KMP 结构适配鸿蒙:应用架构最佳实践理论知识
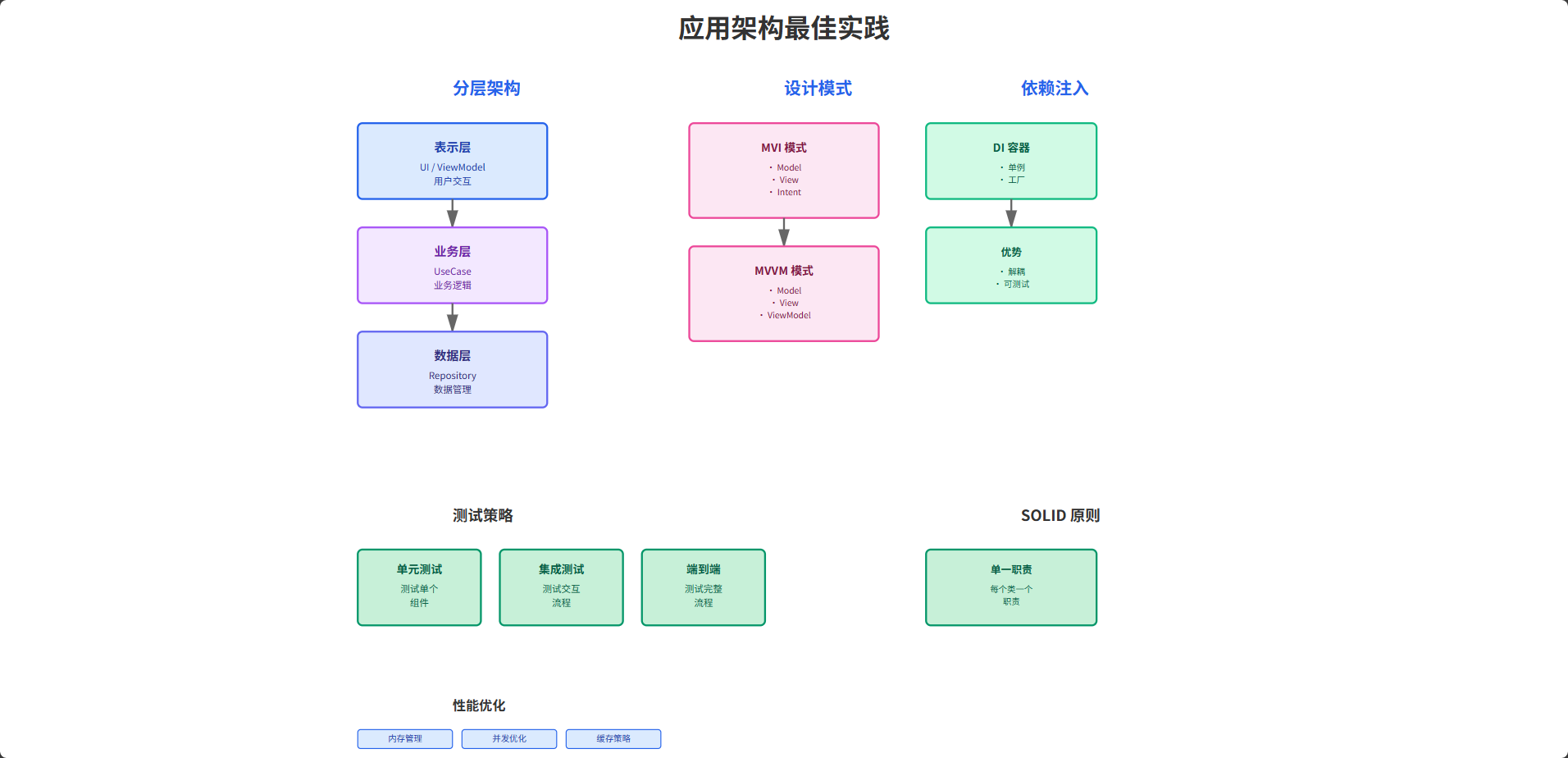
本文介绍了在Kotlin Multiplatform(KMP)框架下实现高效应用架构的方法。通过分层架构(表示层、业务层、数据层)将平台相关代码与共享逻辑分离,采用依赖注入管理组件生命周期,并展示了MVI和MVVM两种设计模式。文章提供了可落地的架构模板,适用于从零搭建KMP项目或重构现有项目,重点解决多端代码复用、测试覆盖率和可维护性问题。核心思路是通过接口隔离平台特性,将业务逻辑集中到comm
·

项目概述
应用架构是决定应用质量和可维护性的关键因素。在 KMP 框架下,我们需要遵循最佳实践来构建可扩展、可测试和易于维护的应用。本文详细介绍了如何在 Kotlin Multiplatform 中实现高效的应用架构,包括分层架构、依赖注入、测试策略和鸿蒙系统特定的架构考虑。
本篇更加偏“方法论 + 模板”,适用于:
- 从零搭建一个 KMP + 鸿蒙 的多端项目,希望一开始就有清晰架构;
- 已有项目逐步引入 KMP,希望整理业务层/数据层,减少平台间重复代码;
- 希望在多端统一测试、优化性能、提升可维护性。
目标是给出一套可以落地的参考架构:
- 上层 UI/Ability/页面与平台强相关;
- 中层业务用例、状态管理与 ViewModel 主要放在
commonMain; - 底层数据访问和平台能力通过
expect/actual与接口适配。
第一部分:架构核心概念
分层架构
// commonMain/kotlin/com/example/architecture/layers/PresentationLayer.kt
// 表示层 - 处理 UI 逻辑和用户交互
interface PresentationLayer {
fun displayData(data: Any)
fun showError(error: String)
fun showLoading(isLoading: Boolean)
}
// commonMain/kotlin/com/example/architecture/layers/DomainLayer.kt
// 业务层 - 包含业务逻辑和用例
interface UseCase<in Input, out Output> {
suspend fun execute(input: Input): Output
}
data class GetUserUseCase(private val repository: UserRepository) : UseCase<String, User> {
override suspend fun execute(input: String): User {
return repository.getUserById(input)
}
}
// commonMain/kotlin/com/example/architecture/layers/DataLayer.kt
// 数据层 - 处理数据获取和存储
interface Repository<T> {
suspend fun getAll(): List<T>
suspend fun getById(id: String): T?
suspend fun save(item: T): Boolean
suspend fun delete(id: String): Boolean
}
interface UserRepository : Repository<User> {
suspend fun getUserByEmail(email: String): User?
}
这一部分展示的是经典的三层架构在 KMP 下的拆分方式:
- 表示层(PresentationLayer):关注 UI 状态、用户交互,与具体平台 UI 技术(Compose/SwiftUI/鸿蒙 UI)结合;
- 业务层(UseCase):聚焦业务规则与用例组合,尽量写在
commonMain,方便跨端复用; - 数据层(Repository):封装网络、本地数据库、缓存等数据来源,通过接口隐藏实现细节。
在 KMP 项目中,这种分层可以让你:
- 将与具体平台强相关的部分(Ability/Activity/Controller)限制在少数边界层;
- 将复杂业务流程和数据处理逻辑抽出到共享模块,减少“多端各写一遍”的情况;
- 提高单元测试覆盖率:绝大多数业务逻辑可以在 commonTest 中直接测试。
依赖注入
// commonMain/kotlin/com/example/architecture/di/Container.kt
class DIContainer {
private val singletons = mutableMapOf<String, Any>()
private val factories = mutableMapOf<String, () -> Any>()
inline fun <reified T> singleton(name: String = T::class.simpleName!!, factory: () -> T) {
factories[name] = factory
}
inline fun <reified T> get(name: String = T::class.simpleName!!): T {
return singletons.getOrPut(name) {
factories[name]?.invoke() ?: throw IllegalArgumentException("No factory for $name")
} as T
}
}
// 使用示例
val container = DIContainer().apply {
singleton<UserRepository> { UserRepositoryImpl() }
singleton<GetUserUseCase> { GetUserUseCase(get()) }
singleton<UserViewModel> { UserViewModel(get()) }
}
状态管理
// commonMain/kotlin/com/example/architecture/state/StateHolder.kt
sealed class UIState<T> {
object Loading : UIState<Nothing>()
data class Success<T>(val data: T) : UIState<T>()
data class Error(val exception: Exception) : UIState<Nothing>()
}
class StateHolder<T> {
private val _state = MutableStateFlow<UIState<T>>(UIState.Loading)
val state: StateFlow<UIState<T>> = _state.asStateFlow()
suspend fun setState(newState: UIState<T>) {
_state.emit(newState)
}
}
第二部分:设计模式
MVI 模式
// commonMain/kotlin/com/example/architecture/mvi/MVIArchitecture.kt
// Model - 数据模型
data class UserModel(
val id: String,
val name: String,
val email: String
)
// View - UI 接口
interface UserView {
fun render(state: UserViewState)
}
// Intent - 用户意图
sealed class UserIntent {
data class LoadUser(val userId: String) : UserIntent()
data class UpdateUser(val user: UserModel) : UserIntent()
object DeleteUser : UserIntent()
}
// ViewState - 视图状态
data class UserViewState(
val isLoading: Boolean = false,
val user: UserModel? = null,
val error: String? = null
)
// Presenter - 业务逻辑
class UserPresenter(private val useCase: GetUserUseCase) {
suspend fun handleIntent(intent: UserIntent): UserViewState {
return when (intent) {
is UserIntent.LoadUser -> {
try {
val user = useCase.execute(intent.userId)
UserViewState(user = user)
} catch (e: Exception) {
UserViewState(error = e.message)
}
}
else -> UserViewState()
}
}
}
MVVM 模式
// commonMain/kotlin/com/example/architecture/mvvm/MVVMArchitecture.kt
class UserViewModel(private val useCase: GetUserUseCase) {
private val _user = MutableStateFlow<User?>(null)
val user: StateFlow<User?> = _user.asStateFlow()
private val _isLoading = MutableStateFlow(false)
val isLoading: StateFlow<Boolean> = _isLoading.asStateFlow()
private val _error = MutableStateFlow<String?>(null)
val error: StateFlow<String?> = _error.asStateFlow()
fun loadUser(userId: String) {
GlobalScope.launch {
_isLoading.emit(true)
try {
val user = useCase.execute(userId)
_user.emit(user)
} catch (e: Exception) {
_error.emit(e.message)
} finally {
_isLoading.emit(false)
}
}
}
}
第三部分:测试策略
单元测试
// commonTest/kotlin/com/example/architecture/UserRepositoryTest.kt
class UserRepositoryTest {
private lateinit var repository: UserRepository
@Before
fun setup() {
repository = UserRepositoryImpl()
}
@Test
fun testGetUserById() = runTest {
val userId = "123"
val user = repository.getUserById(userId)
assertEquals("123", user?.id)
assertEquals("John Doe", user?.name)
}
@Test
fun testSaveUser() = runTest {
val user = User("456", "Jane Doe", "jane@example.com")
val result = repository.save(user)
assertTrue(result)
}
}
集成测试
// commonTest/kotlin/com/example/architecture/UserUseCaseTest.kt
class UserUseCaseTest {
private lateinit var useCase: GetUserUseCase
private lateinit var repository: UserRepository
@Before
fun setup() {
repository = MockUserRepository()
useCase = GetUserUseCase(repository)
}
@Test
fun testExecuteGetUser() = runTest {
val user = useCase.execute("123")
assertNotNull(user)
assertEquals("John Doe", user.name)
}
}
第四部分:性能优化
内存管理
// commonMain/kotlin/com/example/architecture/performance/MemoryOptimization.kt
class MemoryOptimizedCache<K, V>(private val maxSize: Int = 100) {
private val cache = LinkedHashMap<K, V>(maxSize, 0.75f, true)
fun get(key: K): V? = cache[key]
fun put(key: K, value: V) {
if (cache.size >= maxSize) {
val iterator = cache.iterator()
iterator.next()
iterator.remove()
}
cache[key] = value
}
fun clear() = cache.clear()
}
并发优化
// commonMain/kotlin/com/example/architecture/performance/ConcurrencyOptimization.kt
class OptimizedRepository(
private val dispatcher: CoroutineDispatcher = Dispatchers.Default
) {
suspend fun fetchDataConcurrently(ids: List<String>): List<Data> {
return withContext(dispatcher) {
ids.map { id ->
async { fetchData(id) }
}.awaitAll()
}
}
}
第五部分:鸿蒙系统特定考虑
鸿蒙应用架构
// ohos/kotlin/com/example/architecture/HarmonyOSArchitecture.kt
// Ability 层 - 鸿蒙特定的生命周期管理
class UserAbility : Ability() {
private lateinit var viewModel: UserViewModel
override fun onStart(intent: Intent) {
super.onStart(intent)
viewModel = UserViewModel(container.get())
// 绑定视图和 ViewModel
bindViewModel()
}
private fun bindViewModel() {
// 处理 ViewModel 状态更新
GlobalScope.launch {
viewModel.user.collect { user ->
updateUI(user)
}
}
}
}
// 鸿蒙特定的数据持久化
class HarmonyOSDataStore(private val context: Context) {
private val preferences = context.getSharedPreferences("app_data", Context.MODE_PRIVATE)
fun saveData(key: String, value: String) {
preferences.edit().putString(key, value).apply()
}
fun getData(key: String): String? {
return preferences.getString(key, null)
}
}
总结
应用架构是决定应用质量的关键因素。通过遵循最佳实践,我们可以构建可扩展、可测试和易于维护的应用。在 KMP 框架下,我们需要在共享代码中实现通用的架构模式,同时在各平台上适配特定的生命周期和 API。鸿蒙系统提供了完整的应用框架,使得跨平台架构实现相对平顺。关键是要选择合适的架构模式、遵循 SOLID 原则和进行充分的测试。
在工程实践中,可以重点思考:
- 当前项目是否已经明确了分层边界和依赖方向?
- 有多少业务逻辑可以迁移到
commonMain,从而减少多端重复? - 现有测试是否覆盖了关键用例,是否易于在多端回归?
建议的落地步骤:
- 先在一个中等复杂度的业务模块上试点上述分层 + DI + 状态管理方案;
- 逐步将成功经验推广到全局,并配合测试与性能优化策略;
- 针对鸿蒙端梳理清晰的 UI 与 Ability 层边界,让共享业务层尽可能保持纯 Kotlin、可测试和可复用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容







所有评论(0)