【精通篇】打造React Native鸿蒙跨平台开发高级复合组件库开发系列:Layout 布局(row 和 col 两个组件来进行行列布)
本文介绍了在React Native中实现类似鸿蒙系统布局的三种方法:1)使用原生Flexbox布局,通过flexDirection等属性控制行列排列;2)采用第三方库如react-native-flex-grid实现网格布局;3)自定义Grid组件进行精细化控制。文中提供了完整的代码示例,包括基础Flexbox实现、第三方库应用以及自定义网格组件的开发方法。此外,还演示了包含图标组件、行列组件的
在鸿蒙(HarmonyOS)的布局设计中,鸿蒙系统使用的是类似于Android Jetpack的CompositionLayout,这是一种基于XML的布局方式,类似于Flexbox的布局方式,但不完全兼容。如果你想在React Native中实现类似鸿蒙的布局方式,你可以使用一些第三方库或者自定义组件来实现。
方法1:使用Flexbox布局
React Native原生支持Flexbox布局,这是实现行列布局的一个非常强大的工具。你可以使用<View>组件和style属性中的flexDirection、justifyContent、alignItems等属性来控制布局。
示例代码:
import React from 'react';
import { View, Text, StyleSheet } from 'react-native';
const App = () => {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.row}>
<View style={styles.col}>
<Text>Column 1</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.col}>
<Text>Column 2</Text>
</View>
</View>
<View style={styles.row}>
<View style={styles.col}>
<Text>Column 3</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.col}>
<Text>Column 4</Text>
</View>
</View>
</View>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
},
row: {
flexDirection: 'row', // 水平方向排列子元素
},
col: {
flex: 1, // 每个列平分剩余空间
justifyContent: 'center', // 垂直居中内容
alignItems: 'center', // 水平居中内容
margin: 10, // 外边距
},
});
export default App;
方法2:使用第三方库如react-native-grid-component或react-native-flex-grid
这些库提供了更接近于鸿蒙的Grid布局方式,允许你更灵活地控制行列布局。例如,react-native-flex-grid库:
安装库:
npm install react-native-flex-grid --save
使用示例:
import React from 'react';
import { Container, Row, Col } from 'react-native-flex-grid';
import { Text } from 'react-native';
const App = () => {
return (
<Container>
<Row>
<Col>
<Text>Column 1</Text>
</Col>
<Col>
<Text>Column 2</Text>
</Col>
</Row>
<Row>
<Col>
<Text>Column 3</Text>
</Col>
<Col>
<Text>Column 4</Text>
</Col>
</Row>
</Container>
);
};
export default App;
方法3:自定义组件实现Grid布局
如果你需要完全自定义或者更精细的控制,你可以自己实现一个Grid布局组件。这通常涉及到计算每个单元格的宽度和高度,并动态地渲染它们。例如:
import React from 'react';
import { View, Text, StyleSheet } from 'react-native';
import { Dimensions } from 'react-native'; // 获取屏幕尺寸以计算列宽等。
const Grid = ({ children }) => {
const numColumns = 2; // 假设有两列,可根据需要调整。
const width = Dimensions.get('window').width / numColumns; // 计算每列宽度。
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
{React.Children.map(children, (child, index) => (
<View key={index} style={[styles.col, { width }]}>
{child} // 渲染子元素。每个子元素都应该是一个Col组件。
</View>
))}
</View>
);
};
```然后在你的应用中使用它:
```jsx
const App = () => {
return (
<Grid>
<Text>Column 1</Text> // 这些将是Grid的子元素。每个都应该占据一列。如果有更多列则继续添加。
组件真实实际案例演示:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { View, Text, StyleSheet, TouchableOpacity, ScrollView, Dimensions } from 'react-native';
// Simple Icon Component using Unicode symbols
interface IconProps {
name: string;
size?: number;
color?: string;
style?: object;
}
const Icon: React.FC<IconProps> = ({
name,
size = 24,
color = '#333333',
style
}) => {
const getIconSymbol = () => {
switch (name) {
case 'layout': return '⚏';
case 'grid': return '⊞';
case 'flex': return '⥊';
case 'align': return '⇳';
case 'justify': return '⇔';
default: return '●';
}
};
return (
<View style={[{ width: size, height: size, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center' }, style]}>
<Text style={{ fontSize: size * 0.8, color, includeFontPadding: false, textAlign: 'center' }}>
{getIconSymbol()}
</Text>
</View>
);
};
// Row Component
interface RowProps {
children: React.ReactNode;
gutter?: number;
align?: 'flex-start' | 'center' | 'flex-end' | 'stretch';
justify?: 'flex-start' | 'center' | 'flex-end' | 'space-between' | 'space-around';
style?: object;
}
const Row: React.FC<RowProps> = ({
children,
gutter = 0,
align = 'flex-start',
justify = 'flex-start',
style
}) => {
return (
<View
style={[
styles.row,
{
marginHorizontal: -gutter / 2,
alignItems: align,
justifyContent: justify,
},
style
]}
>
{React.Children.map(children, (child) => {
if (React.isValidElement(child)) {
return React.cloneElement(child, {
style: [
child.props.style,
{
marginHorizontal: gutter / 2
}
]
});
}
return child;
})}
</View>
);
};
// Col Component
interface ColProps {
children: React.ReactNode;
span?: number;
offset?: number;
style?: object;
}
const Col: React.FC<ColProps> = ({
children,
span = 24,
offset = 0,
style
}) => {
const percentage = (span / 24) * 100;
const offsetPercentage = (offset / 24) * 100;
return (
<View
style={[
styles.col,
{
width: `${percentage}%`,
marginLeft: `${offsetPercentage}%`,
},
style
]}
>
{children}
</View>
);
};
// Layout Example Data
const layoutExamples = [
{ id: 1, title: '基础栅格', description: '24栅格系统' },
{ id: 2, title: '间隔布局', description: '带间距的Row' },
{ id: 3, title: '对齐方式', description: '垂直居中对齐' },
{ id: 4, title: '偏移布局', description: '列偏移效果' },
];
// Layout Showcase Component
const LayoutExample: React.FC<{
title: string;
description: string;
children: React.ReactNode;
}> = ({ title, description, children }) => {
return (
<View style={styles.exampleContainer}>
<Text style={styles.exampleTitle}>{title}</Text>
<Text style={styles.exampleDescription}>{description}</Text>
<View style={styles.exampleContent}>
{children}
</View>
</View>
);
};
// Main App Component
const LayoutComponentApp = () => {
const [selectedExample, setSelectedExample] = useState<number>(1);
return (
<ScrollView style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.headerTitle}>栅格布局组件</Text>
<Text style={styles.headerSubtitle}>基于Flexbox的响应式布局系统</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.section}>
<Text style={styles.sectionTitle}>组件介绍</Text>
<View style={styles.componentsInfo}>
<View style={styles.componentCard}>
<View style={styles.iconWrapper}>
<Icon name="layout" size={32} color="#4361ee" />
</View>
<Text style={styles.componentName}>Row</Text>
<Text style={styles.componentDesc}>水平排列容器</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.componentCard}>
<View style={styles.iconWrapper}>
<Icon name="grid" size={32} color="#4cc9f0" />
</View>
<Text style={styles.componentName}>Col</Text>
<Text style={styles.componentDesc}>栅格列容器</Text>
</View>
</View>
</View>
<View style={styles.section}>
<Text style={styles.sectionTitle}>布局示例</Text>
<View style={styles.examplesContainer}>
{layoutExamples.map((example) => (
<TouchableOpacity
key={example.id}
style={[
styles.exampleTab,
selectedExample === example.id && styles.selectedExampleTab
]}
onPress={() => setSelectedExample(example.id)}
>
<Text style={[
styles.exampleTabText,
selectedExample === example.id && styles.selectedExampleTabText
]}>
{example.title}
</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
))}
</View>
{selectedExample === 1 && (
<LayoutExample
title="基础栅格"
description="使用24栅格系统的布局"
>
<Row gutter={10}>
<Col span={8}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#4361ee' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>span=8</Text>
</View>
</Col>
<Col span={8}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#3a0ca3' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>span=8</Text>
</View>
</Col>
<Col span={8}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#7209b7' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>span=8</Text>
</View>
</Col>
</Row>
<Row gutter={10} style={{ marginTop: 10 }}>
<Col span={12}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#f72585' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>span=12</Text>
</View>
</Col>
<Col span={12}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#b5179e' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>span=12</Text>
</View>
</Col>
</Row>
</LayoutExample>
)}
{selectedExample === 2 && (
<LayoutExample
title="间隔布局"
description="带有间距的栅格布局"
>
<Row gutter={15}>
<Col span={6}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#4cc9f0' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>gutter=15</Text>
</View>
</Col>
<Col span={6}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#4895ef' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>gutter=15</Text>
</View>
</Col>
<Col span={6}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#4361ee' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>gutter=15</Text>
</View>
</Col>
<Col span={6}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#3a0ca3' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>gutter=15</Text>
</View>
</Col>
</Row>
</LayoutExample>
)}
{selectedExample === 3 && (
<LayoutExample
title="对齐方式"
description="不同的对齐选项"
>
<Row gutter={10} align="center">
<Col span={6}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#f72585', height: 60 }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>高60</Text>
</View>
</Col>
<Col span={6}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#b5179e', height: 80 }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>高80</Text>
</View>
</Col>
<Col span={6}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#7209b7', height: 100 }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>高100</Text>
</View>
</Col>
<Col span={6}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#560bad', height: 70 }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>高70</Text>
</View>
</Col>
</Row>
</LayoutExample>
)}
{selectedExample === 4 && (
<LayoutExample
title="偏移布局"
description="列偏移效果"
>
<Row gutter={10}>
<Col span={6}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#4cc9f0' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>span=6</Text>
</View>
</Col>
<Col span={6} offset={6}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#4895ef' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>span=6 offset=6</Text>
</View>
</Col>
</Row>
<Row gutter={10} style={{ marginTop: 10 }}>
<Col span={8} offset={4}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#4361ee' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>span=8 offset=4</Text>
</View>
</Col>
<Col span={8} offset={4}>
<View style={[styles.demoBox, { backgroundColor: '#3a0ca3' }]}>
<Text style={styles.boxText}>span=8 offset=4</Text>
</View>
</Col>
</Row>
</LayoutExample>
)}
</View>
<View style={styles.usageSection}>
<Text style={styles.sectionTitle}>使用方法</Text>
<View style={styles.codeBlock}>
<Text style={styles.codeText}>{'<Row gutter={10}>'}</Text>
<Text style={styles.codeText}> {'<Col span={12}>内容</Col>'}</Text>
<Text style={styles.codeText}> {'<Col span={12}>内容</Col>'}</Text>
<Text style={styles.codeText}>{'</Row>'}</Text>
</View>
<Text style={styles.description}>
Row组件用于创建水平布局容器,Col组件用于创建栅格列。通过gutter属性设置间距,
通过span属性设置列宽度(总共24份),通过offset属性设置列偏移。
</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.featuresSection}>
<Text style={styles.sectionTitle}>功能特性</Text>
<View style={styles.featuresList}>
<View style={styles.featureItem}>
<Icon name="flex" size={20} color="#4361ee" style={styles.featureIcon} />
<Text style={styles.featureText}>基于Flexbox布局</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.featureItem}>
<Icon name="align" size={20} color="#4cc9f0" style={styles.featureIcon} />
<Text style={styles.featureText}>灵活的对齐选项</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.featureItem}>
<Icon name="justify" size={20} color="#f72585" style={styles.featureIcon} />
<Text style={styles.featureText}>多种排列方式</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.featureItem}>
<Icon name="grid" size={20} color="#7209b7" style={styles.featureIcon} />
<Text style={styles.featureText}>24栅格系统</Text>
</View>
</View>
</View>
<View style={styles.footer}>
<Text style={styles.footerText}>© 2023 栅格布局组件 | 响应式布局解决方案</Text>
</View>
</ScrollView>
);
};
const { width } = Dimensions.get('window');
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#f8f9fa',
},
header: {
backgroundColor: '#ffffff',
paddingVertical: 30,
paddingHorizontal: 20,
marginBottom: 10,
borderBottomWidth: 1,
borderBottomColor: '#e9ecef',
},
headerTitle: {
fontSize: 28,
fontWeight: '700',
color: '#212529',
textAlign: 'center',
marginBottom: 5,
},
headerSubtitle: {
fontSize: 16,
color: '#6c757d',
textAlign: 'center',
},
section: {
marginBottom: 20,
},
sectionTitle: {
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: '700',
color: '#212529',
paddingHorizontal: 20,
paddingBottom: 15,
},
componentsInfo: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-around',
paddingHorizontal: 15,
},
componentCard: {
backgroundColor: '#ffffff',
borderRadius: 15,
padding: 20,
width: (width - 60) / 2,
alignItems: 'center',
elevation: 3,
shadowColor: '#000',
shadowOffset: { width: 0, height: 2 },
shadowOpacity: 0.08,
shadowRadius: 4,
},
iconWrapper: {
width: 60,
height: 60,
borderRadius: 30,
backgroundColor: '#f1f3f5',
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
marginBottom: 15,
},
componentName: {
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: '700',
color: '#212529',
marginBottom: 5,
},
componentDesc: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#6c757d',
textAlign: 'center',
},
examplesContainer: {
flexDirection: 'row',
paddingHorizontal: 15,
marginBottom: 15,
},
exampleTab: {
flex: 1,
paddingVertical: 12,
backgroundColor: '#e9ecef',
marginHorizontal: 5,
borderRadius: 10,
alignItems: 'center',
},
selectedExampleTab: {
backgroundColor: '#4361ee',
},
exampleTabText: {
fontSize: 14,
fontWeight: '600',
color: '#495057',
},
selectedExampleTabText: {
color: '#ffffff',
},
exampleContainer: {
backgroundColor: '#ffffff',
marginHorizontal: 15,
borderRadius: 15,
padding: 20,
marginBottom: 20,
elevation: 3,
shadowColor: '#000',
shadowOffset: { width: 0, height: 2 },
shadowOpacity: 0.08,
shadowRadius: 4,
},
exampleTitle: {
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: '700',
color: '#212529',
marginBottom: 5,
},
exampleDescription: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#6c757d',
marginBottom: 15,
},
exampleContent: {
padding: 10,
},
row: {
flexDirection: 'row',
flexWrap: 'wrap',
},
col: {
flexDirection: 'column',
},
demoBox: {
padding: 15,
borderRadius: 8,
minHeight: 50,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
},
boxText: {
color: '#ffffff',
fontWeight: '600',
textAlign: 'center',
},
usageSection: {
backgroundColor: '#ffffff',
marginHorizontal: 15,
borderRadius: 15,
padding: 20,
marginBottom: 20,
elevation: 3,
shadowColor: '#000',
shadowOffset: { width: 0, height: 2 },
shadowOpacity: 0.08,
shadowRadius: 4,
},
codeBlock: {
backgroundColor: '#2b3541',
borderRadius: 8,
padding: 15,
marginBottom: 15,
},
codeText: {
fontFamily: 'monospace',
color: '#e9ecef',
fontSize: 14,
lineHeight: 22,
},
description: {
fontSize: 15,
color: '#495057',
lineHeight: 22,
},
featuresSection: {
backgroundColor: '#ffffff',
marginHorizontal: 15,
borderRadius: 15,
padding: 20,
marginBottom: 20,
elevation: 3,
shadowColor: '#000',
shadowOffset: { width: 0, height: 2 },
shadowOpacity: 0.08,
shadowRadius: 4,
},
featuresList: {
paddingLeft: 10,
},
featureItem: {
flexDirection: 'row',
alignItems: 'center',
marginBottom: 15,
},
featureIcon: {
marginRight: 15,
},
featureText: {
fontSize: 16,
color: '#212529',
},
footer: {
paddingVertical: 20,
alignItems: 'center',
},
footerText: {
color: '#6c757d',
fontSize: 14,
},
});
export default LayoutComponentApp;
这段React Native代码实现了一个完整的栅格布局系统,其架构设计基于Flexbox布局模型,构建了一个响应式的24栅格布局解决方案。整个系统由多个高度专业化的组件构成,每个组件都承担着特定的布局职责。
图标组件设计原理
Icon组件采用了Unicode符号的渲染策略,这种设计避免了图片资源的依赖,提供了极致的性能优化。组件通过TypeScript接口定义了严格的属性约束,包括图标名称、尺寸、颜色和自定义样式。这种类型约束确保了组件使用的可靠性,防止了运行时错误的发生。
图标符号的映射机制通过getIconSymbol函数实现,该函数采用switch-case条件判断来匹配不同的图标名称。布局图标使用"⚏"符号,栅格图标使用"⊞"符号,弹性布局图标使用"⥊"符号,对齐图标使用"⇳"符号,两端对齐图标使用"⇔"符号,默认情况下使用"●"作为通用图标。这种符号选择体现了语义化设计原则,使得图标能够直观地传达其功能含义。
行容器组件架构
Row组件作为水平排列容器,其设计哲学建立在负边距补偿技术上。通过marginHorizontal: -gutter / 2的设置,抵消了列间距对整体布局的影响。这种设计确保了栅格系统的精确对齐和间距控制。
组件的对齐系统支持多种垂直对齐方式,包括flex-start、center、flex-end和stretch,这些选项覆盖了Flexbox布局中常见的对齐需求。水平方向的对齐支持包括flex-start、center、flex-end、space-between和space-around,这种全面的对齐支持使得布局系统具有极高的灵活性。
列容器组件实现
Col组件实现了经典的24栅格系统,这种设计源于Ant Design等成熟UI框架的布局理念。每个列都可以定义span属性来指定占据的栅格数量,offset属性用于实现列的偏移效果。这种栅格系统的设计使得布局可以实现精确的百分比控制。
布局示例数据模型
系统通过layoutExamples数组定义了四种核心布局场景。基础栅格示例展示了标准的24栅格系统的工作原理,间隔布局示例演示了带间距的Row容器的实现方式,对齐方式示例重点展示垂直居中对齐的效果,偏移布局示例则体现了列偏移的视觉效果。
示例展示组件结构
LayoutExample组件作为布局示例的展示容器,其设计采用了清晰的层次结构。标题使用突出的字体样式,描述文本提供详细的说明信息,内容区域承载具体的布局演示。
打包
接下来通过打包命令npn run harmony将reactNative的代码打包成为bundle,这样可以进行在开源鸿蒙OpenHarmony中进行使用。
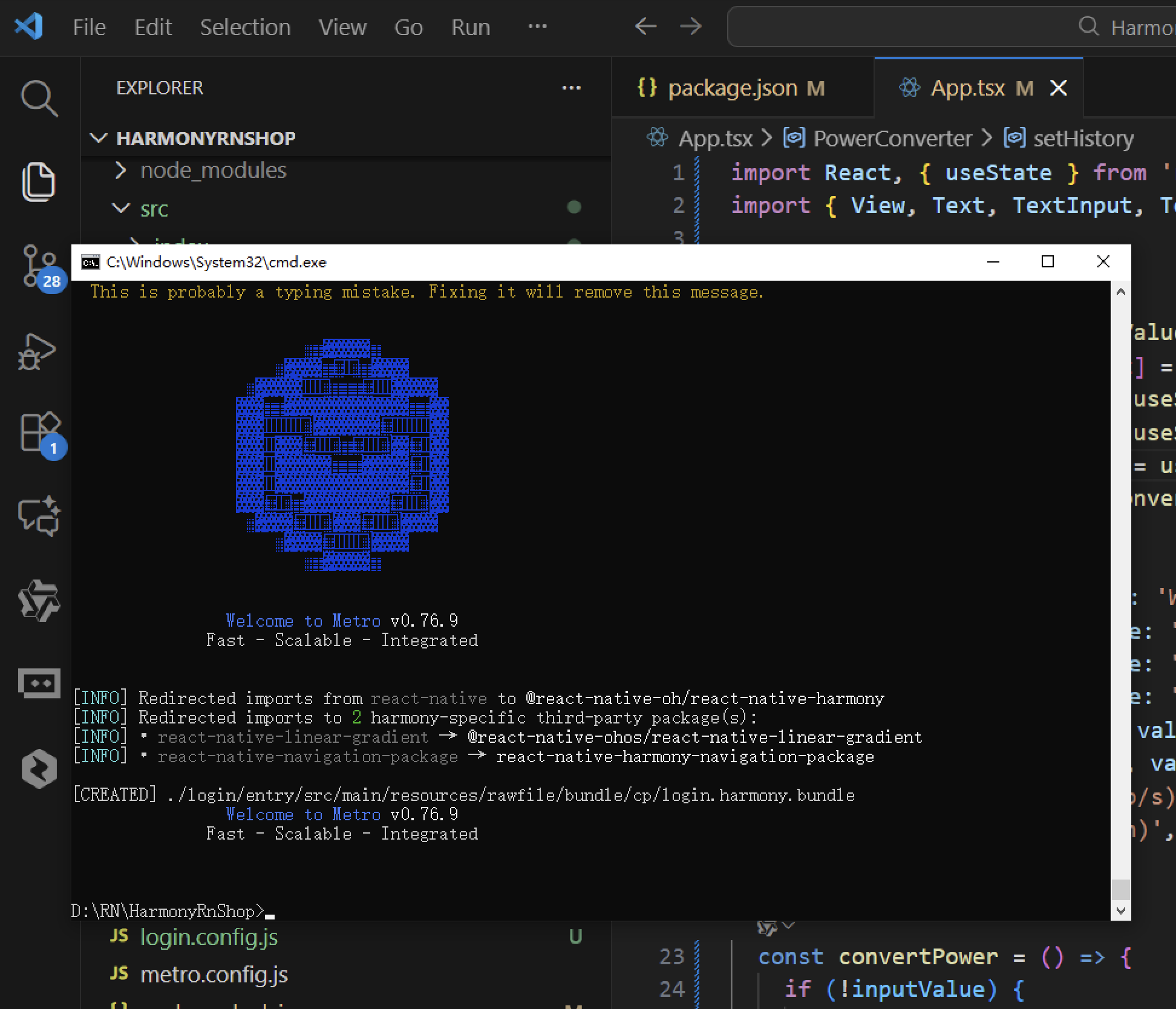
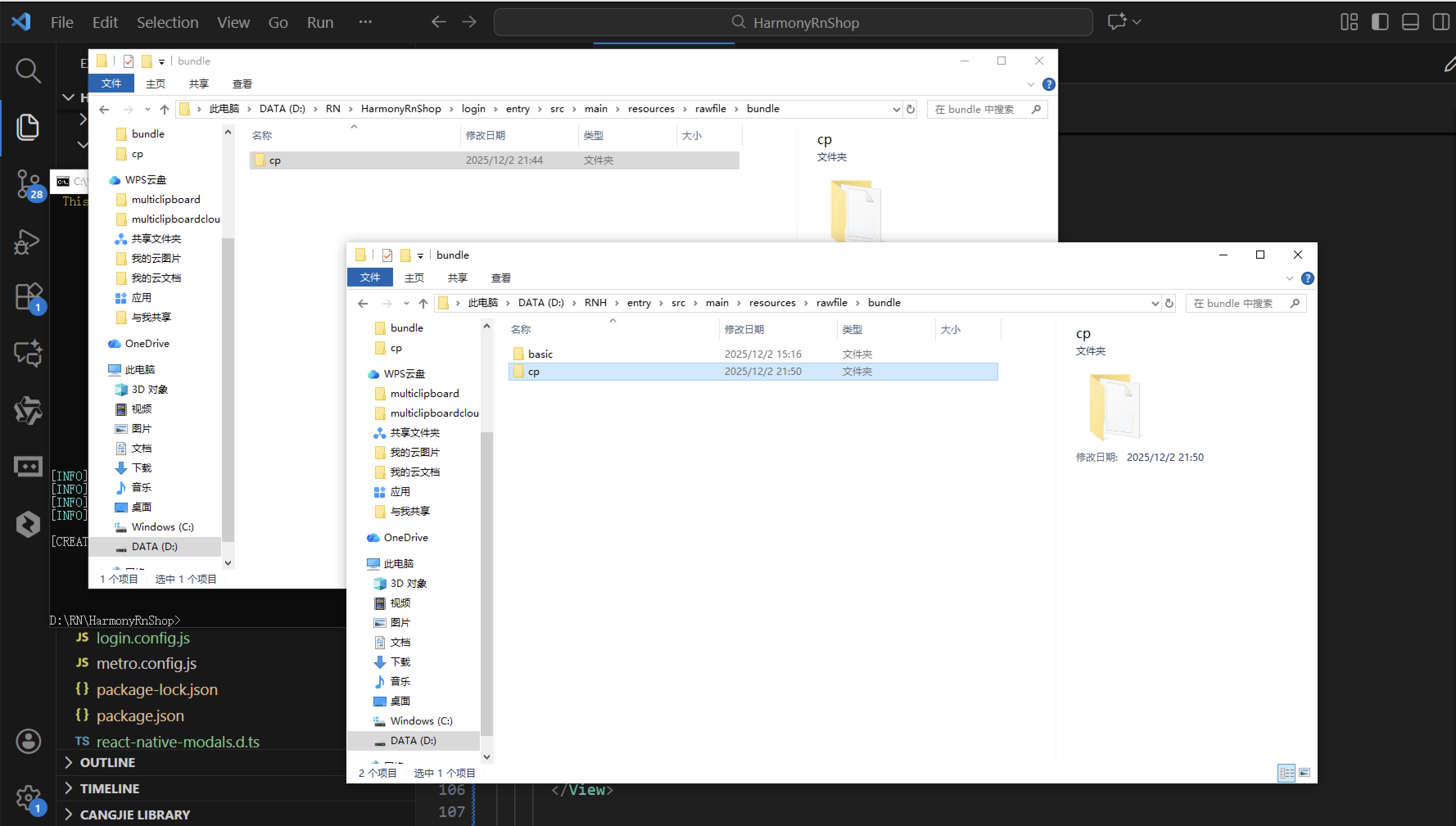
打包之后再将打包后的鸿蒙OpenHarmony文件拷贝到鸿蒙的DevEco-Studio工程目录去:
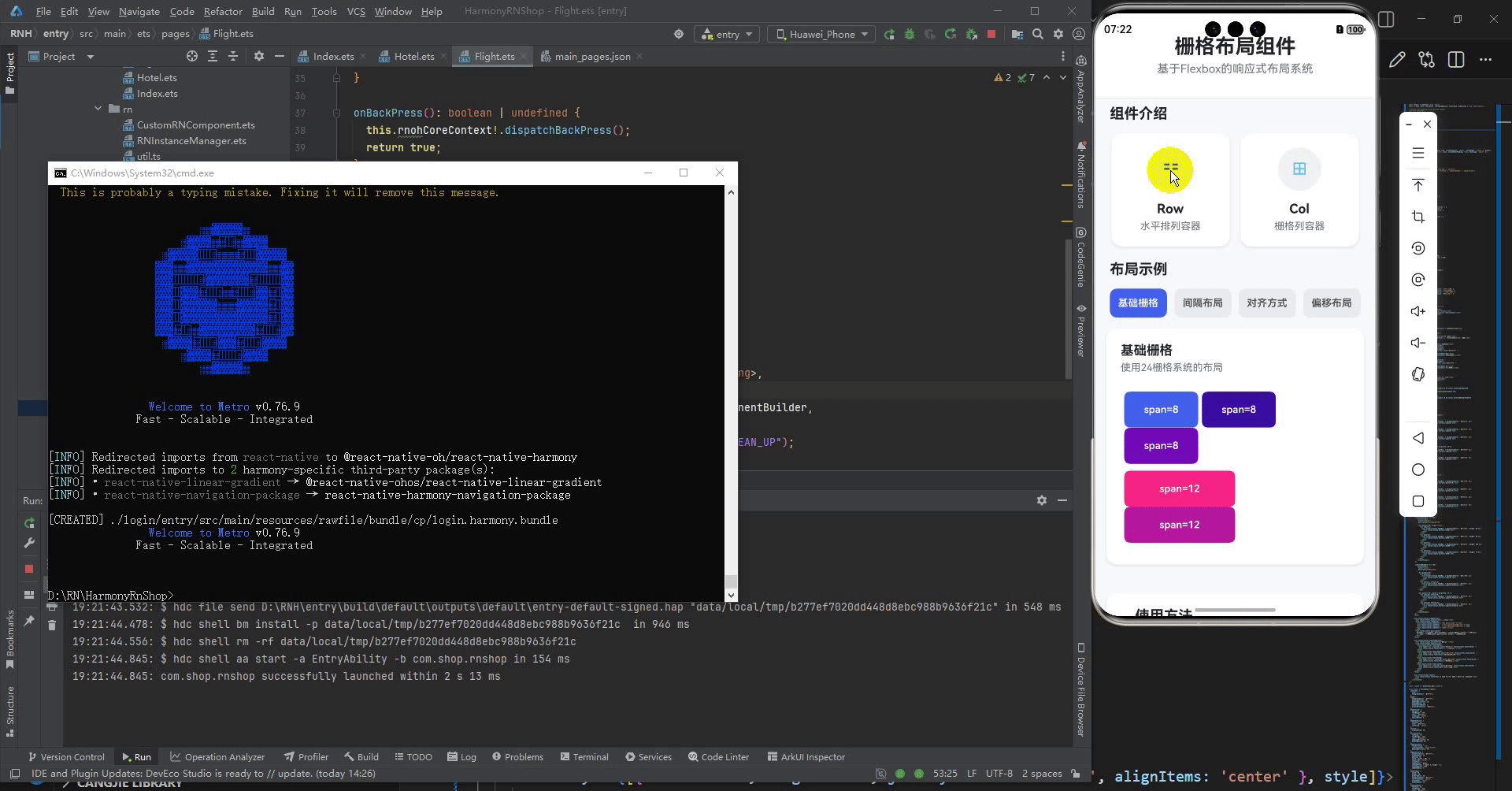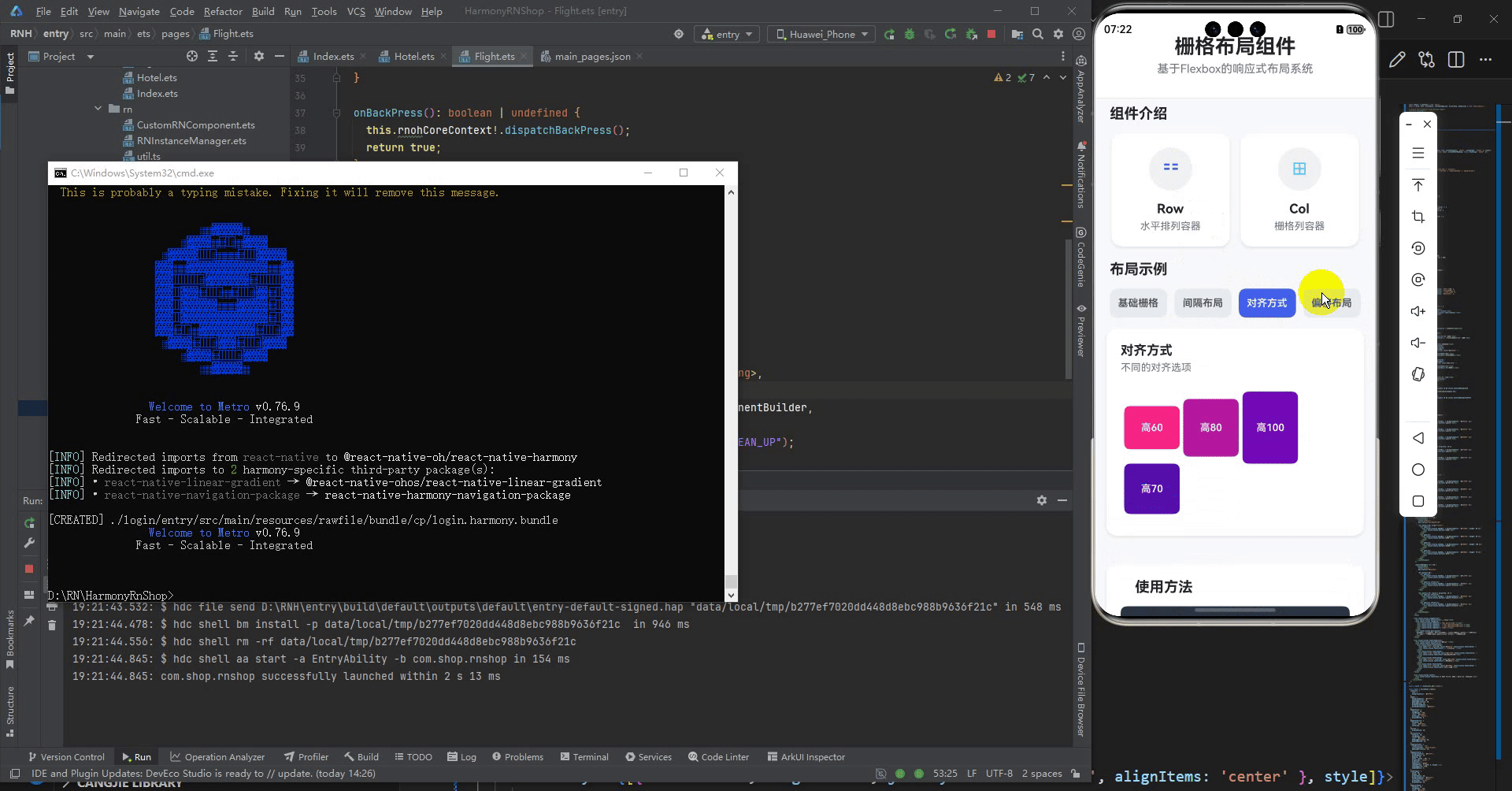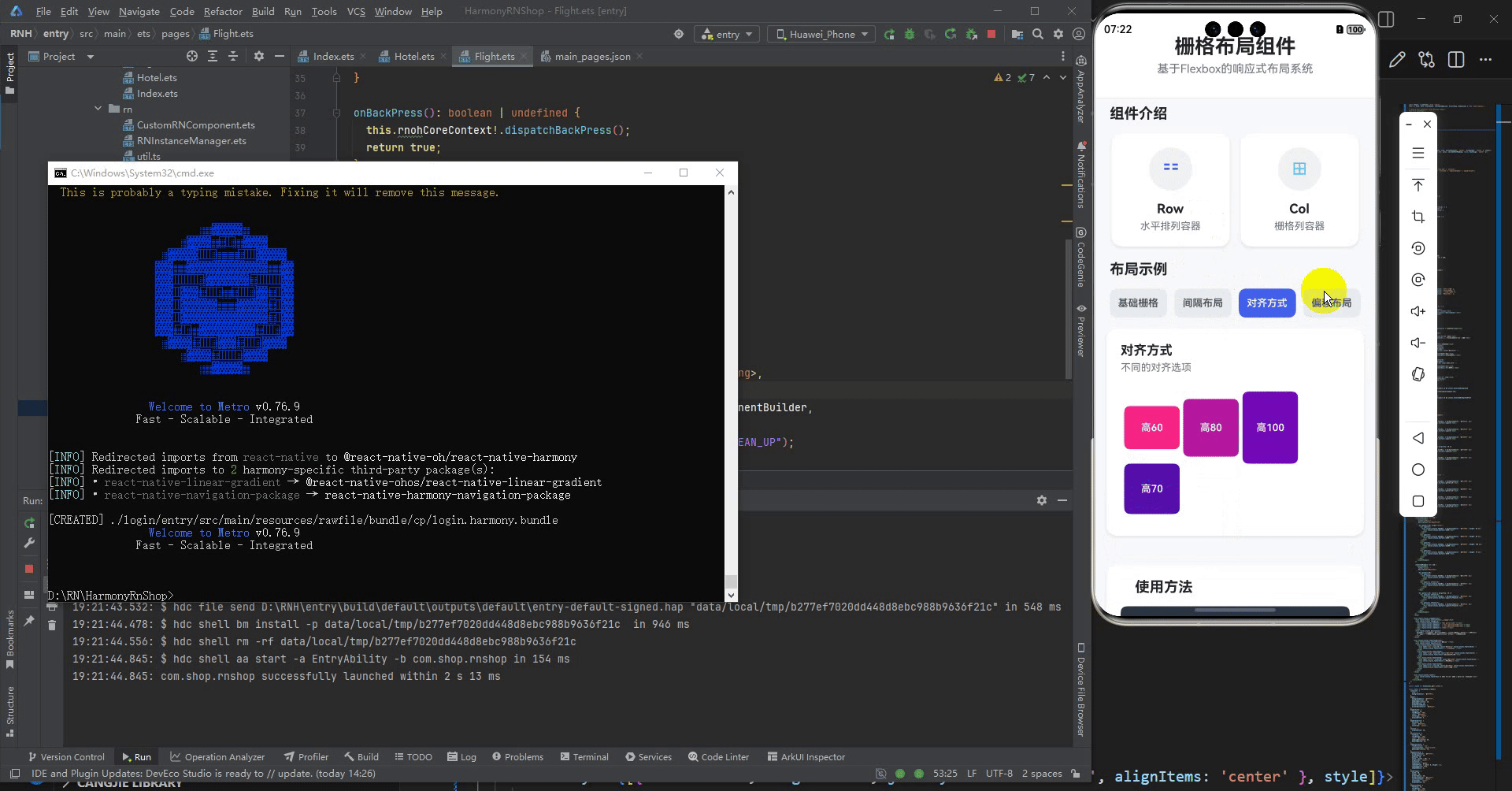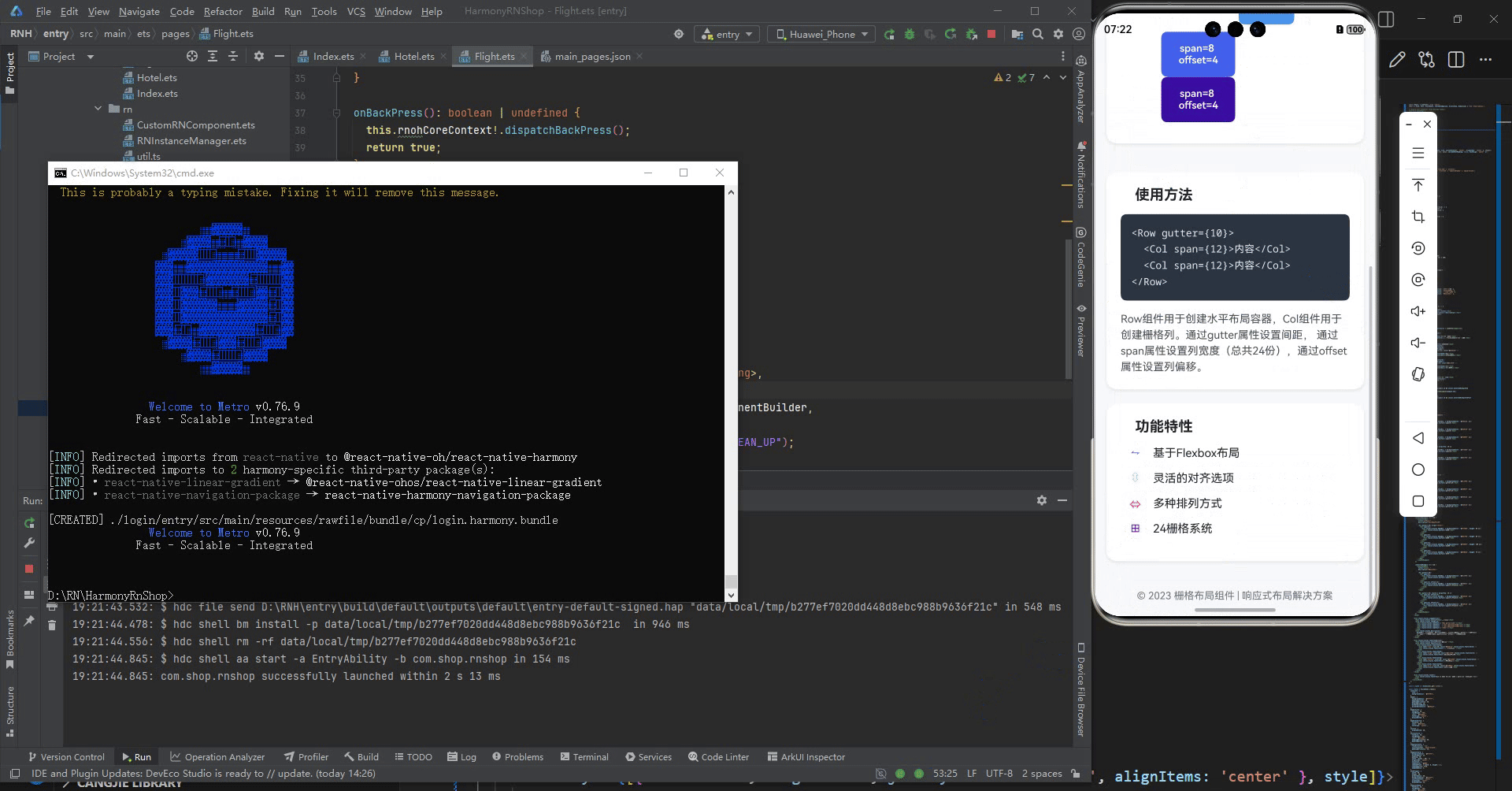
最后运行效果图如下显示:
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容









所有评论(0)