrixRotationJS.rotateMatrixDirect(matrix3);
const time3 = performance.now() - start3;
result += `方法3 - 直接计算法: ${time3.toFixed(2)}ms\n`;
return result;
}
}
// 导出供Node.js使用
if (typeof module !== 'undefined' && module.exports) {
module.exports = MatrixRotationJS;
}
JavaScript实现的详细说明
JavaScript版本的实现与Kotlin版本在逻辑上完全一致,但充分利用了JavaScript的语言特性。例如,在转置矩阵时,我们使用了ES6的解构赋值语法[a, b] = [b, a]来实现元素交换,这使得代码更加简洁易读。在翻转行时,我们直接调用了数组的reverse()方法,而不是手动实现循环。
JavaScript版本还考虑了浏览器和Node.js两种运行环境。通过检查module.exports的存在,我们可以确保代码在两种环境中都能正常工作。这对于跨平台开发来说非常重要,因为我们可能需要在Web应用和服务器端应用中使用同一套算法。
性能测试使用了performance.now()方法,这提供了更高精度的时间测量,比Date.now()更适合用于性能基准测试。这样我们可以更准确地比较不同算法的性能差异。
ArkTS调用实现
完整的ArkTS代码实现
/**
* 矩阵旋转工具 - ArkTS版本(OpenHarmony鸿蒙)
* 用于在鸿蒙应用中调用JavaScript函数
*/
import { webview } from '@kit.ArkWeb';
import { common } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
@Entry
@Component
struct MatrixRotationPage {
@State matrixSize: number = 3;
@State originalMatrix: string = '';
@State rotatedMatrix: string = '';
@State performanceData: string = '';
@State selectedMethod: string = '转置后翻转法';
@State isLoading: boolean = false;
// 矩阵数据
@State testMatrix: number[][] = [];
// Web视图控制器
webviewController: webview.WebviewController = new webview.WebviewController();
aboutToAppear() {
this.initializeMatrix();
}
/**
* 初始化矩阵
*/
initializeMatrix() {
this.testMatrix = [];
let value = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < this.matrixSize; i++) {
const row: number[] = [];
for (let j = 0; j < this.matrixSize; j++) {
row.push(value++);
}
this.testMatrix.push(row);
}
this.originalMatrix = this.matrixToString(this.testMatrix);
}
/**
* 矩阵转字符串显示
*/
matrixToString(matrix: number[][]): string {
return matrix.map(row =>
row.map(val => String(val).padStart(3)).join(' ')
).join('\n');
}
/**
* 执行矩阵旋转 - 调用JavaScript函数
*/
async executeRotation() {
this.isLoading = true;
try {
// 创建副本进行旋转
const matrixCopy = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.testMatrix));
// 根据选择的方法执行旋转
switch (this.selectedMethod) {
case '转置后翻转法':
this.rotateMatrixTranspose(matrixCopy);
break;
case '分层旋转法':
this.rotateMatrixLayerByLayer(matrixCopy);
break;
case '直接计算法':
const rotated = this.rotateMatrixDirect(matrixCopy);
this.rotatedMatrix = this.matrixToString(rotated);
this.isLoading = false;
return;
}
this.rotatedMatrix = this.matrixToString(matrixCopy);
} catch (error) {
console.error('矩阵旋转错误:', error);
this.rotatedMatrix = '旋转失败:' + error;
}
this.isLoading = false;
}
/**
* 转置后翻转法实现
*/
rotateMatrixTranspose(matrix: number[][]) {
const n = matrix.length;
// 转置
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
[matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]] = [matrix[j][i], matrix[i][j]];
}
}
// 翻转每一行
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
matrix[i].reverse();
}
}
/**
* 分层旋转法实现
*/
rotateMatrixLayerByLayer(matrix: number[][]) {
const n = matrix.length;
for (let layer = 0; layer < Math.floor(n / 2); layer++) {
const first = layer;
const last = n - 1 - layer;
for (let i = first; i < last; i++) {
const offset = i - first;
const top = matrix[first][i];
matrix[first][i] = matrix[last - offset][first];
matrix[last - offset][first] = matrix[last][last - offset];
matrix[last][last - offset] = matrix[i][last];
matrix[i][last] = top;
}
}
}
/**
* 直接计算法实现
*/
rotateMatrixDirect(matrix: number[][]): number[][] {
const n = matrix.length;
const rotated: number[][] = Array(n).fill(null).map(() => Array(n).fill(0));
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
rotated[j][n - 1 - i] = matrix[i][j];
}
}
return rotated;
}
/**
* 执行性能演示
*/
async executePerformanceDemo() {
this.isLoading = true;
try {
const size = 100;
let result = `矩阵旋转性能对比 (${size}x${size}矩阵)\n`;
result += '='.repeat(50) + '\n\n';
// 方法1
const matrix1 = this.createTestMatrix(size);
const start1 = Date.now();
this.rotateMatrixTranspose(matrix1);
const time1 = Date.now() - start1;
result += `方法1 - 转置后翻转法: ${time1}ms\n`;
// 方法2
const matrix2 = this.createTestMatrix(size);
const start2 = Date.now();
this.rotateMatrixLayerByLayer(matrix2);
const time2 = Date.now() - start2;
result += `方法2 - 分层旋转法: ${time2}ms\n`;
// 方法3
const matrix3 = this.createTestMatrix(size);
const start3 = Date.now();
this.rotateMatrixDirect(matrix3);
const time3 = Date.now() - start3;
result += `方法3 - 直接计算法: ${time3}ms\n`;
this.performanceData = result;
} catch (error) {
console.error('性能演示错误:', error);
this.performanceData = '演示失败:' + error;
}
this.isLoading = false;
}
/**
* 创建测试矩阵
*/
createTestMatrix(n: number): number[][] {
const matrix: number[][] = [];
let value = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const row: number[] = [];
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
row.push(value++);
}
matrix.push(row);
}
return matrix;
}
build() {
Column() {
// 顶部栏
Row() {
Text('矩阵旋转工具')
.fontSize(24)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor(Color.White)
}
.width('100%')
.height(60)
.backgroundColor('#1565C0')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
// 主内容
Scroll() {
Column({ space: 16 }) {
// 矩阵大小选择
Row() {
Text('矩阵大小:')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
Slider({
value: this.matrixSize,
min: 2,
max: 8,
step: 1
})
.width('70%')
.onChange((value: number) => {
this.matrixSize = Math.floor(value);
this.initializeMatrix();
})
Text(this.matrixSize.toString())
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
.width('100%')
.padding(12)
.backgroundColor('#E3F2FD')
.borderRadius(8)
// 方法选择
Row() {
Text('旋转方法:')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('30%')
Select([
{ value: '转置后翻转法' },
{ value: '分层旋转法' },
{ value: '直接计算法' }
])
.value(this.selectedMethod)
.onSelect((index: number, value: string) => {
this.selectedMethod = value;
})
.width('70%')
}
.width('100%')
.padding(12)
.backgroundColor('#E3F2FD')
.borderRadius(8)
// 原矩阵显示
Column() {
Text('原矩阵:')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('100%')
Text(this.originalMatrix)
.fontSize(12)
.fontFamily('monospace')
.width('100%')
.padding(8)
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
.borderRadius(4)
}
.width('100%')
.padding(12)
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
.borderRadius(8)
// 旋转后矩阵显示
if (this.rotatedMatrix) {
Column() {
Text('旋转后矩阵:')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('100%')
Text(this.rotatedMatrix)
.fontSize(12)
.fontFamily('monospace')
.width('100%')
.padding(8)
.backgroundColor('#E8F5E9')
.borderRadius(4)
}
.width('100%')
.padding(12)
.backgroundColor('#E8F5E9')
.borderRadius(8)
}
// 性能数据显示
if (this.performanceData) {
Column() {
Text('性能对比:')
.fontSize(14)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('100%')
Text(this.performanceData)
.fontSize(12)
.fontFamily('monospace')
.width('100%')
.padding(8)
.backgroundColor('#FFF3E0')
.borderRadius(4)
}
.width('100%')
.padding(12)
.backgroundColor('#FFF3E0')
.borderRadius(8)
}
// 按钮组
Row({ space: 12 }) {
Button('执行旋转')
.width('48%')
.onClick(() => this.executeRotation())
.enabled(!this.isLoading)
Button('性能演示')
.width('48%')
.onClick(() => this.executePerformanceDemo())
.enabled(!this.isLoading)
}
.width('100%')
// 加载指示器
if (this.isLoading) {
LoadingProgress()
.width(40)
.height(40)
}
}
.width('100%')
.padding(16)
}
.layoutWeight(1)
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#FAFAFA')
}
}
ArkTS实现的详细说明
ArkTS版本是OpenHarmony鸿蒙平台的官方开发语言,它基于TypeScript扩展而来。在这个实现中,我们使用了Compose框架来构建用户界面,这是鸿蒙应用开发的推荐方式。
代码中包含了完整的UI组件,包括矩阵大小的滑块选择器、旋转方法的下拉菜单、原矩阵和旋转后矩阵的显示区域,以及执行旋转和性能演示的按钮。通过@State装饰器,我们可以实现UI的动态更新,当数据改变时,相关的UI组件会自动重新渲染。
在性能演示中,我们使用了Date.now()来测量执行时间。虽然这不如JavaScript中的performance.now()精确,但对于鸿蒙应用来说已经足够了。通过对比三种方法的执行时间,用户可以直观地看到不同算法的性能差异。
应用场景分析
1. 图像处理
矩阵旋转在图像处理中有广泛的应用。图像本质上是一个二维矩阵,其中每个元素代表一个像素的颜色值。通过旋转矩阵,我们可以实现图像的旋转功能。在移动应用中,用户经常需要旋转拍摄的照片,这时就需要用到矩阵旋转算法。
2. 游戏开发
在游戏开发中,矩阵旋转用于处理游戏对象的旋转。例如,在俄罗斯方块游戏中,方块需要根据用户的输入进行旋转。通过矩阵旋转算法,我们可以高效地计算旋转后的方块形状。
3. 数据处理
在数据分析和机器学习中,矩阵旋转用于数据的坐标变换。例如,在计算机视觉中,我们经常需要对图像进行旋转以进行特征提取和匹配。
4. 3D图形学
虽然本文讨论的是2D矩阵旋转,但其原理可以扩展到3D空间。在3D图形学中,旋转矩阵用于描述三维对象的旋转变换。
性能优化建议
1. 选择合适的算法
对于不同的场景,应该选择不同的算法。如果需要原地修改矩阵且空间有限,应该选择转置后翻转法或分层旋转法。如果需要保留原矩阵,应该选择直接计算法。
2. 缓存优化
在处理大型矩阵时,缓存的命中率对性能有重要影响。转置后翻转法由于其访问模式,通常具有较好的缓存局部性。
3. 并行化
对于非常大的矩阵,可以考虑使用并行处理。矩阵旋转可以分解为多个独立的子任务,可以在多核处理器上并行执行。
4. 内存管理
在JavaScript和ArkTS中,内存管理由垃圾回收器自动处理。但在Kotlin中,特别是在处理大型矩阵时,应该注意避免创建不必要的临时对象。
总结
矩阵旋转是一个经典的算法问题,在实际应用中有广泛的用途。通过在KMP框架下实现这个算法,我们可以在多个平台上使用同一套代码,提高开发效率。本文提供的三种实现方法各有优缺点,开发者应该根据具体的应用场景选择合适的方法。
在OpenHarmony鸿蒙平台上,我们可以通过ArkTS调用Kotlin编译的JavaScript代码,实现真正的跨平台开发。这种方式既保证了代码的可复用性,又能充分利用各个平台的特性,是现代跨平台开发的最佳实践。
希望这篇文章能够帮助开发者更好地理解矩阵旋转算法,并在实际项目中灵活应用。随着移动应用的发展,掌握这类基础算法将对提升开发能力大有裨益。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容









所有评论(0)