【开源鸿蒙跨平台开发学习笔记 】DAY10: Flutter开发之 ListView 与 下拉刷新与上拉加载更多
支持完全自定义 Header 和 Footer。
今天终于来到列表页面啦,用户的仓库列表,就学习一下列表的使用,以及列表的下拉刷新与上拉加载更多。
一、ListView
ListView是最常用的可滚动组件之一,它可以沿一个方向线性排布所有子组件,并且它也支持列表项懒加载
1、默认构造函数
ListView({
super.key,
super.scrollDirection, // 滚动方向
super.reverse, // 是否反向
super.controller, // 滚动控制器
super.primary, // 是否为主滚动视图
super.physics, // 滚动物理效果
super.shrinkWrap, // 是否包裹内容
super.padding, // 内边距
this.itemExtent, // 固定子项高度
this.itemExtentBuilder, // 动态子项高度构建器
this.prototypeItem, // 原型子项
bool addAutomaticKeepAlives = true, // 自动保持子项状态
bool addRepaintBoundaries = true, // 添加重绘边界
bool addSemanticIndexes = true, // 添加语义索引
super.cacheExtent, // 预加载区域
List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[], // 子组件列表
int? semanticChildCount, // 语义子项数量
super.dragStartBehavior, // 拖拽开始行为
super.keyboardDismissBehavior, // 键盘隐藏行为
super.restorationId, // 恢复ID
super.clipBehavior, // 裁剪行为
super.hitTestBehavior, // 点击测试行为
})1)基础滚动属性
scrollDirection
scrollDirection: Axis.vertical, // 默认,垂直滚动
scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal, // 水平滚动
// 示例
ListView(
scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal,
children: [...],
)reverse
reverse: false, // 默认,从顶部开始
reverse: true, // 反向,从底部开始
// 示例 - 聊天应用
ListView(
reverse: true, // 最新消息在底部
children: messages.map((msg) => MessageBubble(msg)).toList(),
)controller
final ScrollController _controller = ScrollController();
// 示例 - 滚动到指定位置
ListView(
controller: _controller,
children: [...],
)
// 滚动到某个位置
_controller.animateTo(
500.0,
duration: Duration(seconds: 1),
curve: Curves.easeInOut,
);2)布局控制属性
shrinkWrap
该属性表示是否根据子组件的总长度来设置ListView的长度,默认值为false 。默认情况下,ListView会在滚动方向尽可能多的占用空间。当ListView在一个无边界(滚动方向上)的容器中时,shrinkWrap必须为true。
shrinkWrap: false, // 默认,占用尽可能多的空间
shrinkWrap: true, // 只占用子项所需空间
// 示例 - 嵌套在Column中
Column(
children: [
Text('标题'),
ListView(
shrinkWrap: true, // 重要:避免无限高度
physics: NeverScrollableScrollPhysics(), // 禁止自身滚动
children: [...],
),
],
)padding
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16.0),
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 8.0, bottom: 16.0),
// 示例
ListView(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16.0),
children: [...],
)3)性能优化属性
addAutomaticKeepAlives
addAutomaticKeepAlives: true, // 默认,保持子项状态
addAutomaticKeepAlives: false, // 不保持状态
// 使用场景
ListView(
addAutomaticKeepAlives: false, // 子项不需要保持状态时
children: List.generate(100, (index) => Text('Item $index')),
)addRepaintBoundaries
addRepaintBoundaries: true, // 默认,添加重绘边界
addRepaintBoundaries: false, // 不添加重绘边界
// 示例 - 简单列表可以关闭以提高性能
ListView(
addRepaintBoundaries: false,
children: [
for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++)
Container(
height: 50,
color: Colors.primaries[i % Colors.primaries.length],
),
],
)addSemanticIndexes
addSemanticIndexes: true, // 默认,为无障碍功能添加索引
addSemanticIndexes: false, // 不添加语义索引
// 对于动态变化或无需无障碍支持的列表可以关闭cacheExtent
cacheExtent: 250.0, // 预加载250逻辑像素的区域
cacheExtent: 0.0, // 不预加载
cacheExtent: null, // 使用默认值(约250.0)
// 示例 - 图片列表优化
ListView.builder(
cacheExtent: 500.0, // 预加载更多
itemCount: images.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) => ImageItem(images[index]),
)4)尺寸相关属性
itemExtent (固定高度)
该参数如果不为null,则会强制children的“长度”为itemExtent的值;这里的“长度”是指滚动方向上子组件的长度,也就是说如果滚动方向是垂直方向,则itemExtent代表子组件的高度;如果滚动方向为水平方向,则itemExtent就代表子组件的宽度。在ListView中,指定itemExtent比让子组件自己决定自身长度会有更好的性能,这是因为指定itemExtent后,滚动系统可以提前知道列表的长度,而无需每次构建子组件时都去再计算一下,尤其是在滚动位置频繁变化时(滚动系统需要频繁去计算列表高度)。
itemExtent: 50.0, // 所有子项固定高度50
// 示例 - 等高列表
ListView(
itemExtent: 60.0,
children: List.generate(
20,
(index) => ListTile(
title: Text('Item $index'),
),
),
)itemExtentBuilder (动态高度)
ListView.builder(
itemExtentBuilder: (index, _) {
// 根据索引返回不同高度
if (index % 3 == 0) return 80.0;
if (index % 3 == 1) return 100.0;
return 60.0;
},
itemCount: 50,
itemBuilder: (context, index) => ItemWidget(index),
)prototypeItem (原型子项)
如果知道列表中的所有列表项长度都相同但不知道具体是多少,这时我们可以指定一个列表项,该列表项被称为 prototypeItem(列表项原型)。指定 prototypeItem 后,可滚动组件会在 layout 时计算一次它延主轴方向的长度,这样也就预先知道了所有列表项的延主轴方向的长度,所以和指定 itemExtent 一样,指定 prototypeItem 会有更好的性能。注意,itemExtent 和prototypeItem 互斥,不能同时指定它们。
ListView(
prototypeItem: ListTile(
title: Text('原型项'),
subtitle: Text('用于测量高度'),
),
children: [...],
)
// 更实用的示例
ListView(
prototypeItem: Container(
height: 80,
child: Card(
child: Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16),
child: Text('示例内容'),
),
),
),
children: items.map((item) => ItemCard(item)).toList(),
)5)滚动物理效果
// 常用物理效果
physics: AlwaysScrollableScrollPhysics(), // 总是可滚动
physics: NeverScrollableScrollPhysics(), // 禁止滚动
physics: BouncingScrollPhysics(), // 弹性效果(iOS风格)
physics: ClampingScrollPhysics(), // 夹紧效果(Android风格)
physics: FixedExtentScrollPhysics(), // 固定范围滚动
// 示例
ListView(
physics: BouncingScrollPhysics(),
children: [...],
)
// 分页加载时
ListView(
physics: AlwaysScrollableScrollPhysics(),
controller: _controller,
children: [...],
)6) 行为控制属性
primary
primary: true, // 主滚动视图
primary: false, // 非主滚动视图
// 通常用于判断是否需要AppBar的滚动监听
ListView(
primary: true, // 可以响应PageUp/PageDown键
children: [...],
)dragStartBehavior
dragStartBehavior: DragStartBehavior.start, // 立即开始拖拽
dragStartBehavior: DragStartBehavior.down, // 按下时开始拖拽
// 示例
ListView(
dragStartBehavior: DragStartBehavior.down,
children: [...],
)keyboardDismissBehavior
keyboardDismissBehavior: ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual, // 手动
keyboardDismissBehavior: ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.onDrag, // 拖拽时隐藏
keyboardDismissBehavior: ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.onTap, // 点击时隐藏
// 示例 - 搜索页面
ListView(
keyboardDismissBehavior: ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.onDrag,
children: [...],
)clipBehavior
clipBehavior: Clip.hardEdge, // 硬边裁剪
clipBehavior: Clip.antiAlias, // 抗锯齿裁剪(默认)
clipBehavior: Clip.none, // 不裁剪
// 示例 - 需要阴影效果时不裁剪
ListView(
clipBehavior: Clip.none,
children: items.map((item) =>
Card(
elevation: 4,
child: ListTile(title: Text(item)),
)
).toList(),
)hitTestBehavior
hitTestBehavior: HitTestBehavior.deferToChild, // 传递给子项
hitTestBehavior: HitTestBehavior.opaque, // 不透明区域
hitTestBehavior: HitTestBehavior.translucent, // 透明区域
// 示例
ListView(
hitTestBehavior: HitTestBehavior.opaque,
children: [...],
)8)恢复
// 保存和恢复滚动位置
ListView(
restorationId: 'my_list_view',
children: [...],
)
// 需要在MaterialApp中配置
MaterialApp(
restorationScopeId: 'app',
home: MyHomePage(),
)2、ListView.builder
ListView.builder适合列表项比较多或者列表项不确定的情况使用
核心参数:
ListView.builder({
// ListView公共参数已省略
...
required IndexedWidgetBuilder itemBuilder,
int itemCount,
...
})itemBuilder:它是列表项的构建器,类型为IndexedWidgetBuilder,返回值为一个widget。当列表滚动到具体的index位置时,会调用该构建器构建列表项。
itemCount:列表项的数量,如果为null,则为无限列表。
3、ListView.separated
ListView.separated可以在生成的列表项之间添加一个分割组件,它比ListView.builder多了一个separatorBuilder参数,该参数是一个分割组件生成器。
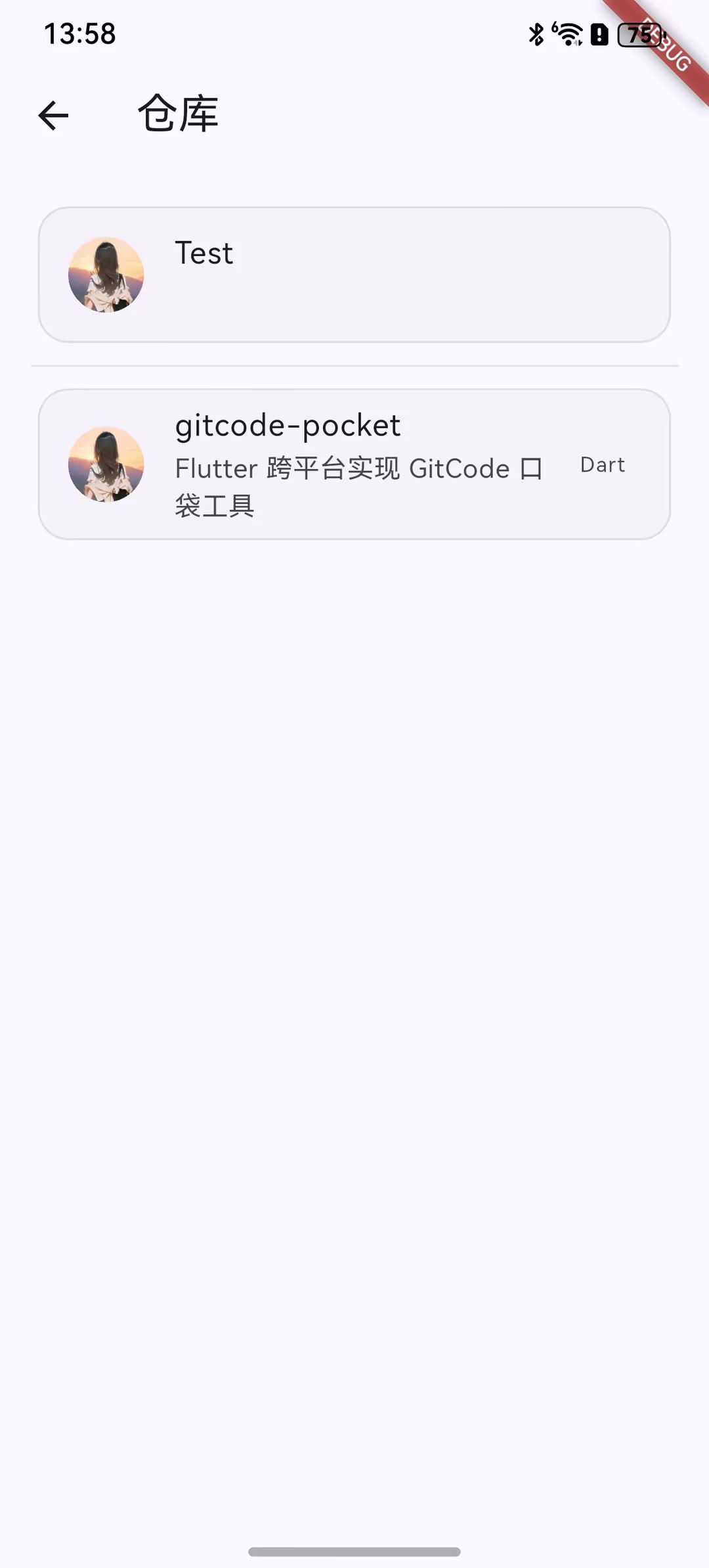
Widget _buildSeparatedListview() {
final theme = Theme.of(context);
final borderColor = theme.colorScheme.outlineVariant.withValues(alpha: 0.5);
return ListView.separated(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16),
itemCount: _repositoryList.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final repo = _repositoryList[index];
return _buildListItem(context: context, repo: repo);
},
separatorBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) {
return Divider(color: borderColor);
},
);
}
Widget _buildListview() {
return ListView.builder(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16),
itemCount: _repositoryList.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final repo = _repositoryList[index];
return _buildListItem(context: context, repo: repo);
},
);
}4、固定高度列表
前面说过,给列表指定 itemExtent 或 prototypeItem 会有更高的性能,所以当我们知道列表项的高度都相同时,强烈建议指定 itemExtent 或 prototypeItem
class FixedExtentList extends StatelessWidget {
const FixedExtentList({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('FixedExtentList')),
body: ListView.builder(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16),
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
//LayoutLogPrint是一个自定义组件,在布局时可以打印当前上下文中父组件给子组件的约束信息
return LayoutLogPrint(
tag: index,
child: ListTile(title: Text("$index")),
);
},
),
);
}
}因为列表项都是一个 ListTile,高度相同,但是我们不知道 ListTile 的高度是多少,所以指定了prototypeItem ,运行后,控制台打印:
flutter settings log message: 0: Size(342.2, 56.0)
flutter settings log message: 1: Size(342.2, 56.0)
flutter settings log message: 2: Size(342.2, 56.0)
flutter settings log message: 3: Size(342.2, 56.0)
flutter settings log message: 4: Size(342.2, 56.0)
flutter settings log message: 5: Size(342.2, 56.0)
flutter settings log message: 6: Size(342.2, 56.0)
flutter settings log message: 7: Size(342.2, 56.0)ListTitle 高度时56,指定 itemExtent 为 56也是可以的。但是建议优先指定原型,这样的话在列表项布局修改后,仍然可以正常工作(前提是每个列表项的高度相同)。
5、ListView 原理
ListView 内部组合了 Scrollable、Viewport 和 Sliver,需要注意:
1)ListView 中的列表项组件都是 RenderBox,并不是 Sliver, 这个一定要注意。
2)一个 ListView 中只有一个Sliver,对列表项进行按需加载的逻辑是 Sliver 中实现的。
3)ListView 的 Sliver 默认是 SliverList,如果指定了 itemExtent ,则会使用 SliverFixedExtentList;如果 prototypeItem 属性不为空,则会使用 SliverPrototypeExtentList,无论是是哪个,都实现了子组件的按需加载模型。
二、下拉刷新与上拉加载更多
关于下拉刷新以及加载更多这个功能小鱼选择了pull_to_refresh 插件,因为能满足大部分需求,其特点如下:
丰富的内置样式:经典、水滴、Material 等多种风格
灵活的自定义能力:支持完全自定义 Header 和 Footer
完善的状态管理:通过 RefreshController 管理所有状态
良好的性能:支持大量数据的流畅滚动
多种使用场景:支持普通列表、网格、Sliver 等
下面就一一介绍其安装使用,以及功能详解啦。
1、安装
dependencies:
pull_to_refresh: ^2.0.02、基本使用
Widget _buildSmartListview() {
return SmartRefresher(
controller: _refreshController,
enablePullDown: true,
enablePullUp: true,
header: ClassicHeader(),
footer: ClassicFooter(),
onRefresh: _refresh,
onLoading: _loadMore,
child: ListView.builder(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16),
itemCount: _repositoryList.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final repo = _repositoryList[index];
return _buildListItem(context: context, repo: repo);
},
),
);
}
Future<void> _refresh() async {
_page = 1;
_hasMore = true;
await _loadData(_page);
_refreshController.refreshCompleted();
}
Future<void> _loadMore() async {
if (_isLoading || !_hasMore) return;
await _loadData(_page);
_refreshController.loadComplete();
}3、详解RefreshController
class RefreshController {
// 刷新相关
void refreshCompleted() // 刷新完成
void refreshFailed() // 刷新失败
void refreshToIdle() // 恢复到空闲状态
// 加载相关
void loadComplete() // 加载完成
void loadFailed() // 加载失败
void loadNoData() // 没有更多数据
// 状态判断
bool get isRefresh // 是否正在刷新
bool get isLoading // 是否正在加载
bool get isTwoLevel // 是否在二级刷新
// 手动触发
Future<void> requestRefresh({Duration duration}) // 手动触发刷新
Future<void> requestLoading({Duration duration}) // 手动触发加载
// 重置
void resetNoData() // 重置无数据状态
// 状态监听
void addStatusListener(RefreshListener listener)
void removeStatusListener(RefreshListener listener)
}
示例:
import 'dart:math';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:pull_to_refresh/pull_to_refresh.dart';
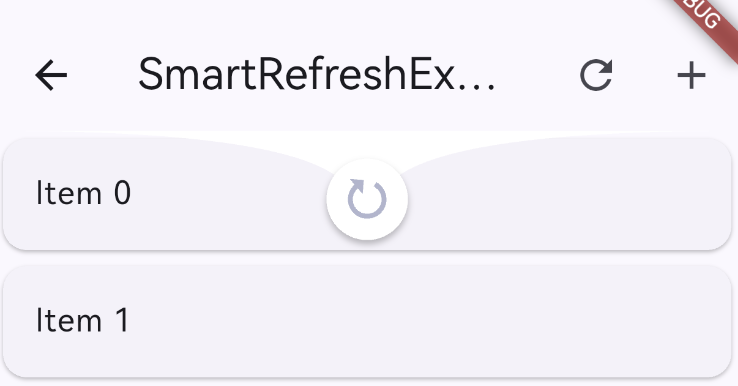
class SmartRefreshExample extends StatefulWidget {
const SmartRefreshExample({super.key});
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() {
return _SmartRefreshExample();
}
}
class _SmartRefreshExample extends State<SmartRefreshExample> {
final RefreshController _controller = RefreshController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('SmartRefreshExample'),
actions: [
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.refresh),
onPressed: () {
// 手动触发刷新
_controller.requestRefresh();
},
),
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed: () {
// 手动触发加载
_controller.requestLoading();
},
),
],
),
body: SmartRefresher(
// key: _refreshKey,
controller: _controller,
enablePullDown: true,
enablePullUp: true,
header: ClassicHeader(
completeText: "刷新完成",
failedText: "刷新失败",
idleText: "下拉刷新",
releaseText: "释放刷新",
refreshingText: "正在刷新...",
),
footer: CustomFooter(
builder: (context, mode) {
Widget body;
if (mode == LoadStatus.idle) {
body = Text("上拉加载");
} else if (mode == LoadStatus.loading) {
body = CircularProgressIndicator();
} else if (mode == LoadStatus.failed) {
body = Text("加载失败,点击重试");
} else if (mode == LoadStatus.canLoading) {
body = Text("释放加载更多");
} else {
body = Text("没有更多数据了");
}
return Container(
height: 55.0,
child: Center(child: body),
);
},
),
onRefresh: () async {
// 模拟网络延迟
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 3));
// 模拟随机失败
if (Random().nextBool()) {
_controller.refreshFailed();
} else {
_controller.refreshCompleted();
}
},
onLoading: () async {
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2));
// 模拟数据加载完毕
if (Random().nextInt(20) > 10) {
_controller.loadNoData();
} else {
_controller.loadComplete();
}
},
child: ListView.builder(
itemBuilder: (c, i) => Card(child: ListTile(title: Text("Item $i"))),
itemCount: 20,
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
child: Icon(Icons.info),
onPressed: () {
// 获取当前状态
print('刷新状态: ${_controller.isRefresh}');
print('加载状态: ${_controller.isLoading}');
print('无数据状态: ${_controller.footerStatus == LoadStatus.noMore}');
},
),
);
}
}4、详解Header
1)经典样式
ClassicHeader(
height: 80.0, // 高度
refreshStyle: RefreshStyle.Follow, // 刷新样式
completeDuration: Duration(milliseconds: 500), // 完成停留时间
textStyle: TextStyle(color: Colors.grey), // 文本样式
failedIcon: Icon(Icons.error, color: Colors.red), // 失败图标
completeIcon: Icon(Icons.done, color: Colors.green), // 完成图标
idleIcon: Icon(Icons.arrow_downward, color: Colors.grey), // 空闲图标
releaseIcon: Icon(Icons.arrow_upward, color: Colors.grey), // 释放图标
refreshingIcon: SizedBox(
width: 25.0,
height: 25.0,
child: CircularProgressIndicator(strokeWidth: 2.0),
), // 刷新中图标
// 国际化文本
idleText: "下拉刷新",
releaseText: "释放刷新",
refreshingText: "正在刷新...",
completeText: "刷新完成",
failedText: "刷新失败",
// 其他配置
spacing: 15.0, // 图标和文本间距
outerBuilder: (child) => Container( // 外部包装
color: Colors.white,
child: child,
),
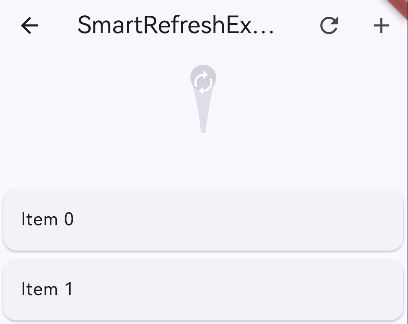
)2)水滴样式
WaterDropHeader(
waterDropColor: Colors.blue, // 水滴颜色
idleIcon: Icon(Icons.autorenew, size: 25), // 空闲图标
complete: Icon(Icons.done, size: 25), // 完成图标
refresh: CircularProgressIndicator( // 刷新中图标
strokeWidth: 2.0,
valueColor: AlwaysStoppedAnimation(Colors.white),
),
)
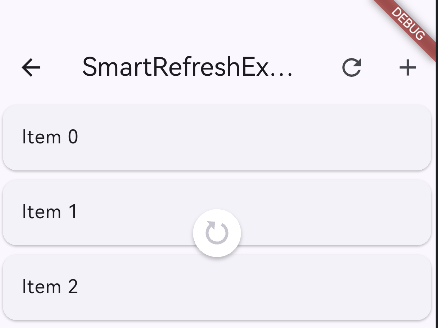
3) MaterialClassicHeader(Material 风格)
MaterialClassicHeader(
color: Colors.blue, // 颜色
backgroundColor: Colors.white, // 背景色
distance: 40.0, // 触发距离
)
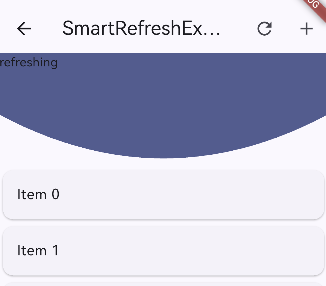
4) BezierHeader(贝塞尔曲线)
BezierHeader(
bezierColor: Theme.of(context).primaryColor, // 颜色
child: child: Text('refreshing'), // 自定义内容
)
5) WaterDropMaterialHeader(Material 水滴)
WaterDropMaterialHeader(
backgroundColor: Colors.white, // 背景色
color: Theme.of(context).primaryColor, // 颜色
)
5、详解Footer
1)ClassicFooter
ClassicFooter(
height: 60.0, // 高度
loadStyle: LoadStyle.ShowAlways, // 显示方式
textStyle: TextStyle(color: Colors.grey), // 文本样式
failedIcon: Icon(Icons.error, color: Colors.red),
noDataIcon: Icon(Icons.inbox, color: Colors.grey),
canLoadingIcon: Icon(Icons.arrow_upward, color: Colors.grey),
idleIcon: Icon(Icons.arrow_downward, color: Colors.grey),
loadingIcon: SizedBox(
width: 25.0,
height: 25.0,
child: CircularProgressIndicator(strokeWidth: 2.0),
),
// 文本
idleText: "上拉加载",
canLoadingText: "释放加载更多",
loadingText: "正在加载...",
noDataText: "没有更多数据了",
failedText: "加载失败,点击重试",
)2)CustomFooter
CustomFooter(
builder: (BuildContext context, LoadStatus? mode) {
Widget body;
if (mode == LoadStatus.idle) {
body = Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(Icons.arrow_upward, color: Colors.grey),
SizedBox(width: 10),
Text("上拉加载", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.grey)),
],
);
} else if (mode == LoadStatus.loading) {
body = Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
SizedBox(
width: 20,
height: 20,
child: CircularProgressIndicator(strokeWidth: 2),
),
SizedBox(width: 10),
Text("正在加载...", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.grey)),
],
);
} else if (mode == LoadStatus.failed) {
body = Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(Icons.error_outline, color: Colors.red),
SizedBox(width: 10),
Text("加载失败,点击重试", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.red)),
],
);
} else if (mode == LoadStatus.canLoading) {
body = Text("释放加载更多");
} else {
body = Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(Icons.done_all, color: Colors.green),
SizedBox(width: 10),
Text("没有更多数据了", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.green)),
],
);
}
return Container(
height: 55.0,
child: Center(child: body),
);
},
)6、使用建议
- 对于简单需求,使用
ClassicHeader和ClassicFooter - 需要 Material 风格时,使用
MaterialClassicHeader - 需要高度定制时,使用
CustomHeader和CustomFooter - 注意处理空状态和错误状态
- 合理使用控制器管理状态
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容









所有评论(0)