将小智 AI 打造为可扩展、可编程的 “第二大脑“
本文系统介绍了基于小智AI构建"第二大脑"的开发实践,涵盖三大核心项目:1)智能家居控制系统,实现语音指令解析与设备联动;2)AI对话系统,集成意图识别与上下文管理;3)插件化功能扩展系统,支持模块化开发。通过详细的技术架构、代码实现和Prompt工程示例,展示了如何将小智AI打造为可扩展的智能中枢。文章还提供了Docker部署方案和性能监控方案,为开发者构建个性化AI系统提供
·
作为工程师,将小智 AI 打造为可扩展、可编程的 "第二大脑",不仅能大幅提升开发效率,更能构建个性化智能系统。本文将通过智能家居控制、AI 对话系统、功能扩展三大实战项目,结合代码实现、流程图解、Prompt 工程等维度,全面解析基于小智 AI 的开发方法论。
一、技术架构总览
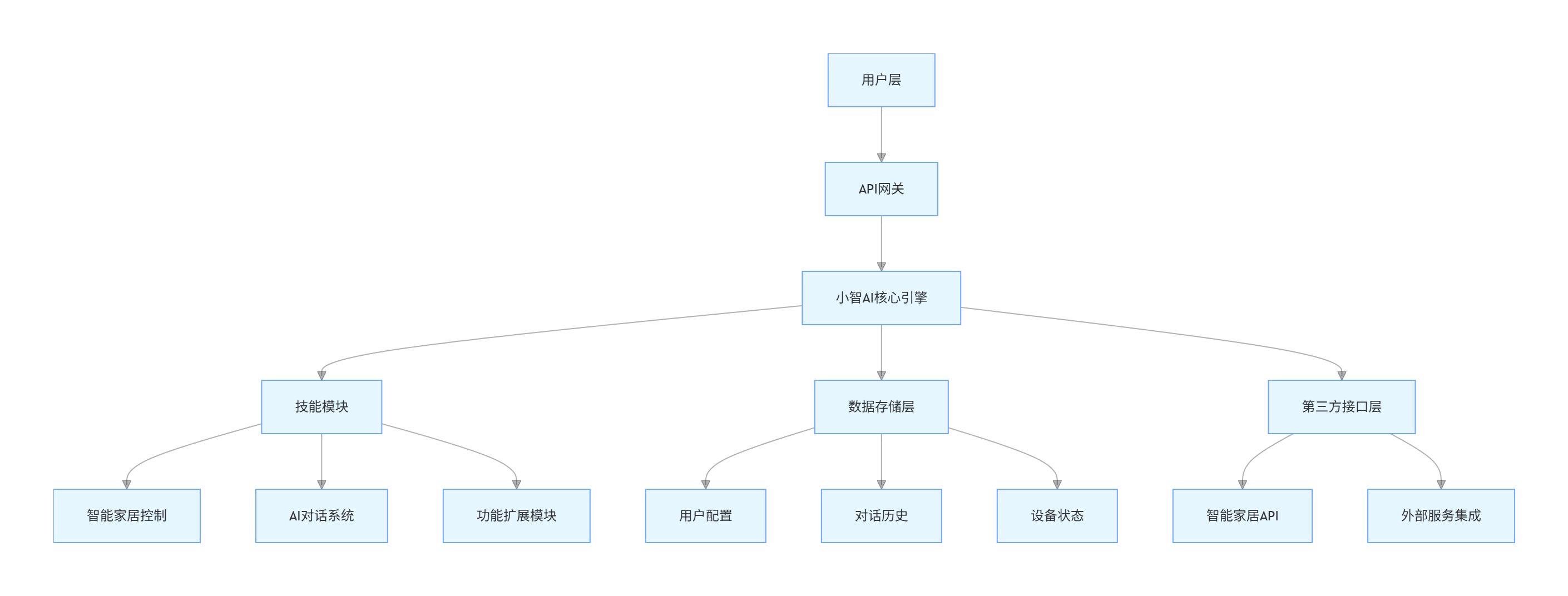
1.1 系统架构图
graph TD
A[用户层] --> B[API网关]
B --> C[小智AI核心引擎]
C --> D[技能模块]
D --> D1[智能家居控制]
D --> D2[AI对话系统]
D --> D3[功能扩展模块]
C --> E[数据存储层]
E --> E1[用户配置]
E --> E2[对话历史]
E --> E3[设备状态]
C --> F[第三方接口层]
F --> F1[智能家居API]
F --> F2[外部服务集成]
1.2 核心技术栈
| 技术领域 | 推荐选择 | 备选方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 编程语言 | Python 3.9+ | Node.js/Java |
| API 交互 | FastAPI | Flask/Django |
| 数据存储 | SQLite/Redis | MongoDB/PostgreSQL |
| 消息队列 | MQTT | RabbitMQ/Kafka |
| 前端展示 | Vue.js/React | Flutter |
二、实战项目一:智能家居控制系统
2.1 系统设计
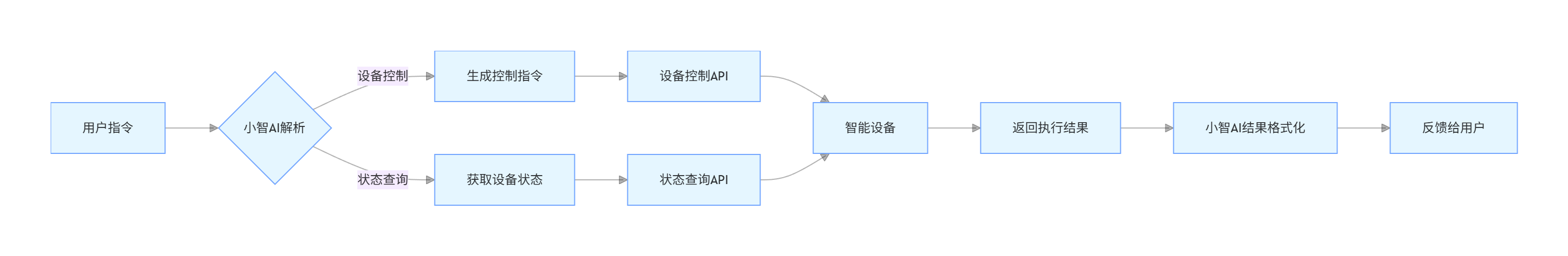
2.1.1 功能流程图
flowchart LR
A[用户指令] --> B{小智AI解析}
B -->|设备控制| C[生成控制指令]
B -->|状态查询| D[获取设备状态]
C --> E[设备控制API]
D --> F[状态查询API]
E --> G[智能设备]
F --> G
G --> H[返回执行结果]
H --> I[小智AI结果格式化]
I --> J[反馈给用户]
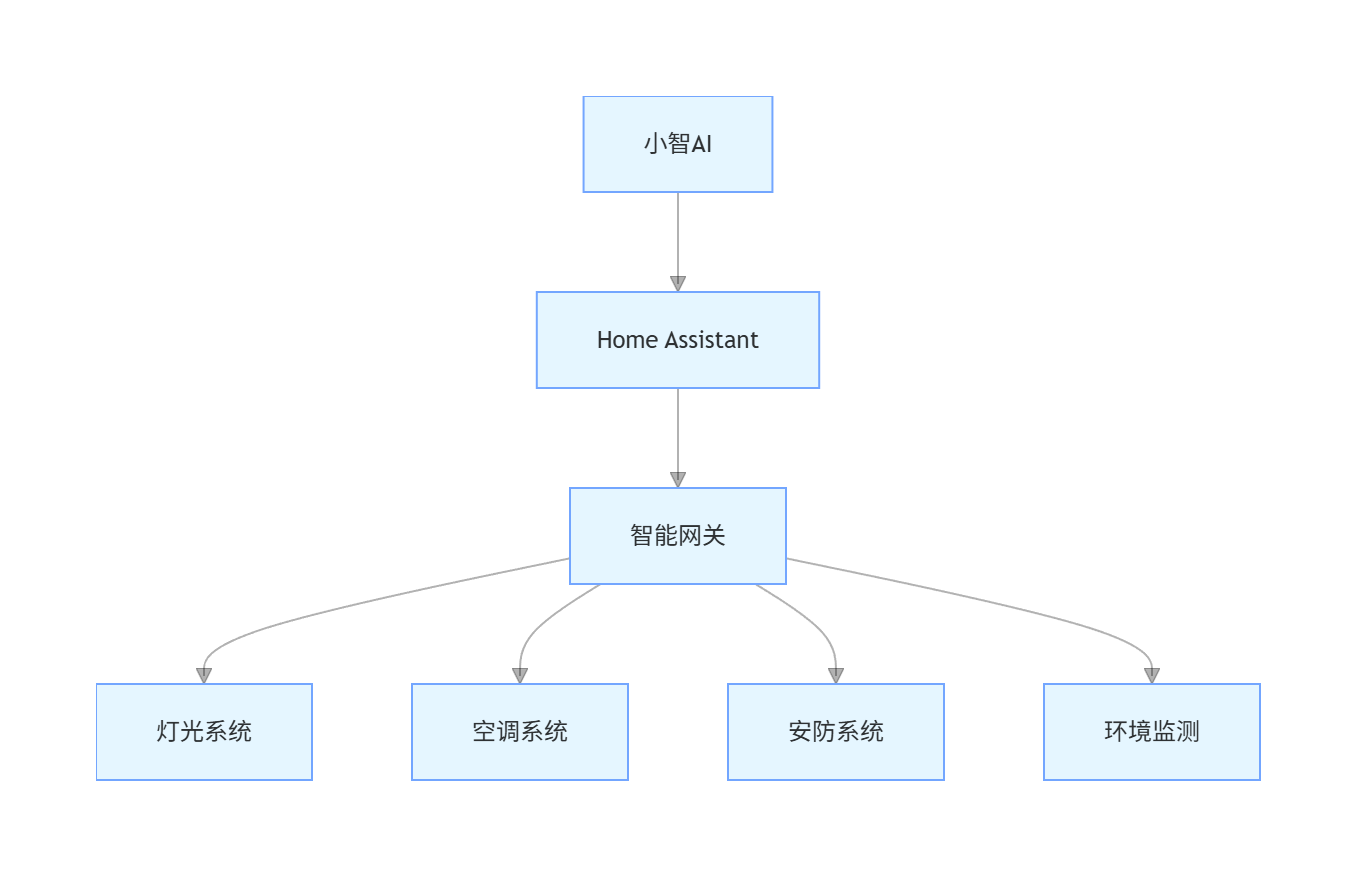
2.1.2 硬件架构
graph TD
A[小智AI] --> B[Home Assistant]
B --> C[智能网关]
C --> D[灯光系统]
C --> E[空调系统]
C --> F[安防系统]
C --> G[环境监测]
2.2 代码实现
2.2.1 小智 AI 交互模块
python
运行
import requests
import json
from datetime import datetime
class XiaoZhiClient:
def __init__(self, api_key, base_url="https://api.xiaozhi.com/v1"):
self.api_key = api_key
self.base_url = base_url
self.headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
def send_message(self, message, user_id="default_user", context=None):
"""发送消息给小智AI并获取回复"""
payload = {
"message": message,
"user_id": user_id,
"context": context or [],
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()
}
response = requests.post(
f"{self.base_url}/chat/completions",
headers=self.headers,
json=payload
)
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.json()
else:
raise Exception(f"API请求失败: {response.status_code} - {response.text}")
def parse_home_command(self, ai_response):
"""解析小智AI返回的智能家居指令"""
# 提取AI回复中的结构化数据
try:
# 假设AI返回的content中包含JSON格式的指令
content = ai_response.get("choices", [{}])[0].get("message", {}).get("content", "")
# 使用Prompt工程让AI返回标准化的JSON
if "{" in content and "}" in content:
json_start = content.index("{")
json_end = content.rindex("}") + 1
command_data = json.loads(content[json_start:json_end])
return command_data
else:
return {"type": "text", "content": content}
except Exception as e:
print(f"解析指令失败: {e}")
return {"type": "text", "content": ai_response}
2.2.2 智能家居控制模块
python
运行
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
import json
from typing import Dict, Any
class SmartHomeController:
def __init__(self, mqtt_broker="localhost", mqtt_port=1883):
self.mqtt_client = mqtt.Client()
self.mqtt_broker = mqtt_broker
self.mqtt_port = mqtt_port
self.device_states = {}
# 连接MQTT
self.mqtt_client.on_connect = self.on_connect
self.mqtt_client.on_message = self.on_message
self.mqtt_client.connect(mqtt_broker, mqtt_port, 60)
self.mqtt_client.loop_start()
def on_connect(self, client, userdata, flags, rc):
print(f"MQTT连接成功,状态码: {rc}")
client.subscribe("smarthome/#")
def on_message(self, client, userdata, msg):
"""处理设备状态更新"""
try:
payload = json.loads(msg.payload.decode())
self.device_states[msg.topic] = payload
print(f"设备状态更新: {msg.topic} = {payload}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理消息失败: {e}")
def control_device(self, device_type: str, device_id: str, action: str, params: Dict[str, Any] = None):
"""控制智能设备"""
topic = f"smarthome/{device_type}/{device_id}/command"
payload = {
"action": action,
"params": params or {},
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()
}
result = self.mqtt_client.publish(topic, json.dumps(payload))
status = result[0]
if status == 0:
return {"success": True, "message": f"已发送指令到 {device_type} {device_id}"}
else:
return {"success": False, "message": f"发送指令失败,状态码: {status}"}
def get_device_status(self, device_type: str = None, device_id: str = None):
"""获取设备状态"""
if device_type and device_id:
topic = f"smarthome/{device_type}/{device_id}/status"
return self.device_states.get(topic, {"status": "unknown"})
elif device_type:
return {k: v for k, v in self.device_states.items() if k.startswith(f"smarthome/{device_type}/")}
else:
return self.device_states
2.2.3 主程序集成
python
运行
def main():
# 初始化组件
xiaozhi_client = XiaoZhiClient(api_key="your_api_key_here")
home_controller = SmartHomeController()
# 对话循环
print("智能家居控制系统已启动,输入'exit'退出")
while True:
user_input = input("你: ")
if user_input.lower() == "exit":
break
# 发送消息给小智AI
ai_response = xiaozhi_client.send_message(user_input)
# 解析指令
command = xiaozhi_client.parse_home_command(ai_response)
# 执行指令
if command.get("type") == "device_control":
device_type = command.get("device_type")
device_id = command.get("device_id")
action = command.get("action")
params = command.get("params", {})
result = home_controller.control_device(device_type, device_id, action, params)
print(f"小智: {result['message']}")
elif command.get("type") == "status_query":
device_type = command.get("device_type")
device_id = command.get("device_id")
status = home_controller.get_device_status(device_type, device_id)
print(f"小智: 当前设备状态:\n{json.dumps(status, indent=2)}")
else:
print(f"小智: {command.get('content', '无法识别的指令')}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2.3 Prompt 工程设计
2.3.1 系统 Prompt
plaintext
你是一个智能家居控制专家,需要解析用户指令并返回标准化的JSON格式响应。
指令类型包括:
1. device_control - 设备控制
2. status_query - 状态查询
3. text - 普通文本回复
返回格式要求:
{
"type": "指令类型",
"device_type": "设备类型(如light/aircon/curtain)",
"device_id": "设备ID(如livingroom/bedroom)",
"action": "操作动作(如on/off/set_temp)",
"params": {"参数名": "参数值"},
"content": "文本回复内容"
}
只返回JSON数据,不要额外解释。如果无法识别为设备控制或状态查询,type设为text。
2.3.2 用户指令示例及响应
| 用户指令 | AI 响应 |
|---|---|
| "打开客厅灯" | {"type":"device_control","device_type":"light","device_id":"livingroom","action":"on","params":{},"content":"已为你打开客厅灯"} |
| "把卧室空调调到 26 度" | {"type":"device_control","device_type":"aircon","device_id":"bedroom","action":"set_temp","params":{"temperature":26},"content":"已将卧室空调温度设置为26度"} |
| "查看所有设备状态" | {"type":"status_query","device_type":"all","device_id":"all","action":"query","params":{},"content":"正在查询所有设备状态..."} |
| "今天天气怎么样" | {"type":"text","content":"今天天气晴朗,气温25-32度"} |
2.4 系统测试与优化
2.4.1 测试用例设计
python
运行
import unittest
from unittest.mock import Mock, patch
class TestSmartHomeSystem(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.xiaozhi_client = XiaoZhiClient(api_key="test_key")
self.home_controller = SmartHomeController(mqtt_broker="test_broker")
@patch('requests.post')
def test_message_parsing(self, mock_post):
# 模拟AI响应
mock_response = Mock()
mock_response.status_code = 200
mock_response.json.return_value = {
"choices": [{
"message": {
"content": '{"type":"device_control","device_type":"light","device_id":"livingroom","action":"on","params":{}}'
}
}]
}
mock_post.return_value = mock_response
# 测试解析
response = self.xiaozhi_client.send_message("打开客厅灯")
command = self.xiaozhi_client.parse_home_command(response)
self.assertEqual(command["type"], "device_control")
self.assertEqual(command["device_type"], "light")
def test_device_control(self):
# 测试设备控制
result = self.home_controller.control_device("light", "livingroom", "on")
self.assertTrue(result["success"])
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
三、实战项目二:AI 对话系统
3.1 系统架构设计
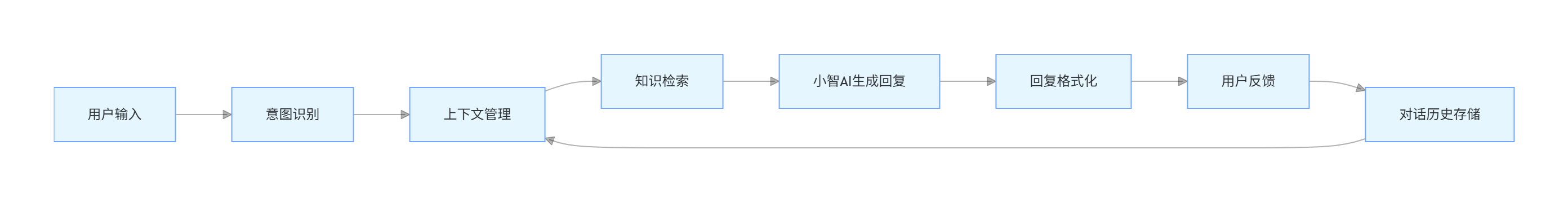
3.1.1 对话流程
flowchart LR
A[用户输入] --> B[意图识别]
B --> C[上下文管理]
C --> D[知识检索]
D --> E[小智AI生成回复]
E --> F[回复格式化]
F --> G[用户反馈]
G --> H[对话历史存储]
H --> C
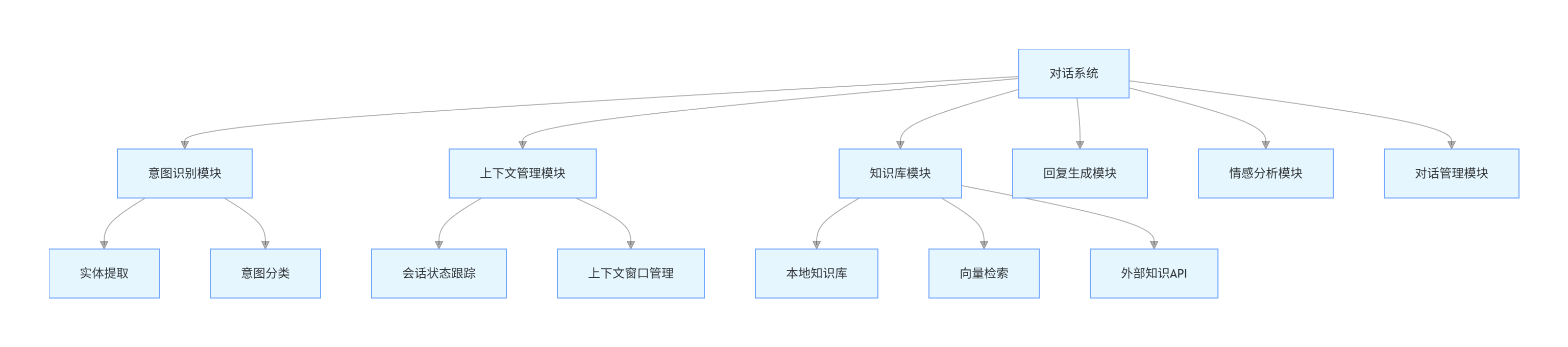
3.1.2 功能模块划分
graph TD
A[对话系统] --> B[意图识别模块]
A --> C[上下文管理模块]
A --> D[知识库模块]
A --> E[回复生成模块]
A --> F[情感分析模块]
A --> G[对话管理模块]
B --> B1[实体提取]
B --> B2[意图分类]
C --> C1[会话状态跟踪]
C --> C2[上下文窗口管理]
D --> D1[本地知识库]
D --> D2[向量检索]
D --> D3[外部知识API]
3.2 代码实现
3.2.1 上下文管理模块
python
运行
import json
from datetime import datetime
from collections import deque
class ContextManager:
def __init__(self, max_history=10):
self.conversations = {} # {user_id: deque}
self.max_history = max_history
def add_message(self, user_id, role, content, metadata=None):
"""添加消息到对话历史"""
if user_id not in self.conversations:
self.conversations[user_id] = deque(maxlen=self.max_history)
message = {
"role": role,
"content": content,
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"metadata": metadata or {}
}
self.conversations[user_id].append(message)
def get_context(self, user_id, limit=None):
"""获取对话上下文"""
if user_id not in self.conversations:
return []
history = list(self.conversations[user_id])
if limit:
history = history[-limit:]
return history
def clear_context(self, user_id):
"""清除用户对话历史"""
if user_id in self.conversations:
del self.conversations[user_id]
def get_context_summary(self, user_id, xiaozhi_client):
"""生成上下文摘要"""
if user_id not in self.conversations or len(self.conversations[user_id]) == 0:
return "无对话历史"
history_text = "\n".join([f"{msg['role']}: {msg['content']}"
for msg in self.conversations[user_id]])
prompt = f"请简要总结以下对话内容,控制在50字以内:\n{history_text}"
response = xiaozhi_client.send_message(prompt)
return response.get("choices", [{}])[0].get("message", {}).get("content", "")
3.2.2 意图识别模块
python
运行
import re
from enum import Enum
class IntentType(Enum):
CHAT = "chat" # 普通聊天
KNOWLEDGE = "knowledge" # 知识查询
TODO = "todo" # 待办事项
CALCULATE = "calculate" # 计算
UNKNOWN = "unknown" # 未知意图
class IntentRecognizer:
def __init__(self):
# 意图关键词配置
self.intent_keywords = {
IntentType.KNOWLEDGE: ["什么是", "解释", "定义", "原理", "为什么", "如何"],
IntentType.TODO: ["提醒", "待办", "任务", "计划", "安排"],
IntentType.CALCULATE: ["计算", "加", "减", "乘", "除", "等于", "+-*/"]
}
# 正则表达式模式
self.patterns = {
IntentType.CALCULATE: re.compile(r'\d+[\+\-\*\/]\d+'),
IntentType.TODO: re.compile(r'提醒我.*|记得.*|帮我.*')
}
def recognize(self, text):
"""识别用户意图"""
text_lower = text.lower()
# 检查关键词
for intent, keywords in self.intent_keywords.items():
if any(keyword in text_lower for keyword in keywords):
return intent
# 检查正则模式
for intent, pattern in self.patterns.items():
if pattern.search(text):
return intent
# 默认返回聊天意图
return IntentType.CHAT
def extract_entities(self, text, intent):
"""提取实体信息"""
entities = {"intent": intent.value}
if intent == IntentType.CALCULATE:
# 提取计算表达式
match = self.patterns[IntentType.CALCULATE].search(text)
if match:
entities["expression"] = match.group()
elif intent == IntentType.TODO:
# 提取待办事项内容
entities["content"] = text.replace("提醒我", "").replace("记得", "").strip()
return entities
3.2.3 对话系统主程序
python
运行
class AdvancedChatSystem:
def __init__(self, api_key):
self.xiaozhi_client = XiaoZhiClient(api_key)
self.context_manager = ContextManager(max_history=20)
self.intent_recognizer = IntentRecognizer()
self.knowledge_base = KnowledgeBase()
self.todo_manager = TodoManager()
def process_message(self, user_id, message):
"""处理用户消息"""
# 识别意图
intent = self.intent_recognizer.recognize(message)
entities = self.intent_recognizer.extract_entities(message, intent)
# 添加用户消息到上下文
self.context_manager.add_message(user_id, "user", message, {"intent": intent.value})
# 根据意图处理
if intent == IntentType.KNOWLEDGE:
# 知识查询
knowledge_result = self.knowledge_base.query(message)
prompt = f"基于以下知识回答问题:\n{knowledge_result}\n\n问题:{message}"
ai_response = self.xiaozhi_client.send_message(prompt, user_id,
self.context_manager.get_context(user_id, 5))
elif intent == IntentType.TODO:
# 待办事项管理
if "添加" in message or "创建" in message:
self.todo_manager.add_task(user_id, entities.get("content", message))
ai_response = {"choices": [{"message": {"content": "已添加到你的待办事项列表"}}]}
else:
tasks = self.todo_manager.get_tasks(user_id)
ai_response = {"choices": [{"message": {"content": f"你的待办事项:\n{tasks}"}}]}
elif intent == IntentType.CALCULATE:
# 计算处理
expression = entities.get("expression", "")
try:
# 安全的表达式计算
result = eval(expression) # 生产环境应使用更安全的计算方式
ai_response = {"choices": [{"message": {"content": f"{expression} = {result}"}}]}
except:
ai_response = self.xiaozhi_client.send_message(message, user_id,
self.context_manager.get_context(user_id, 5))
else:
# 普通聊天
ai_response = self.xiaozhi_client.send_message(message, user_id,
self.context_manager.get_context(user_id, 10))
# 提取AI回复
ai_message = ai_response.get("choices", [{}])[0].get("message", {}).get("content", "")
# 添加AI回复到上下文
self.context_manager.add_message(user_id, "assistant", ai_message)
return {
"response": ai_message,
"intent": intent.value,
"entities": entities
}
# 知识库和待办事项管理的简单实现
class KnowledgeBase:
def query(self, query):
# 实际应用中可以连接向量数据库或搜索引擎
return f"关于'{query}'的相关知识..."
class TodoManager:
def __init__(self):
self.tasks = {}
def add_task(self, user_id, task):
if user_id not in self.tasks:
self.tasks[user_id] = []
self.tasks[user_id].append({"task": task, "created": datetime.now().isoformat(), "completed": False})
def get_tasks(self, user_id):
return self.tasks.get(user_id, [])
# 使用示例
def chat_demo():
chat_system = AdvancedChatSystem(api_key="your_api_key_here")
print("高级AI对话系统已启动(输入'exit'退出)")
user_id = "test_user_001"
while True:
user_input = input("你: ")
if user_input.lower() == "exit":
break
result = chat_system.process_message(user_id, user_input)
print(f"小智: {result['response']}")
print(f"[意图: {result['intent']}]")
if __name__ == "__main__":
chat_demo()
3.3 Prompt 工程优化
3.3.1 多轮对话 Prompt
plaintext
你是一个智能对话助手,需要根据上下文进行连贯的对话。
要求:
1. 保持回复简洁明了,避免冗余
2. 记住对话历史中的关键信息
3. 根据用户意图提供专业回答
4. 对知识类问题提供准确信息
5. 保持友好的语气
当前对话历史:
{context}
用户当前问题:{user_message}
3.3.2 情感分析 Prompt
plaintext
分析用户消息的情感倾向,并返回JSON格式结果:
用户消息:{message}
返回格式:
{
"sentiment": "positive/negative/neutral",
"confidence": 0.0-1.0,
"emotion": "happy/sad/angry/surprise/fear/disgust/neutral",
"response_strategy": "回应策略建议"
}
3.4 性能优化
3.4.1 缓存机制实现
python
运行
import redis
import hashlib
from functools import wraps
class CacheManager:
def __init__(self, host="localhost", port=6379, db=0):
self.redis_client = redis.Redis(host=host, port=port, db=db)
def get_cache(self, key):
"""获取缓存"""
value = self.redis_client.get(key)
if value:
return json.loads(value)
return None
def set_cache(self, key, value, expire=3600):
"""设置缓存"""
self.redis_client.setex(key, expire, json.dumps(value))
def cache_decorator(self, expire=3600):
"""缓存装饰器"""
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 创建缓存键
key_parts = [func.__name__] + list(args) + [f"{k}={v}" for k, v in kwargs.items()]
key = hashlib.md5("|".join(map(str, key_parts)).encode()).hexdigest()
# 尝试获取缓存
cached = self.get_cache(key)
if cached is not None:
return cached
# 执行函数并缓存结果
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
self.set_cache(key, result, expire)
return result
return wrapper
return decorator
# 使用缓存优化知识库查询
cache_manager = CacheManager()
class OptimizedKnowledgeBase(KnowledgeBase):
@cache_manager.cache_decorator(expire=86400) # 缓存24小时
def query(self, query):
# 优化的知识查询实现
return super().query(query)
四、实战项目三:功能扩展系统
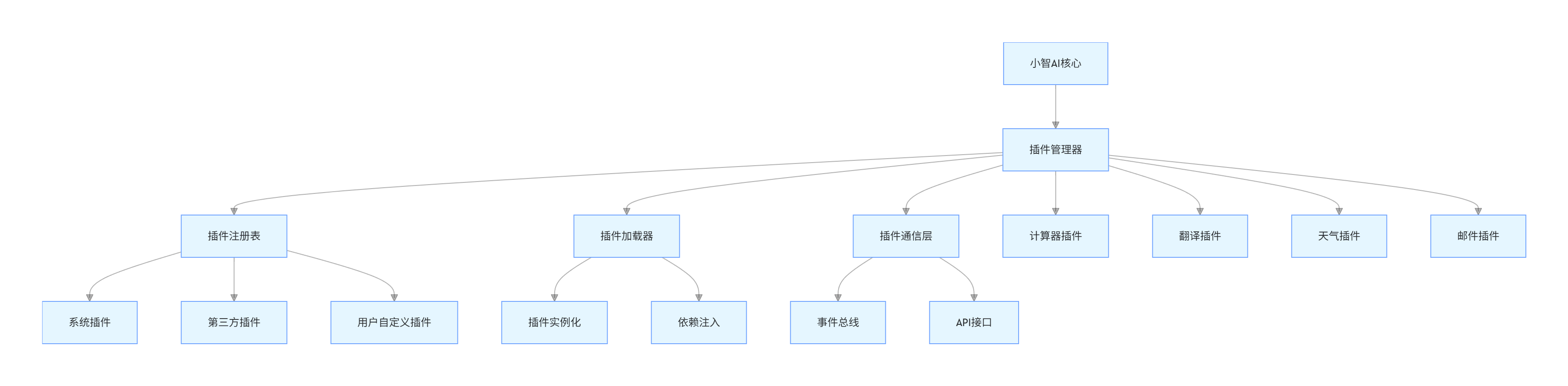
4.1 插件化架构设计
4.1.1 架构图
graph TD
A[小智AI核心] --> B[插件管理器]
B --> C[插件注册表]
B --> D[插件加载器]
B --> E[插件通信层]
C --> C1[系统插件]
C --> C2[第三方插件]
C --> C3[用户自定义插件]
D --> F[插件实例化]
D --> G[依赖注入]
E --> H[事件总线]
E --> I[API接口]
B --> J[计算器插件]
B --> K[翻译插件]
B --> L[天气插件]
B --> M[邮件插件]
4.1.2 插件生命周期
stateDiagram-v2
[*] --> Uninstalled
Uninstalled --> Installed: install()
Installed --> Loaded: load()
Loaded --> Activated: activate()
Activated --> Deactivated: deactivate()
Deactivated --> Loaded: activate()
Loaded --> Uninstalled: uninstall()
Activated --> [*]: error
4.2 代码实现
4.2.1 插件基类定义
python
运行
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Dict, Any, Optional
@dataclass
class PluginMetadata:
"""插件元数据"""
name: str
version: str
author: str
description: str
plugin_type: str
dependencies: list = None
config_schema: Dict[str, Any] = None
class BasePlugin(ABC):
"""插件基类"""
def __init__(self):
self.metadata = self.get_metadata()
self.config = {}
self.is_active = False
@abstractmethod
def get_metadata(self) -> PluginMetadata:
"""获取插件元数据"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def activate(self):
"""激活插件"""
self.is_active = True
@abstractmethod
def deactivate(self):
"""停用插件"""
self.is_active = False
@abstractmethod
def execute(self, command: str, params: Dict[str, Any] = None) -> Any:
"""执行插件功能"""
pass
def configure(self, config: Dict[str, Any]):
"""配置插件"""
self.config.update(config)
def get_status(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取插件状态"""
return {
"name": self.metadata.name,
"version": self.metadata.version,
"active": self.is_active,
"config": self.config
}
4.2.2 插件管理器实现
python
运行
import os
import importlib
import json
from pathlib import Path
from typing import List, Dict, Type
class PluginManager:
def __init__(self, plugin_dir: str = "plugins"):
self.plugin_dir = Path(plugin_dir)
self.plugins: Dict[str, BasePlugin] = {}
self.plugin_classes: Dict[str, Type[BasePlugin]] = {}
# 创建插件目录
self.plugin_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
# 加载插件
self.discover_plugins()
def discover_plugins(self):
"""发现并加载所有插件"""
# 遍历插件目录
for plugin_file in self.plugin_dir.glob("*.py"):
if plugin_file.name.startswith("__"):
continue
# 导入插件模块
module_name = f"plugins.{plugin_file.stem}"
try:
module = importlib.import_module(module_name)
# 查找插件类
for attr in dir(module):
cls = getattr(module, attr)
if isinstance(cls, type) and issubclass(cls, BasePlugin) and cls != BasePlugin:
self.plugin_classes[cls.get_metadata(None).name] = cls
print(f"发现插件: {cls.get_metadata(None).name}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"加载插件失败 {plugin_file.name}: {e}")
def install_plugin(self, plugin_name: str, config: Dict[str, Any] = None) -> bool:
"""安装插件"""
if plugin_name not in self.plugin_classes:
return False
plugin_class = self.plugin_classes[plugin_name]
plugin_instance = plugin_class()
if config:
plugin_instance.configure(config)
plugin_instance.activate()
self.plugins[plugin_name] = plugin_instance
return True
def uninstall_plugin(self, plugin_name: str) -> bool:
"""卸载插件"""
if plugin_name not in self.plugins:
return False
self.plugins[plugin_name].deactivate()
del self.plugins[plugin_name]
return True
def execute_plugin(self, plugin_name: str, command: str, params: Dict[str, Any] = None) -> Any:
"""执行插件功能"""
if plugin_name not in self.plugins:
return {"error": f"插件 {plugin_name} 未安装"}
if not self.plugins[plugin_name].is_active:
return {"error": f"插件 {plugin_name} 未激活"}
try:
result = self.plugins[plugin_name].execute(command, params)
return {"result": result}
except Exception as e:
return {"error": str(e)}
def list_plugins(self) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""列出所有插件"""
installed = []
for name, plugin in self.plugins.items():
installed.append(plugin.get_status())
available = []
for name, cls in self.plugin_classes.items():
if name not in self.plugins:
metadata = cls.get_metadata(None)
available.append({
"name": metadata.name,
"version": metadata.version,
"description": metadata.description,
"installed": False
})
return {"installed": installed, "available": available}
4.2.3 示例插件实现
python
运行
# plugins/calculator_plugin.py
class CalculatorPlugin(BasePlugin):
def get_metadata(self) -> PluginMetadata:
return PluginMetadata(
name="calculator",
version="1.0.0",
author="Developer",
description="提供数学计算功能",
plugin_type="tool",
config_schema={"precision": {"type": "int", "default": 2}}
)
def activate(self):
super().activate()
print("计算器插件已激活")
def deactivate(self):
super().deactivate()
print("计算器插件已停用")
def execute(self, command: str, params: Dict[str, Any] = None) -> Any:
if not params:
return {"error": "缺少计算参数"}
operation = params.get("operation")
a = params.get("a")
b = params.get("b")
precision = self.config.get("precision", 2)
try:
a = float(a)
b = float(b)
if operation == "add":
result = a + b
elif operation == "subtract":
result = a - b
elif operation == "multiply":
result = a * b
elif operation == "divide":
if b == 0:
return {"error": "除数不能为零"}
result = a / b
else:
return {"error": f"不支持的操作: {operation}"}
return {"result": round(result, precision)}
except ValueError:
return {"error": "参数必须是数字"}
# plugins/weather_plugin.py
import requests
class WeatherPlugin(BasePlugin):
def get_metadata(self) -> PluginMetadata:
return PluginMetadata(
name="weather",
version="1.0.0",
author="Developer",
description="提供天气查询功能",
plugin_type="service",
config_schema={"api_key": {"type": "str", "required": True}, "api_url": {"type": "str", "default": "https://api.weatherapi.com/v1"}}
)
def activate(self):
super().activate()
if not self.config.get("api_key"):
raise Exception("需要配置API密钥")
print("天气插件已激活")
def deactivate(self):
super().deactivate()
print("天气插件已停用")
def execute(self, command: str, params: Dict[str, Any] = None) -> Any:
if command == "current":
city = params.get("city", "beijing")
api_key = self.config.get("api_key")
api_url = self.config.get("api_url")
try:
response = requests.get(f"{api_url}/current.json",
params={"key": api_key, "q": city})
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
return {
"location": data["location"]["name"],
"temperature": data["current"]["temp_c"],
"condition": data["current"]["condition"]["text"],
"humidity": data["current"]["humidity"]
}
except Exception as e:
return {"error": f"获取天气失败: {str(e)}"}
return {"error": f"不支持的命令: {command}"}
4.2.4 小智 AI 插件集成
python
运行
class PluginEnhancedXiaoZhi:
def __init__(self, api_key, plugin_dir="plugins"):
self.xiaozhi_client = XiaoZhiClient(api_key)
self.plugin_manager = PluginManager(plugin_dir)
# 初始化系统插件
self._init_system_plugins()
# 插件调用Prompt
self.plugin_prompt = """
分析用户请求是否需要调用插件,如果需要,返回以下JSON格式:
{
"use_plugin": true/false,
"plugin_name": "插件名称",
"command": "插件命令",
"params": {"参数名": "参数值"},
"text_response": "如果不需要插件的文本回复"
}
可用插件:
- calculator: 数学计算(operation: add/subtract/multiply/divide, a, b)
- weather: 天气查询(command: current, city)
只返回JSON,不要其他内容。
"""
def _init_system_plugins(self):
"""初始化系统插件"""
# 安装计算器插件
self.plugin_manager.install_plugin("calculator", {"precision": 4})
# 安装天气插件(需要配置API密钥)
# self.plugin_manager.install_plugin("weather", {"api_key": "your_weather_api_key"})
def process_request(self, user_message, user_id="default"):
"""处理用户请求"""
# 首先让AI判断是否需要调用插件
plugin_decision = self.xiaozhi_client.send_message(
f"{self.plugin_prompt}\n\n用户请求:{user_message}",
user_id=user_id
)
# 解析AI的决策
try:
decision_data = json.loads(plugin_decision.get("choices", [{}])[0].get("message", {}).get("content", "{}"))
if decision_data.get("use_plugin"):
# 调用插件
plugin_name = decision_data.get("plugin_name")
command = decision_data.get("command")
params = decision_data.get("params", {})
plugin_result = self.plugin_manager.execute_plugin(plugin_name, command, params)
# 将插件结果交给AI进行自然语言处理
final_response = self.xiaozhi_client.send_message(
f"根据以下插件执行结果,用自然语言回复用户:\n插件结果:{plugin_result}\n用户原始请求:{user_message}",
user_id=user_id
)
return final_response.get("choices", [{}])[0].get("message", {}).get("content", "")
else:
# 直接返回AI的文本回复
return decision_data.get("text_response", "无法处理你的请求")
except Exception as e:
print(f"插件处理失败: {e}")
# 降级处理:直接使用AI回复
fallback_response = self.xiaozhi_client.send_message(user_message, user_id=user_id)
return fallback_response.get("choices", [{}])[0].get("message", {}).get("content", "")
# 使用示例
def plugin_demo():
enhanced_xiaozhi = PluginEnhancedXiaoZhi(api_key="your_api_key_here")
print("插件增强版小智AI已启动(输入'exit'退出)")
while True:
user_input = input("你: ")
if user_input.lower() == "exit":
break
response = enhanced_xiaozhi.process_request(user_input)
print(f"小智: {response}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
plugin_demo()
4.3 插件市场设计
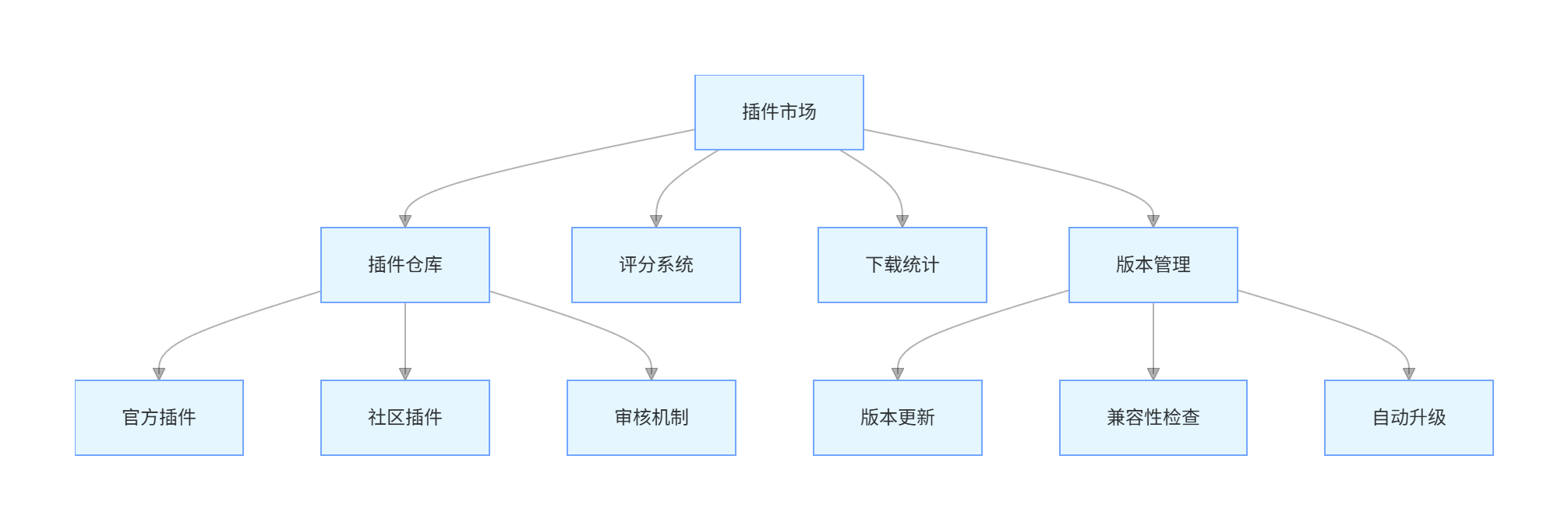
4.3.1 插件市场架构
graph TD
A[插件市场] --> B[插件仓库]
A --> C[评分系统]
A --> D[下载统计]
A --> E[版本管理]
B --> B1[官方插件]
B --> B2[社区插件]
B --> B3[审核机制]
E --> E1[版本更新]
E --> E2[兼容性检查]
E --> E3[自动升级]
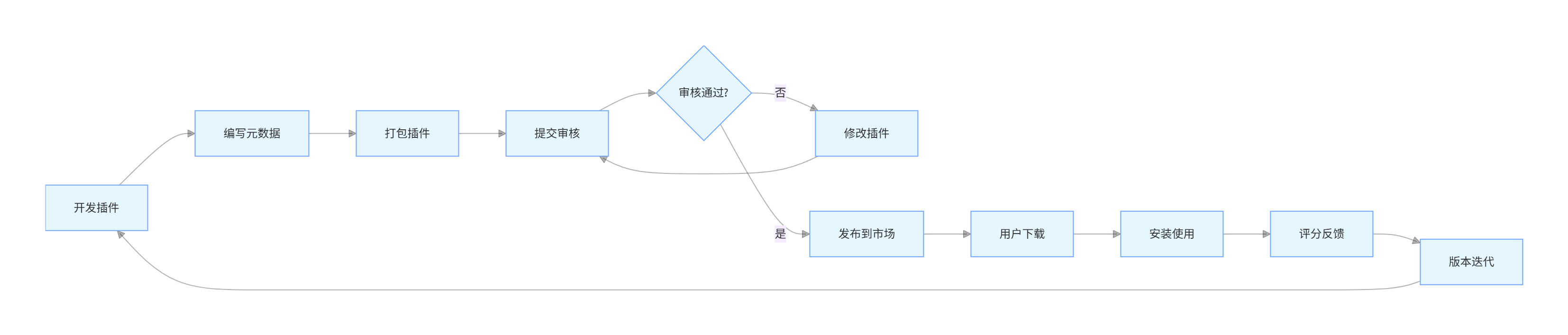
4.3.2 插件发布流程
flowchart LR
A[开发插件] --> B[编写元数据]
B --> C[打包插件]
C --> D[提交审核]
D --> E{审核通过?}
E -->|否| F[修改插件]
E -->|是| G[发布到市场]
F --> D
G --> H[用户下载]
H --> I[安装使用]
I --> J[评分反馈]
J --> K[版本迭代]
K --> A
4.4 安全性设计
4.4.1 插件权限控制
python
运行
class PluginPermission:
"""插件权限类"""
def __init__(self):
self.permissions = {
"network": False,
"file_system": False,
"system_info": False,
"user_data": False
}
def grant(self, permission: str):
"""授予权限"""
if permission in self.permissions:
self.permissions[permission] = True
def revoke(self, permission: str):
"""撤销权限"""
if permission in self.permissions:
self.permissions[permission] = False
def check(self, permission: str) -> bool:
"""检查权限"""
return self.permissions.get(permission, False)
# 在插件基类中集成权限控制
class SecureBasePlugin(BasePlugin):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.permissions = PluginPermission()
def execute(self, command: str, params: Dict[str, Any] = None) -> Any:
"""安全的执行方法"""
# 权限检查示例
if command == "network_request" and not self.permissions.check("network"):
raise PermissionError("插件没有网络访问权限")
return self._execute(command, params)
@abstractmethod
def _execute(self, command: str, params: Dict[str, Any] = None) -> Any:
"""实际执行逻辑"""
pass
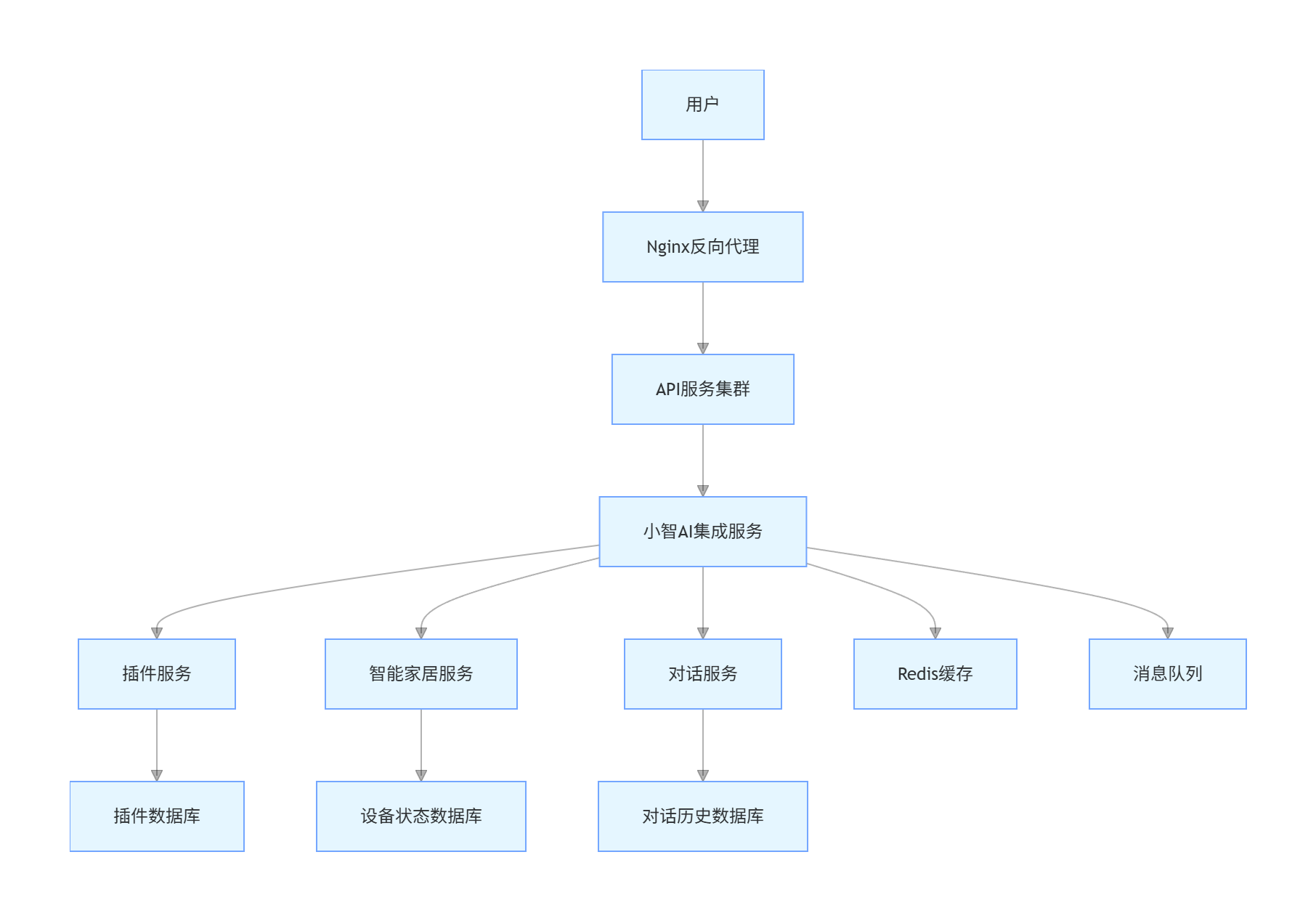
五、系统部署与运维
5.1 部署架构
graph TD
A[用户] --> B[Nginx反向代理]
B --> C[API服务集群]
C --> D[小智AI集成服务]
D --> E[插件服务]
D --> F[智能家居服务]
D --> G[对话服务]
E --> H[插件数据库]
F --> I[设备状态数据库]
G --> J[对话历史数据库]
D --> K[Redis缓存]
D --> L[消息队列]
5.2 Docker 部署配置
dockerfile
# Dockerfile
FROM python:3.9-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1
ENV API_KEY=your_api_key_here
EXPOSE 8000
CMD ["uvicorn", "main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "8000"]
yaml
# docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
app:
build: .
ports:
- "8000:8000"
depends_on:
- redis
- mqtt
environment:
- REDIS_HOST=redis
- MQTT_BROKER=mqtt
redis:
image: redis:alpine
ports:
- "6379:6379"
mqtt:
image: eclipse-mosquitto
ports:
- "1883:1883"
volumes:
- ./mosquitto/config:/mosquitto/config
5.3 监控与日志
python
运行
import logging
from logging.handlers import RotatingFileHandler
import time
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class PerformanceMetrics:
"""性能指标"""
request_id: str
start_time: float
end_time: float = None
latency: float = None
success: bool = True
error: str = None
class MonitoringSystem:
def __init__(self, log_file="app.log"):
# 配置日志
self.logger = logging.getLogger("xiaozhi_app")
self.logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# 文件处理器
file_handler = RotatingFileHandler(log_file, maxBytes=10*1024*1024, backupCount=5)
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
file_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
# 控制台处理器
console_handler = logging.StreamHandler()
console_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
self.logger.addHandler(file_handler)
self.logger.addHandler(console_handler)
# 性能指标存储
self.performance_metrics = []
def track_performance(self, request_id: str) -> PerformanceMetrics:
"""开始跟踪性能"""
metrics = PerformanceMetrics(request_id=request_id, start_time=time.time())
self.performance_metrics.append(metrics)
return metrics
def finish_tracking(self, metrics: PerformanceMetrics, success: bool = True, error: str = None):
"""完成性能跟踪"""
metrics.end_time = time.time()
metrics.latency = metrics.end_time - metrics.start_time
metrics.success = success
metrics.error = error
self.logger.info(f"请求 {metrics.request_id} 完成,耗时: {metrics.latency:.3f}s,成功: {success}")
def log_error(self, message: str, exc_info=None):
"""记录错误"""
self.logger.error(message, exc_info=exc_info)
def log_info(self, message: str):
"""记录信息"""
self.logger.info(message)
def get_performance_stats(self) -> dict:
"""获取性能统计"""
if not self.performance_metrics:
return {"total_requests": 0}
total = len(self.performance_metrics)
success = len([m for m in self.performance_metrics if m.success])
avg_latency = sum(m.latency for m in self.performance_metrics if m.latency) / total
return {
"total_requests": total,
"success_rate": success / total,
"average_latency": avg_latency,
"errors": len([m for m in self.performance_metrics if not m.success])
}
六、总结与展望
通过以上三个实战项目,我们展示了如何将小智 AI 打造为强大的 "第二大脑" 系统:
- 智能家居控制:实现了语音控制、设备状态管理、自动化场景等功能
- AI 对话系统:构建了上下文感知、意图识别、知识增强的智能对话能力
- 功能扩展系统:设计了插件化架构,支持无限扩展功能模块
未来发展方向
- 多模态交互:集成语音、图像、视频等多种交互方式
- 强化学习优化:通过用户反馈持续优化 AI 响应质量
- 边缘计算部署:支持本地部署,提高响应速度和隐私保护
- 联邦学习:在保护隐私的前提下进行模型优化
- 跨平台集成:与更多第三方服务和设备生态系统对接
开发建议
- 模块化设计:保持代码的模块化和可扩展性
- API 版本控制:确保 API 的向后兼容性
- 安全性优先:重视数据安全和隐私保护
- 用户体验:持续优化用户交互体验
- 文档完善:提供详细的开发文档和 API 说明
通过持续迭代和优化,基于小智 AI 的 "第二大脑" 系统将成为个人和企业的智能中枢,赋能各种应用场景。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容










所有评论(0)