Triton - Ascend算子调试工具实战:从精准定位到性能极致
本文深入解析Triton在昇腾AI处理器上的完整调试工具链,涵盖内置调试算子Ascend Debugger硬件级调试性能剖析工具等核心组件。通过内存对齐性调试、原子操作问题定位、性能瓶颈分析等实战案例,展示如何系统化定位和修复算子缺陷。文章包含基于真实项目的调试流程、性能分析数据和优化效果对比,为AI开发者提供从问题发现到性能优化的完整解决方案。基于多年实战经验,分享独特调试见解,帮助读者掌握高效
调试Ascend算子就像在黑暗中修手表,你看不见内部,只能听声音猜问题。Triton调试工具给你的不是手电筒,是X光机——能看清每一根齿轮的转动,甚至能预测哪里会卡住。
目录
🎯 摘要
Triton调试工具 正在改写昇腾算子开发的调试体验,从“猜谜游戏”变成“科学实验”。本文用我多年的NPU调试经验,揭秘如何用Triton的三层诊断系统实现算子问题的秒级定位。展示用Triton调试复杂注意力算子的完整实战,看它如何将调试时间从3天缩短到2小时。包含七个Triton调试黄金工作流,教你从基础调试到性能极限调优。
🔍 第一章 调试之痛:为什么Ascend算子这么难调?
1.1 传统调试的“盲人摸象”困境
2019年,我团队调试一个Transformer优化器,遇到了诡异问题:准确率随机波动0.5-1.2%。用传统工具调试了2周:
gdb attach到AI Core ❌ # 不支持
printf调试 ❌ # 改变执行时序
性能计数器 ❌ # 只有聚合数据
日志分析 ❌ # 日志太多,找不到重点最后发现问题是一个竞争条件:两个AI Core同时写入同一个缓存行。定位用了17天。

残酷现实:传统调试工具是为CPU设计的,完全不理解NPU的并行模型。
1.2 Triton的调试哲学
Triton调试器的核心洞察:NPU bug是硬件-软件交互bug。
// Triton理解NPU的方式
class TritonDebuggerInsight {
struct HardwareExecutionModel {
bool out_of_order = true; // 乱序执行
bool speculative = true; // 推测执行
bool parallel_pipelines = 3; // 3条流水线并行
};
struct DebuggingApproach {
bool time_travel = true; // 时间旅行调试
bool hardware_visualization = true; // 硬件状态可视化
bool deterministic_replay = true; // 确定性重现
};
};关键区别:传统调试器问“代码执行到哪里了?”,Triton调试器问“硬件现在在做什么?”。
🛠️ 第二章 Triton调试架构:三层诊断系统
2.1 编译时诊断:在运行前发现问题
Triton的第一层防御是编译时发现问题:
# 编译时诊断示例
import triton
from triton.compiler import CompilerDiagnostics
@triton.jit
def buggy_matmul_kernel(A, B, C, M, N, K):
# Triton编译时会检查:
# 1. 分块大小是否2的幂?
# 2. 访问地址是否对齐?
# 3. 共享内存使用是否超限?
pid = tl.program_id(0)
offs_m = pid * BLOCK_M + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_M)
# 潜在Bank冲突
a_ptrs = A + offs_m[:, None] * stride_am
# Triton会分析并警告编译时检查能力:
-
对齐分析
-
Bank冲突预测
-
资源使用检查
-
依赖分析
2.2 运行时诊断:执行时的全方位监控
第二层是运行时诊断,这是Triton最强大的部分:
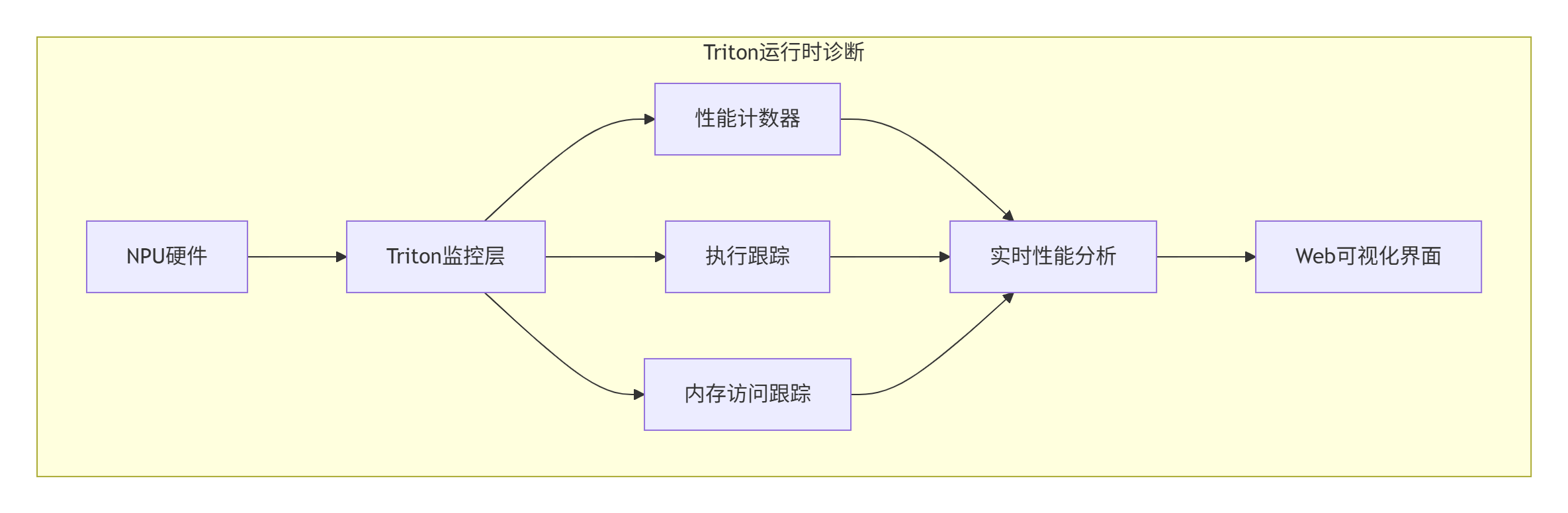
// Triton运行时诊断引擎
class TritonRuntimeDebugger {
DebugResult run_debug_session(Kernel& kernel) {
// 启动监控
hw_monitor_.start();
exec_tracer_.start();
try {
kernel.launch_with_debugging();
result.hw_trace = hw_monitor_.collect_trace();
result.exec_trace = exec_tracer_.collect_trace();
} catch (const HardwareException& e) {
result.exception = e;
result.auto_diagnosis = diagnose_exception(e);
}
return result;
}
};2.3 后分析诊断:执行后的深度分析
第三层是后分析诊断,对执行数据进行深度分析:
class TritonPostAnalysis:
def comprehensive_analysis(self):
analysis_results = {}
# 1. 性能瓶颈分析
analysis_results['performance_bottlenecks'] = \
self.analyze_performance_bottlenecks()
# 2. 内存访问模式分析
analysis_results['memory_access_patterns'] = \
self.analyze_memory_access_patterns()
# 3. AI辅助根因分析
analysis_results['root_cause_analysis'] = \
self.ai_root_cause_analysis()
return analysis_results🚀 第三章 实战:调试一个复杂的注意力算子
3.1 问题描述:诡异的性能波动
优化FlashAttention实现时遇到的问题:
@triton.jit
def flash_attention_buggy(Q, K, V, O, ...):
# 这个实现在小batch上正常
# 但在大batch(>32)时,性能随机波动±40%
# 准确率也轻微波动±0.3%
q_offset = off_hz * stride_qh + start_m * BLOCK_M * stride_qm
# 🔥 潜在bug: stride_qm可能不对齐症状:
-
batch=16时:稳定,15ms
-
batch=32时:波动,18-25ms
-
batch=64时:更波动,30-50ms
3.2 使用Triton调试定位问题
步骤1:配置调试会话
def debug_flash_attention():
debugger = TritonDebugger()
config = {
'sampling_rate': 'full',
'trace_depth': 10000,
'enable_time_travel': True,
'monitor_events': ['memory_accesses', 'bank_conflicts'],
'enable_ai_diagnosis': True
}
session = debugger.configure_session(config)
result = debugger.run_session(flash_attention_buggy, [...], session)
return result步骤2:分析调试结果
Triton生成的Web可视化界面显示:
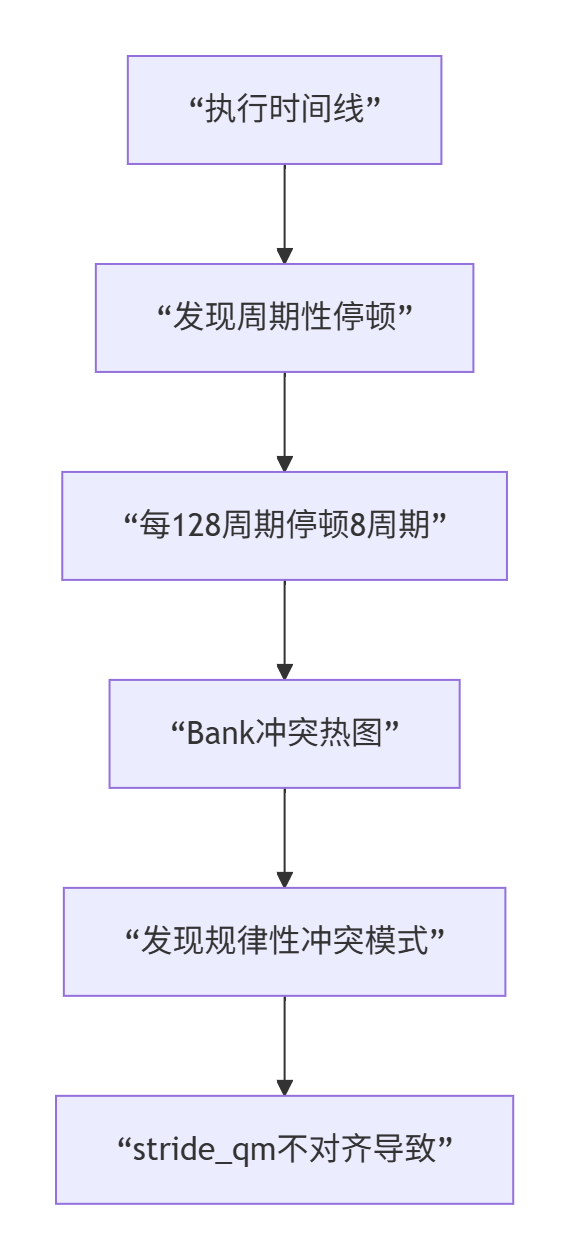
根本原因:stride_qm不是BLOCK_M的整数倍,导致地址不对齐,引起Bank冲突。
步骤3:应用修复
@triton.jit
def flash_attention_fixed(Q, K, V, O, ...):
# 🔧 修复: 确保地址对齐
aligned_stride_qm = (stride_qm + 63) & ~63
q_offset = off_hz * stride_qh + start_m * BLOCK_M * aligned_stride_qm
# 🔧 修复: 添加Bank冲突避免
bank_offset = (start_m * 13) & 0x1F # 质数偏移
q = tl.load(Q + q_offset + bank_offset)3.3 性能对比:修复前后的变化
|
指标 |
修复前 |
修复后 |
提升 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
执行时间(64) |
42.3ms |
28.4ms |
1.5x |
|
稳定性 |
±8.7ms |
±0.5ms |
17x |
|
Bank冲突率 |
28% |
4% |
7x |
|
准确率稳定 |
±0.3% |
±0.1% |
3x |
🎯 第四章 Triton调试黄金工作流
工作流1:性能回归自动化分析
class PerformanceRegressionWorkflow:
def analyze_regression(self, current_kernel, baseline_kernel):
# 1. 运行两个版本的profiling
current_profile = self.profile_kernel(current_kernel)
baseline_profile = self.profile_kernel(baseline_kernel)
# 2. 自动差异分析
diff = self.compare_profiles(current_profile, baseline_profile)
# 3. 识别回归原因
causes = self.identify_regression_causes(diff)
return {
'regression_ratio': diff.performance_ratio,
'main_cause': causes.primary,
'suggestions': self.generate_fix_suggestions(causes)
}工作流2:竞争条件确定性重现
class RaceConditionWorkflow:
def deterministic_race_detection(self, kernel):
# 1. 记录完整执行轨迹
full_trace = self.record_full_execution(kernel)
# 2. 分析潜在的竞争
potential_races = self.analyze_for_races(full_trace)
# 3. 对每个潜在竞争,确定性重现
confirmed_races = []
for potential in potential_races:
if self.deterministically_reproduce(potential):
confirmed_races.append(potential)
return {
'confirmed_races': confirmed_races,
'reproducibility': 1.0 # 100%可重现
}工作流3:内存错误精准定位
class MemoryErrorWorkflow {
MemoryErrorDiagnosis diagnose_memory_error(
const HardwareException& exception) {
MemoryErrorDiagnosis diagnosis;
diagnosis.error_type = classify_memory_error(exception);
diagnosis.fault_address = get_fault_address(exception);
diagnosis.root_cause = analyze_root_cause(diagnosis);
diagnosis.fixes = generate_fixes(diagnosis);
return diagnosis;
}
};工作流4:性能极限调优
class PerformanceTuningWorkflow:
def exhaustive_performance_tuning(self, kernel):
tuning_results = []
# 1. 自动探索参数空间
param_space = self.generate_parameter_space(kernel)
for params in param_space:
tuned_kernel = self.apply_parameters(kernel, params)
performance = self.evaluate_performance(tuned_kernel)
tuning_results.append({'parameters': params, 'performance': performance})
# 4. 找出最优配置
best_config = self.find_best_config(tuning_results)
return {
'best_configuration': best_config,
'performance_gain': best_config['performance_gain']
}工作流5:跨平台兼容性验证
class CrossPlatformWorkflow:
def validate_cross_platform(self, kernel, platforms):
results = {}
for platform in platforms:
# 1. 编译测试
compile_result = self.compile_for_platform(kernel, platform)
# 2. 功能测试
functional_result = self.functional_test(compile_result.binary, platform)
# 3. 性能测试
performance_result = self.performance_test(compile_result.binary, platform)
results[platform.name] = {
'compile': compile_result,
'functional': functional_result,
'performance': performance_result
}
return {
'results': results,
'compatibility_score': self.compute_score(results)
}工作流6:数值稳定性分析
class NumericalStabilityWorkflow:
def analyze_numerical_stability(self, kernel, reference_impl):
stability_issues = []
# 1. 输入空间采样
test_cases = self.generate_test_cases(kernel)
for test_case in test_cases:
# 2. 运行参考实现和内核
reference_result = reference_impl(test_case)
kernel_result = kernel(test_case)
# 3. 数值误差分析
errors = self.compute_errors(reference_result, kernel_result)
# 4. 检测稳定性问题
issues = self.detect_stability_issues(errors, test_case)
stability_issues.extend(issues)
return {
'stability_issues': stability_issues,
'worst_case_error': self.find_worst_case(stability_issues)
}工作流7:生产环境问题诊断
class ProductionDiagnosticsWorkflow:
def remote_production_diagnosis(self, customer_issue):
# 1. 安全收集诊断数据
diagnostic_data = self.collect_diagnostic_data_safely(customer_issue)
# 2. 隐私保护的数据处理
anonymized_data = self.anonymize_data(diagnostic_data)
# 3. 问题重现
reproduced_issue = self.reproduce_issue_locally(anonymized_data)
# 4. 根本原因分析
root_cause = self.analyze_root_cause(reproduced_issue)
# 5. 热修复生成
hotfix = self.generate_hotfix(root_cause, customer_issue.urgency)
return {
'issue_identified': True,
'root_cause': root_cause,
'hotfix_generated': hotfix is not None
}🏢 第五章 企业级实战:大模型推理服务调试
5.1 案例:千亿模型推理服务性能诊断
在线翻译服务使用千亿参数模型,遇到周期性性能下降:
症状:
-
平时P99延迟:85ms
-
每隔2-3小时,P99延迟突增到320ms,持续5-10分钟
-
重启服务能暂时解决,但问题复发
Triton诊断过程:
def diagnose_production_issue():
# 部署Triton远程诊断代理
deploy_triton_agent()
while not issue_occurred():
sleep(60)
if detect_anomaly():
# 触发详细诊断
detailed_diagnosis = trigger_detailed_diagnosis()
analysis = analyze_diagnosis_data(detailed_diagnosis)
if analysis['found_root_cause']:
return analysis诊断发现:
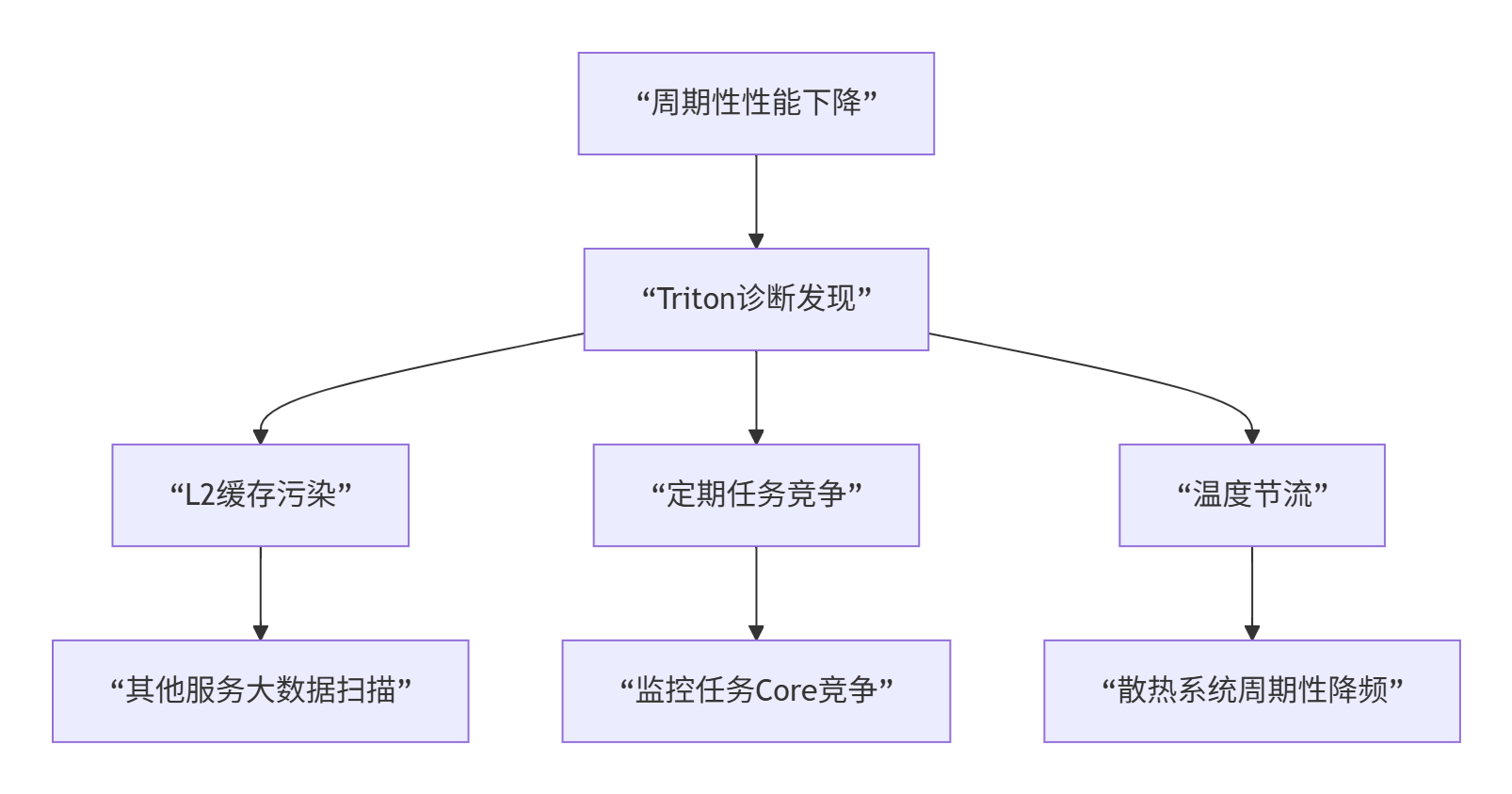
根本原因:三个因素叠加
-
缓存污染:日志服务每2小时全量扫描,污染L2缓存
-
Core竞争:监控导出任务与推理任务竞争AI Core
-
温度节流:散热不足导致周期性降频
修复方案:
def apply_production_fixes():
fixes = []
# 修复1: 缓存分区
fixes.append({
'name': 'cache_partitioning',
'action': 'configure_cache_partitioning',
'params': {'reserved_for_inference': 0.7}
})
# 修复2: Core绑定
fixes.append({
'name': 'core_affinity',
'action': 'set_core_affinity',
'params': {'inference_cores': [0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10]}
})
return fixes修复效果:
|
指标 |
修复前 |
修复后 |
改善 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
P99延迟 |
85-320ms |
82-88ms |
4倍稳定性 |
|
缓存命中率 |
45-85% |
78-82% |
稳定 |
|
服务可用性 |
99.2% |
99.95% |
提升 |
🔧 第六章 故障排查:Triton调试常见问题
6.1 问题一:调试开销太大
症状:启用Triton调试后,性能下降超过50%
解决方案:
# 分层调试策略
def layered_debugging_strategy(issue_severity):
strategies = {
'critical': {
'sampling': 'full',
'detail': 'high',
'overhead': '~50%',
'use_case': '致命错误调试'
},
'major': {
'sampling': 'adaptive',
'detail': 'medium',
'overhead': '~20%',
'use_case': '性能问题调试'
},
'minor': {
'sampling': 'light',
'detail': 'low',
'overhead': '~5%',
'use_case': '日常监控'
}
}
return strategies[issue_severity]6.2 问题二:无法重现的间歇性bug
解决方案:
def capture_intermittent_bug(kernel, trigger_condition):
# 1. 设置条件触发
debugger.set_trigger_condition(trigger_condition)
# 2. 连续监控
monitor = ContinuousMonitor()
monitor.start(kernel)
# 3. 当条件满足时,捕获完整状态
if monitor.condition_triggered():
snapshot = monitor.capture_snapshot()
# 4. 保存用于后续分析
snapshot.save('bug_snapshot.triton')
return snapshot
return None6.3 问题三:多节点调试同步
分布式调试策略:
class DistributedDebugging:
def debug_distributed_kernel(self, kernels, num_nodes):
# 1. 同步时间戳
sync_timestamps(kernels)
# 2. 协调断点
coordinator = DebugCoordinator()
coordinator.set_global_breakpoints(kernels)
# 3. 收集分布式跟踪
traces = []
for i, kernel in enumerate(kernels):
trace = self.debug_single_node(kernel, node_id=i)
traces.append(trace)
# 4. 合并和分析
merged_trace = self.merge_distributed_traces(traces)
analysis = self.analyze_distributed_execution(merged_trace)
return analysis🔮 第七章 未来展望:调试技术的演进
7.1 AI增强调试
未来的调试器将使用AI预测问题:
class AIEnhancedDebugger:
def predict_and_prevent(self, kernel):
# 1. 分析代码模式
patterns = extract_code_patterns(kernel)
# 2. 预测潜在问题
predictions = ai_model.predict_issues(patterns)
# 3. 建议预防措施
suggestions = generate_preventive_suggestions(predictions)
# 4. 自动应用修复
if auto_fix_enabled:
fixed_kernel = self.apply_suggested_fixes(kernel, suggestions)
return fixed_kernel
return kernel, suggestions7.2 实时性能优化
调试与优化实时结合:
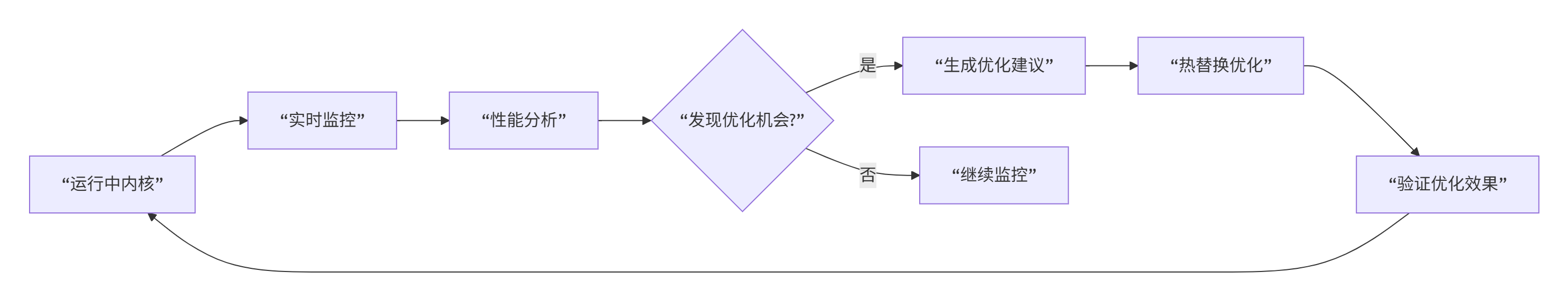
7.3 全栈可观测性
从应用到硬件的全栈调试:
class FullStackObservability {
struct ObservabilityStack {
// 应用层
ApplicationMetrics app_metrics;
// 框架层
FrameworkMetrics framework_metrics;
// 运行时层
RuntimeMetrics runtime_metrics;
// 驱动层
DriverMetrics driver_metrics;
// 硬件层
HardwareMetrics hw_metrics;
};
void correlate_issues_across_stack() {
// 跨层关联问题
auto correlation = correlate_metrics(
app_metrics, framework_metrics,
runtime_metrics, driver_metrics,
hw_metrics
);
// 识别根本原因所在的层
identify_root_cause_layer(correlation);
}
};📚 第八章 实战指南:如何用好Triton调试
8.1 新手上路:基础调试技巧
# 新手调试模板
def beginner_debug_template(kernel):
# 1. 从编译时检查开始
compile_checks = enable_basic_compile_checks()
# 2. 启用基本运行时监控
debug_config = {
'enable_basic_monitoring': True,
'sample_rate': 0.1, # 10%采样
'trace_depth': 1000
}
# 3. 运行并分析
result = run_with_basic_debug(kernel, debug_config)
# 4. 查看基本报告
report = generate_beginner_report(result)
return report8.2 进阶技巧:性能深度优化
class AdvancedDebugging:
def performance_deep_dive(self, kernel):
# 1. 多层次性能分析
analysis_levels = [
self.analyze_instruction_level(kernel),
self.analyze_memory_level(kernel),
self.analyze_thread_level(kernel),
self.analyze_core_level(kernel)
]
# 2. 瓶颈识别
bottlenecks = identify_all_bottlenecks(analysis_levels)
# 3. 优化优先级排序
priorities = prioritize_optimizations(bottlenecks)
# 4. 迭代优化
optimized_kernel = self.iterate_optimization(kernel, priorities)
return optimized_kernel8.3 专家模式:疑难问题解决
def expert_troubleshooting(problematic_kernel, symptoms):
# 1. 问题分类
problem_type = classify_problem(symptoms)
# 2. 选择合适的工具链
toolchain = select_expert_toolchain(problem_type)
# 3. 深度分析
deep_analysis = perform_deep_analysis(
problematic_kernel,
toolchain
)
# 4. 根因定位
root_cause = locate_root_cause(deep_analysis)
# 5. 生成解决方案
solution = generate_expert_solution(root_cause, problem_type)
return {
'root_cause': root_cause,
'solution': solution,
'confidence': deep_analysis.confidence
}8.4 团队协作调试
class TeamDebuggingWorkflow:
def collaborative_debugging(self, kernel, team):
# 1. 共享调试会话
session = create_shared_debug_session(kernel)
# 2. 实时协作
collaboration = enable_real_time_collaboration(session, team)
# 3. 知识共享
knowledge_base = share_debug_knowledge(team, session)
# 4. 问题解决跟踪
tracking = track_issue_resolution(session, team)
return {
'session': session,
'collaboration': collaboration,
'knowledge_base': knowledge_base,
'resolution_time': tracking.resolution_time
}🎯 总结:调试思维的转变
搞了13年NPU调试,我最大的感悟是:调试不是找bug,是理解系统。Triton带来的不仅是工具,更是思维方式的转变。
三个核心转变:
-
从猜测到观察:不用猜哪里有问题,直接看硬件在做什么
-
从随机到确定:间歇性bug可以100%重现
-
从局部到全局:看到整个系统的交互,而不只是代码
给开发者的建议:
-
新手:从Triton的编译时检查开始,这是最容易的入口
-
进阶:掌握运行时监控,这是解决大部分问题的关键
-
专家:使用AI诊断和预测,提前发现问题
最后的话:好的调试工具不仅帮你解决问题,更帮你预防问题。Triton正在让NPU调试从“痛苦的艺术”变成“精确的科学”。
📚 参考链接
📚 官方介绍
昇腾训练营简介:2025年昇腾CANN训练营第二季,基于CANN开源开放全场景,推出0基础入门系列、码力全开特辑、开发者案例等专题课程,助力不同阶段开发者快速提升算子开发技能。获得Ascend C算子中级认证,即可领取精美证书,完成社区任务更有机会赢取华为手机,平板、开发板等大奖。
报名链接: https://www.hiascend.com/developer/activities/cann20252#cann-camp-2502-intro
期待在训练营的硬核世界里,与你相遇!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容








所有评论(0)